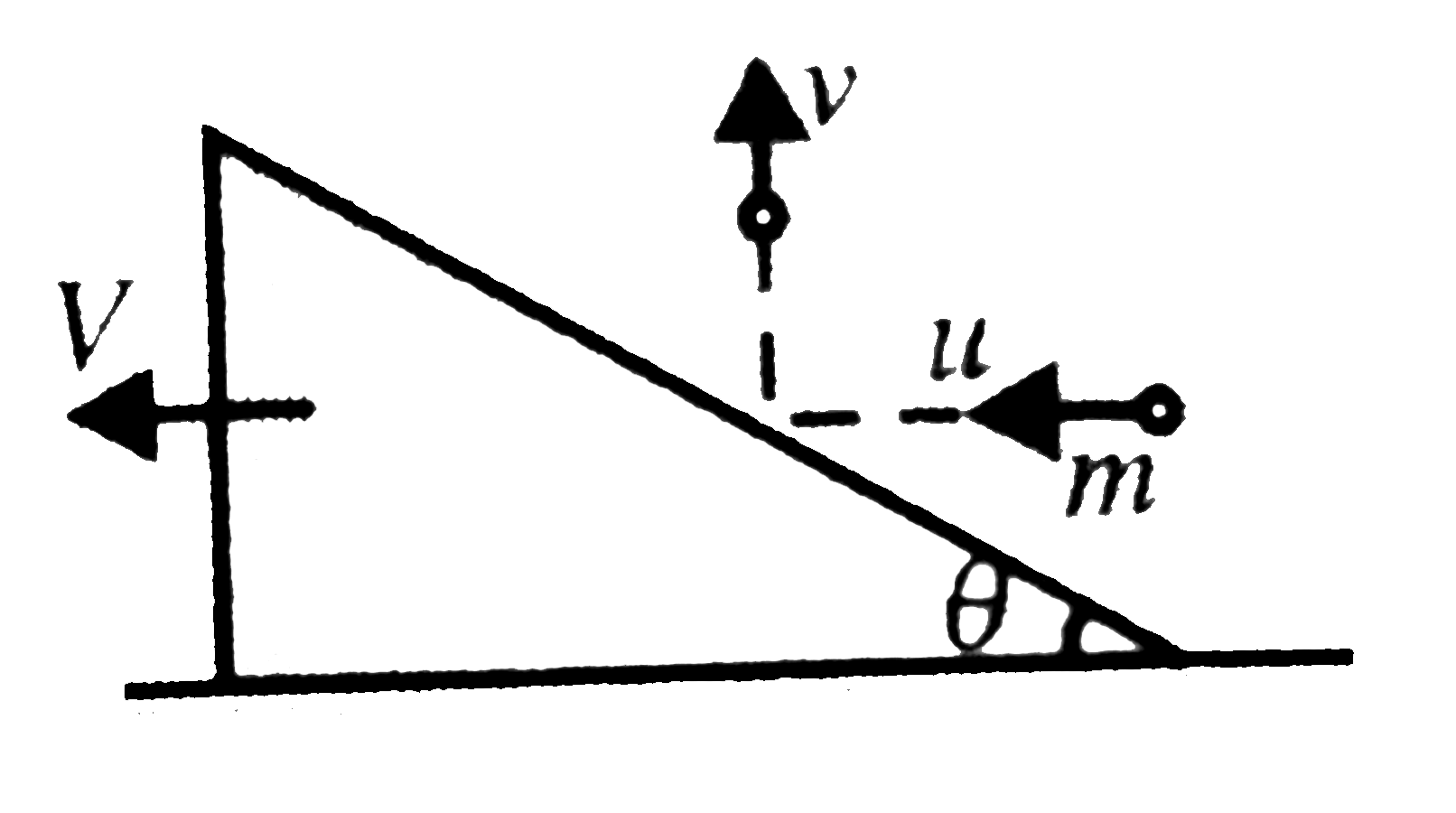
A ball of mass `m` moving horizotally which velocity `u` hits a wedge of mass `M`. The wedge is situated on a smooth horizontal source. If after striking with wedge the ball starts moving in vertical direction and the wedge starts moving in horizotal plane. calculate
a. the velocity of wedge `V`.
b. the velocity `(v)` at which the ball moves in vertical direction.
c. the impulse imparted by the ball on the wedge.
d. the coefficient of restitution `e=?`
A ball of mass `m` moving horizotally which velocity `u` hits a wedge of mass `M`. The wedge is situated on a smooth horizontal source. If after striking with wedge the ball starts moving in vertical direction and the wedge starts moving in horizotal plane. calculate
a. the velocity of wedge `V`.
b. the velocity `(v)` at which the ball moves in vertical direction.
c. the impulse imparted by the ball on the wedge.
d. the coefficient of restitution `e=?`

a. the velocity of wedge `V`.
b. the velocity `(v)` at which the ball moves in vertical direction.
c. the impulse imparted by the ball on the wedge.
d. the coefficient of restitution `e=?`

Text Solution
Verified by Experts
a. As no external force is acting on the system in horizontal direction the linear momentum should be constant and conserved in horizontal direction.
Let velocity of wedge after collision be `V`.
Then `"mu"=MVimpliesV=("mu")/M`………..i
b. As there is no impulse on the ball in the direction parallel to sloping side hence the veloicty of ball along the slope (tangent direction) should remain unchanged,
`implies ucostheta=vsintheta` ..........ii
c. we can find the values of `v` and `V` by impulse approach, when ball hits the wedge the impulse is generated between ball and wedge in the direction perpendicular to slopping surface. (normal direction).

