Let `y_("max")` be the lowest point on the dotted parabola show in figure.
`y_(1)=(r_(1)^(2)omega^(2))/(2g)+y_("min")` and `y_(2)=(r_(2)^(2)omega^(2))/(2g)+y_("min")`
`:.h=y_(2)-y_(1)=((r_(2)^(2)-r_(1)^(2))omega^(2))/(2g)=(omega^(2))/(2g)(r_(2)^(2)=r_(1)^(2))`
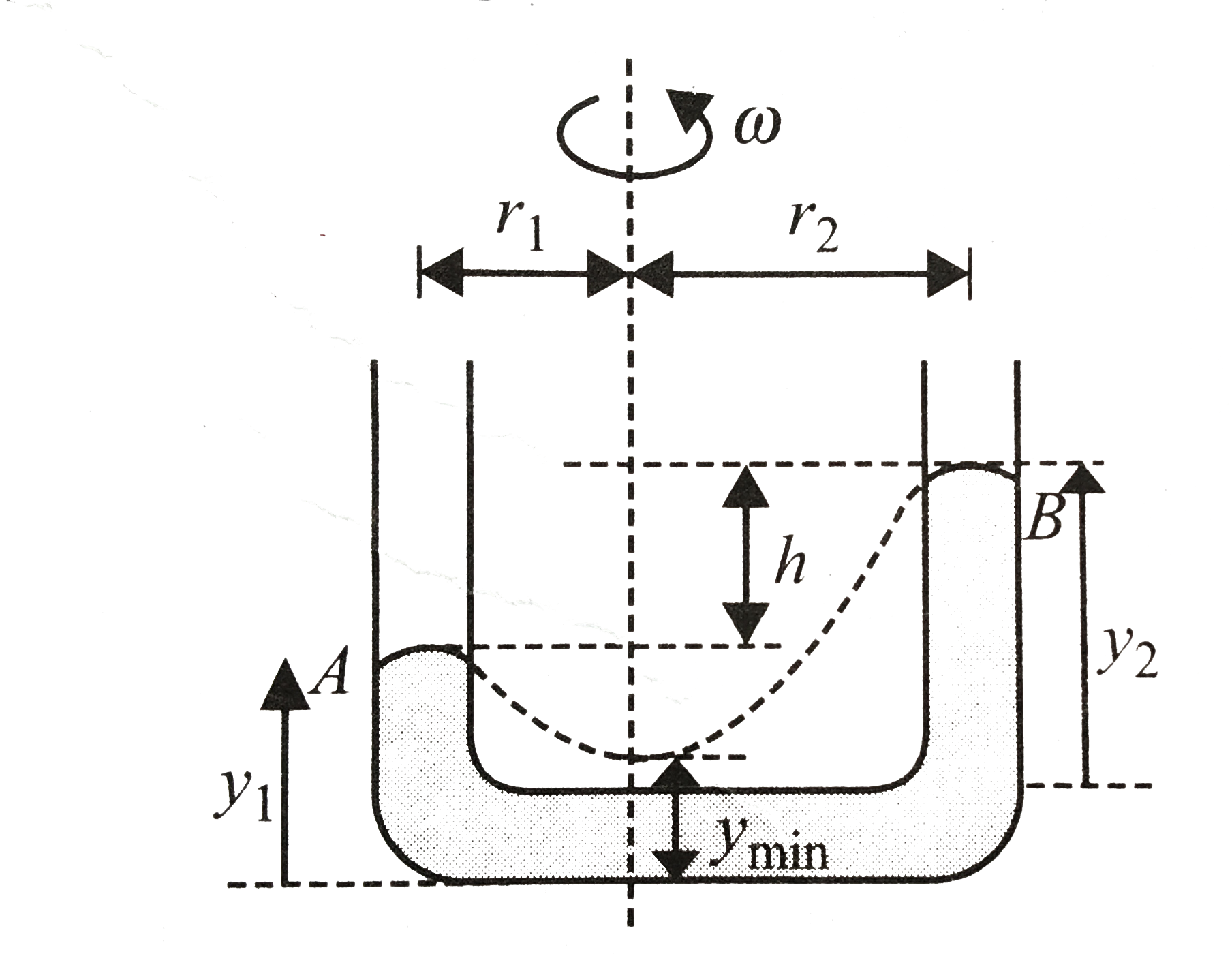
Alternatively, we may apply Bernoulli's equation between point `A` and `B`
`P_(atm)+1/2rho(r_(1)omega)^(2)=P_(atm)+1/2rho(r_(2)omega)^(2)=rhogh`
`implies h=((r_(2)^(2)-r_(1)^(2))/(2g))omega^(2)`