Whenever a liquid comes in contact with solid boundaries it exerts a force on it. the force on the boundary may be obtained by integrating the pressure over the entire area of the boundary. The variations of liquid pressure acting at the base and at the wall the shown in figure `a` and `b` respectively.
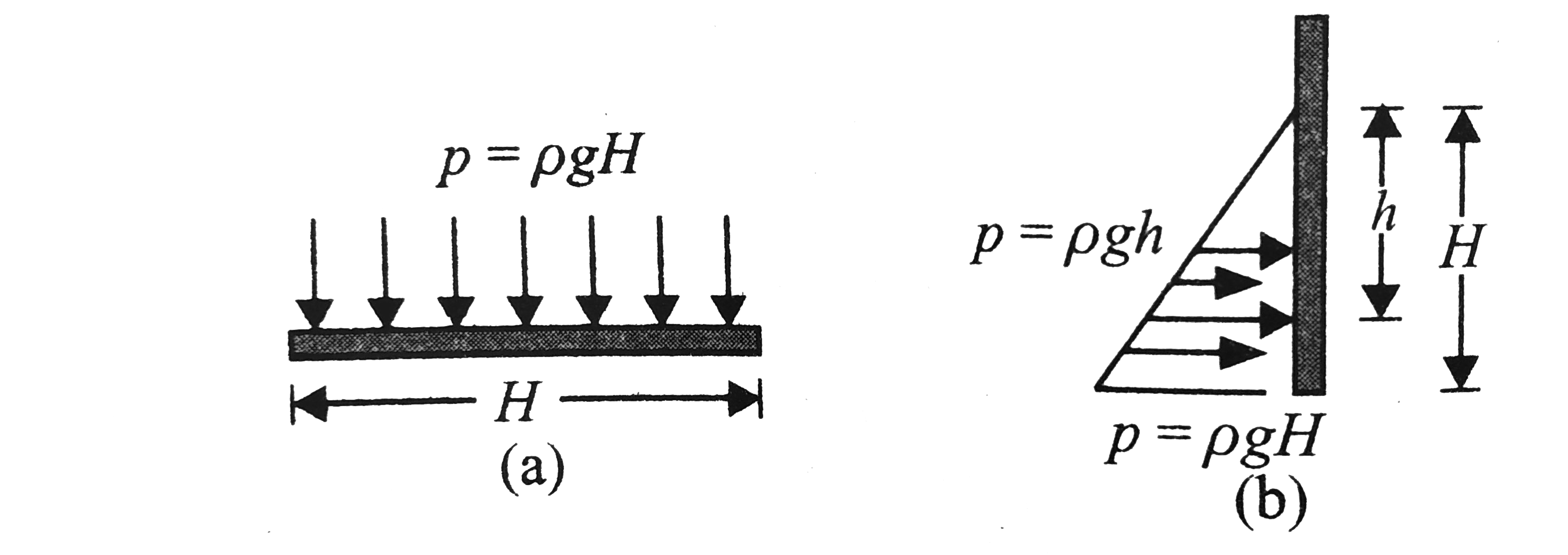
1. Force at the base: Since the pressure is uniform at the base, force acting the base is given by
`F=rhoxx` (area of the base)
since `p=rhoH`, therefore
`F=rhoghH(lb)=rhog(lbH)`
Since `lbH=V` (volume of the liquid) so
`F=rhogV=` weight of the liquid inside the tank
2. Force acting on the vertical wall: Pressure acting on the vertical wall is not uniform but increases linearly with depth, pressure at a depth `h` from the free is `p-rhogh`.