For ball: `"mu"-Jsintheta=0`
`Jsintheta="mu"`
`J cos thetas =mv`
from eqn i and ii `v=ucottheta`
From eqn iii `J="mu" cosec theta,`
`Jsintheta=mVimpliesV=(Jsintheta)/M`
Which gives `V=(mu)/M`
d. The direction of restitution is given as

`(v_(2)-v_(1))_(n)-e(u_(1)-u_(2))_(n)`
` [Vsintheta-(-vcostheta)]=e[usintheta-0]`
`e=(Vsintheta+vcostheta)/(usintheta)`
`e=V/u+v/ucot theta=("mu")/M+(cottheta)cotheta`
`e=m/M+cot^(2)theta`
Let velocity of wedge after collision be `V`.
Then `"mu"=MVimpliesV=("mu")/M`………..i
b. As there is no impulse on the ball in the direction parallel to sloping side hence the veloicty of ball along the slope (tangent direction) should remain unchanged,
`implies ucostheta=vsintheta` ..........ii
c. we can find the values of `v` and `V` by impulse approach, when ball hits the wedge the impulse is generated between ball and wedge in the direction perpendicular to slopping surface. (normal direction).

For ball: `"mu"-Jsintheta=0`
`Jsintheta="mu"`
`J cos thetas =mv`
from eqn i and ii `v=ucottheta`
From eqn iii `J="mu" cosec theta,`
`Jsintheta=mVimpliesV=(Jsintheta)/M`
Which gives `V=(mu)/M`
d. The direction of restitution is given as

`(v_(2)-v_(1))_(n)-e(u_(1)-u_(2))_(n)`
` [Vsintheta-(-vcostheta)]=e[usintheta-0]`
`e=(Vsintheta+vcostheta)/(usintheta)`
`e=V/u+v/ucot theta=("mu")/M+(cottheta)cotheta`
`e=m/M+cot^(2)theta`
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A small particle of mass m = 2 kg moving with constant horizontal velocity u = 10 m//s strikes a wedge shaped block of mass M = 4 kg placed on smooth horizontal surface on its inclined surface as shown in figure. After collision particle starts moving up the inclined plane. Calculate the velocity of wedge immediately after collision.
A particle of mass m moving horizontal with v_(0) strikes a smooth wedge of mass M, as shown in figure. After collision, the ball starts moving up the inclined face of the wedge and rises to a height h. The maximum height h attained by the particle is
A ball mass 2 kg moving horizontally with velocity 10 m/s hits a wedge of mass 5 kg placed on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure. Just after collision klvelocity of wedge is 3.2 m/s. There is no friction at any contact surface. Then (take sin 30^(@)=3//5 )
A particle of mass m moving horizontal with v_(0) strikes a smooth wedge of mass M, as shown in figure. After collision, the ball starts moving up the inclined face of the wedge and rises to a height h. The final velocity of the wedge v_(2) is
A particle of mass m moving horizontal with v_(0) strikes a smooth wedge of mass M, as shown in figure. After collision, the ball starts moving up the inclined face of the wedge and rises to a height h. Choose the correct statement related to the wedge M
A particle of mass m moving horizontal with v_(0) strikes a smooth wedge of mass M, as shown in figure. After collision, the ball starts moving up the inclined face of the wedge and rises to a height h. Choose the correct statement(s) related to particle m
A ball of mass m=1kg falling vertically with a velocity v_(0)=2m//s strikes a wedge of mass M=2kg kept o a smooth, horizontal surface as shown in figure. The coefficient of resitution between the ball and the wege is e=1//2 . Find the velocity of the wedge is e=1/2. find the velocity of the wedge and the ball immediately after collison.
A particle of mass m moving horizontal with v_(0) strikes a smooth wedge of mass M, as shown in figure. After collision, the ball starts moving up the inclined face of the wedge and rises to a height h. Identify the correct statement(s) related to the situation when the particle starts moving downward
A particle of mass m moving horizontal with v_(0) strikes a smooth wedge of mass M, as shown in figure. After collision, the ball starts moving up the inclined face of the wedge and rises to a height h. When the particle has risen to a height h on the wedge, then choose the correct alternative(s)