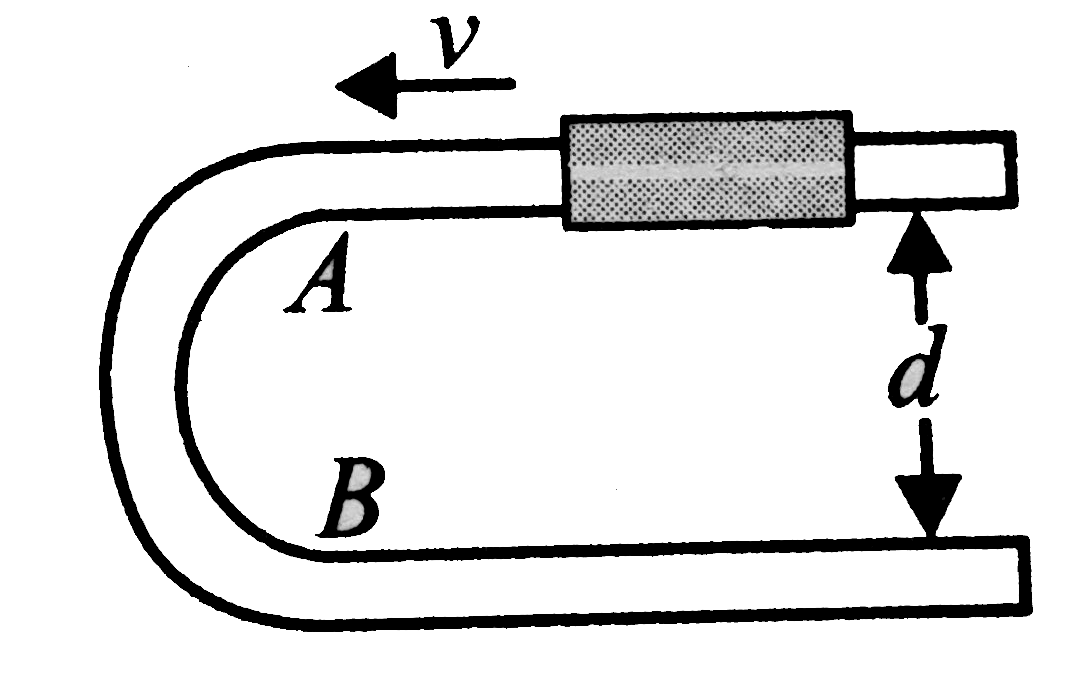
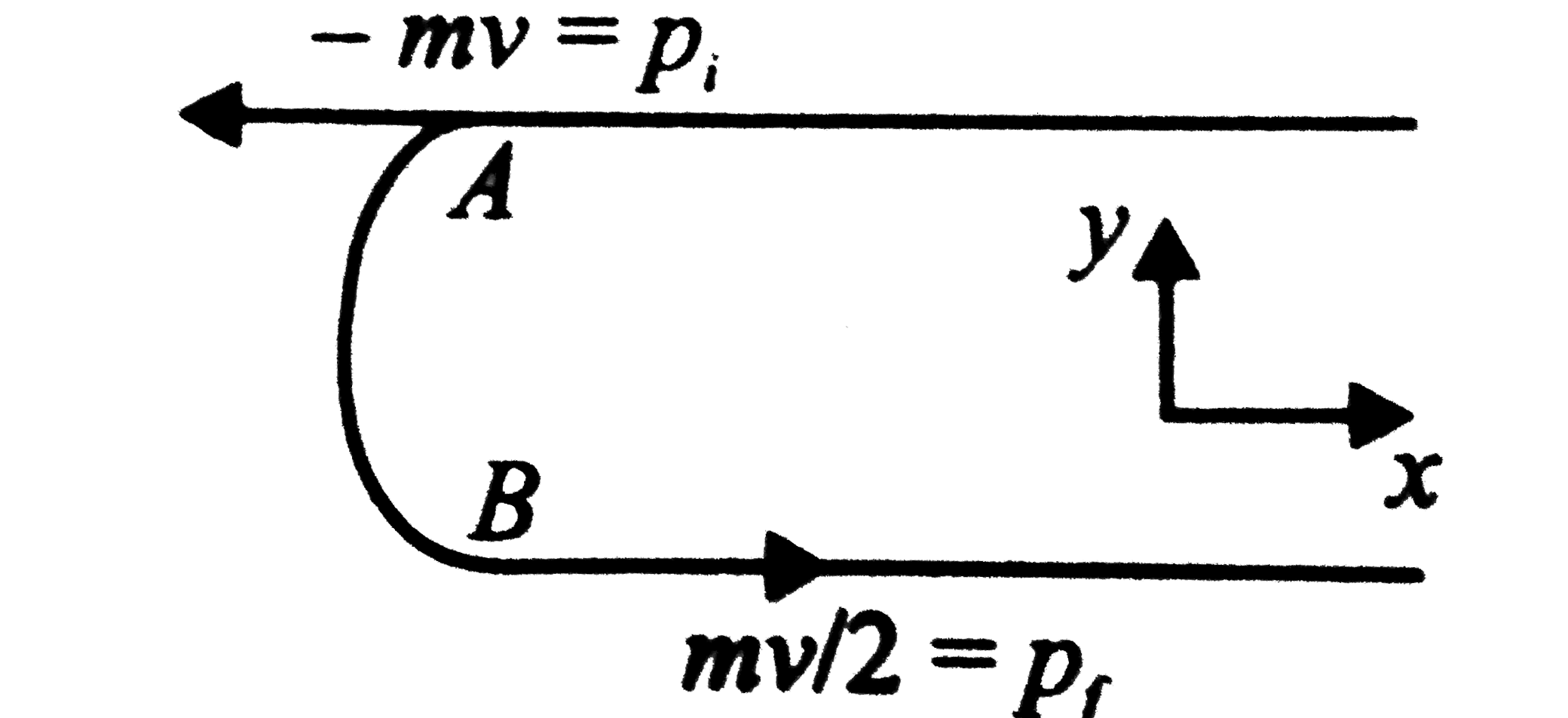A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|25 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion - Reasoning|2 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|23 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Solved Example|13 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-CENTRE OF MASS-Single Correct
- A heavy chain of length 1 m and weight 20 kg hangs vertically with one...
Text Solution
|
- A cannon of mass 1000 kg located at the base of an inclined plane fire...
Text Solution
|
- A U-shaped wire has a semicircular bending between A and B as shown in...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 2 kg moving with a velocity of 3 m//s is acted upon...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 3 kg moving with a velocity of 4 m//s towards left coll...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1)= 2 kg and m(2) = 4 kg are moving in the same...
Text Solution
|
- A cracker is thrown into air with a velocity of 10 m//s at an angle of...
Text Solution
|
- A force exerts an impulse Ion a particle changing its speed from initi...
Text Solution
|
- A ball falls vertically onto a floor with momentum p and then bounces ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball released from a height ho above a horizontal surface rebounds t...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical balls, of equal masses A and B, are lying on a smooth su...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass in is made to move with uniform speed v0 along the ...
Text Solution
|
- A continuous stream of particles, of mass m and velocity r, is emitted...
Text Solution
|
- A ball kept in a close box moves in the box making collisions with the...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moving with a velocity u makes an elastic one-dim...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary body explodes into two fragments of masses m(1) and m(2)....
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is projected with a speed v into the barrel of a spri...
Text Solution
|
- A railway flat car has an artillery gun installed on it. The combined ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 6 kg and 4 kg are attached to the two ends of a m...
Text Solution
|
- The momentum of a moving particle is vectorially given a, vecp=p(0)(co...
Text Solution
|