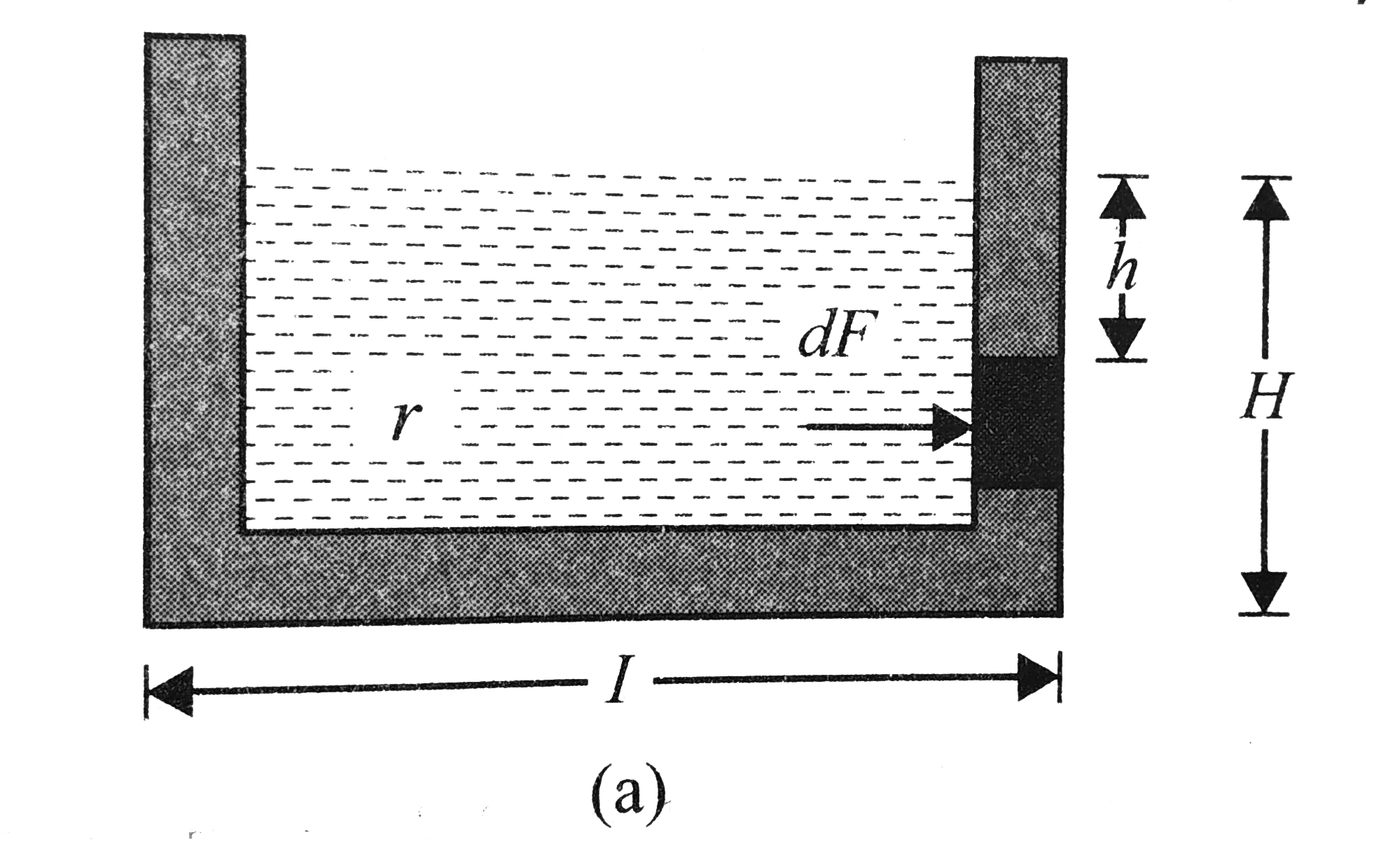
Force `dF` acting on a diferential element of height `dh` is
`dF=p(bdh)=(rhogh)(bdh)=rhoghdh`
The total force is
`F=rhoghint_(0)^(H)hdh=1/2rhogbH^(2)`
The total force acting per unit width of the vertical wall is `F/b=1/2rhogH^(2)`
The point of application (or the centre of force) of the total force form the free surface is given by `h_(C)=1/Rint_(0)^(h)`
Here `int_(0)^(H)h dF=int_(0)^(H)h(rhogpohdh)=rhogbint_(0)^(H)h^(3)dh=1/3rhogbH`
`F=1/2rhogbH6^(2)=rarrh_(C)=2/3H`
The total force acts at a depth `2/3 H` from the force diagram.