A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|25 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion - Reasoning|2 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|23 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Solved Example|13 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-CENTRE OF MASS-Single Correct
- A ball of mass m is attached to a cord of length L, pivoted at point O...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is released from rest relative to elevator at a heigh...
Text Solution
|
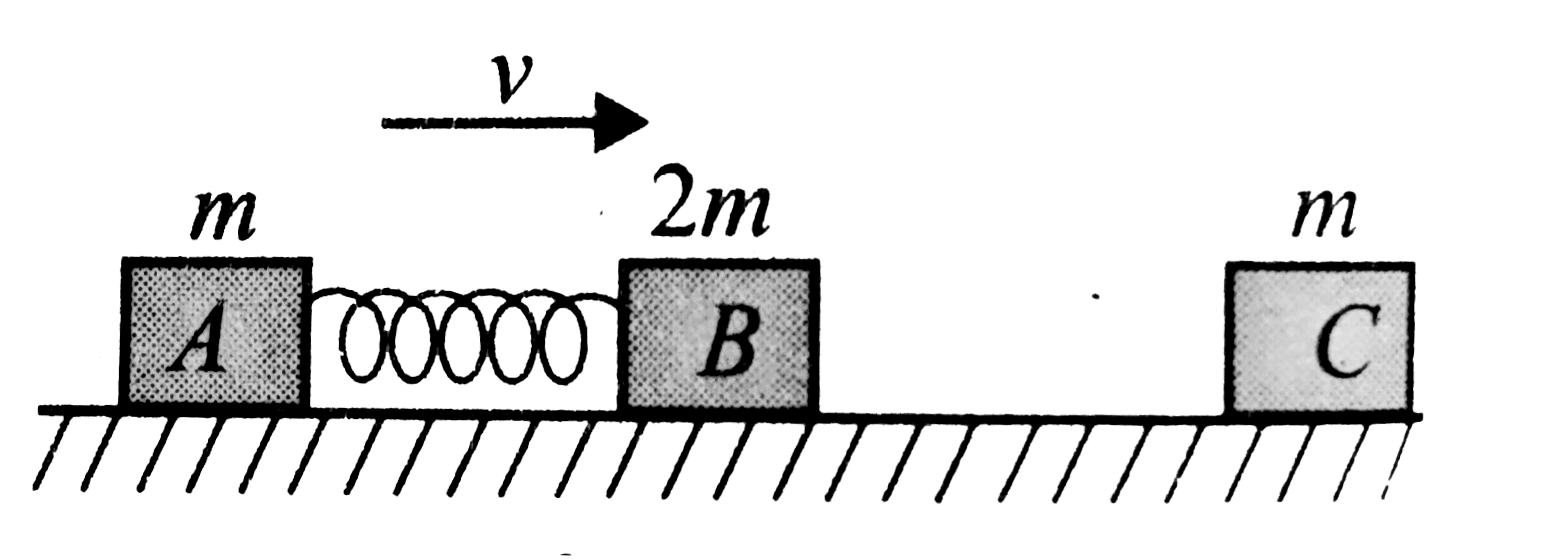
- Two blocks A and B of masses in and 2m, respectively, are connected wi...
Text Solution
|
- A 3000 kg space probe is moving in a gravity free space at a constant ...
Text Solution
|
- After a totally inelastic collision, two objects of the same mass and ...
Text Solution
|
- An object of mass 10 kg is launched from the ground at t = 0, at an an...
Text Solution
|
- For the system shown in Fig. the string is light and pulley is frictio...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of particles of mass m moving with velocity v impinges...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m starts from rest and slides down a frictionless semi...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks are initially placed as shown in the figure. Block A has ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, the two identical balls of mass M and radius R ea...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks are placed on smooth horizontal surface and lie on same h...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is moving along the x-axis with speed v when It c...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is acted on by two forces of equal magnitude F ma...
Text Solution
|
- Three particles of equal masses are placed at the corners of an equila...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected in a direction inclined to the vertical and bounce...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, the heavy ball of mass 2m, rests on the horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, the cart of mass 6m is initially at rest. A parti...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical particles collide in air inelastically. One moves horizo...
Text Solution
|
- A particle at rest is constrained to move on a smooth horizontal surfa...
Text Solution
|