Density of the spherical material `=` specific gravity `xx` density of water `="sr"`
its volme is `V=m/(srho)`
Hence mass of water displaced by the shere is
`V_(rho)=m/(srho) rho=m//s=2/0.5=4kg`
since, the tank is accelerating upwards with acceleration a therefore, apparent value of gravitational acceleration is
`g'=g+a=12ms^(-2)`
Hence, upthrust exerted by water on the sphere is
`F=V_(rho)(g+a)=48N` brgt
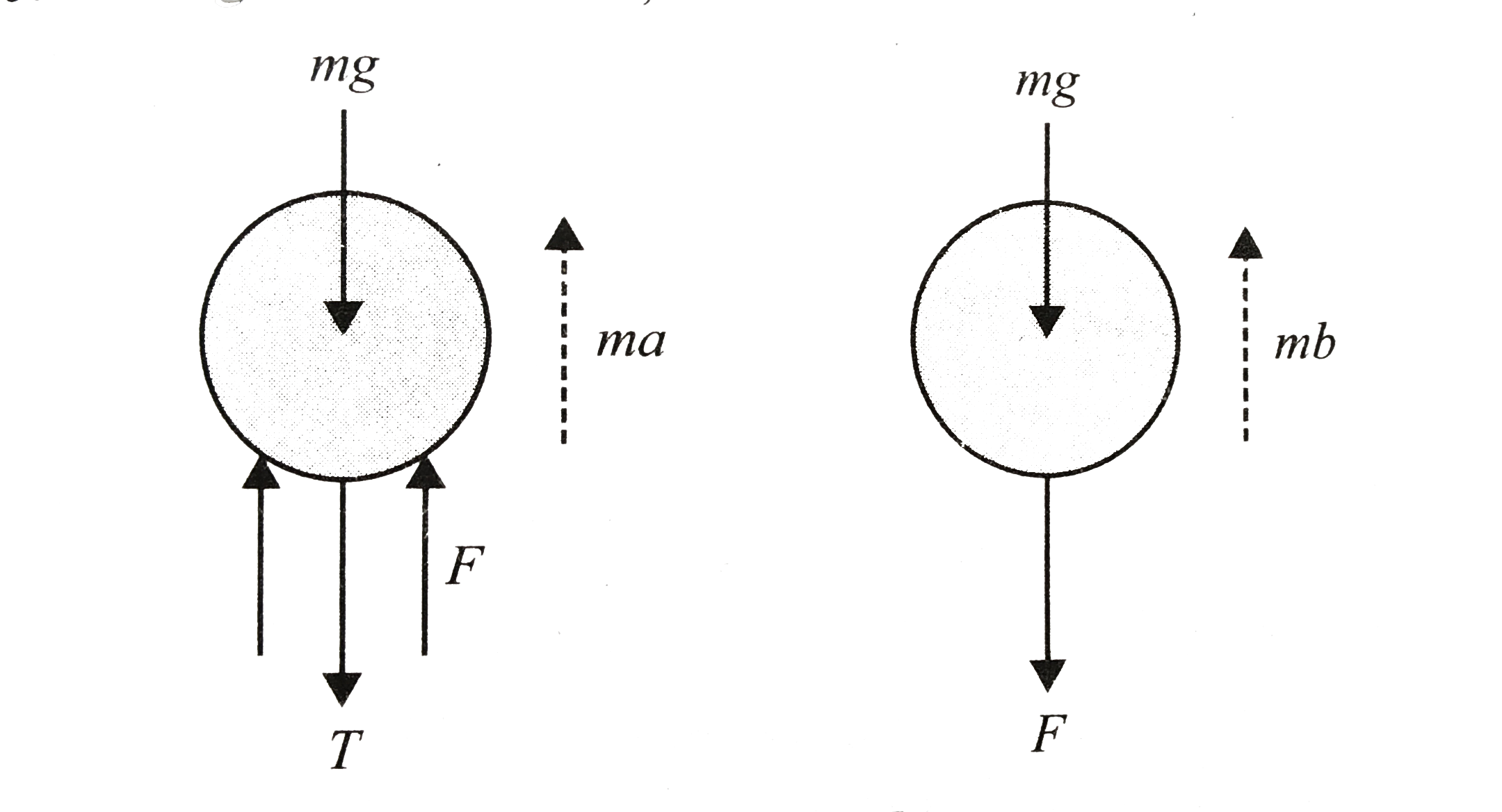
`F=mg-T=ma=.T=F-mg-ma=24N`
When thread snaps, tension `T` disappears. Let the sphere now starts accelerating upwards with acceleration b. Considering the free body diagram.
`F-mg=mb`
`:. b=14ms^(-2)`
Thus is the absolute acceleration of the sphere. But the tank itself is accelerating upwards with acceleration a. Therefore, upward acceleration of the sphere relative to the tank is `b-a=12ms^(-2)`