Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SURFACE CHEMISTRY
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise INTEXT QUESTIONS|8 VideosSURFACE CHEMISTRY
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|50 VideosSOLUTIONS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise INTEXT QUESTIONS|10 VideosTELANGANA MARCH-2019
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise SECTION C|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)-SURFACE CHEMISTRY-LONG ANSWER QUESTION
- Explain the terms absorption, adsorption and sorption. Describe the di...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the characteristics of physical adsorption.
Text Solution
|
- Compare and contrast the phenomenon of physisorption abd chemisorpion.
Text Solution
|
- What is an adsorption isotherm? Discuss the phenomenon of adsorption o...
Text Solution
|
- Give any two applications of adsorption.
Text Solution
|
- What is catalysis ? How is catalysis classified ? Give two examples fo...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the mechanism of heterogeneous catalysts.
Text Solution
|
- What are enzymes ? Give examples ?
Text Solution
|
- What are colloidal solutions ?
Text Solution
|
- How are colloids classified on the basis of the nature of interaction ...
Text Solution
|
- What are micelles ? Discuss the mechanism of micelle formation and cle...
Text Solution
|
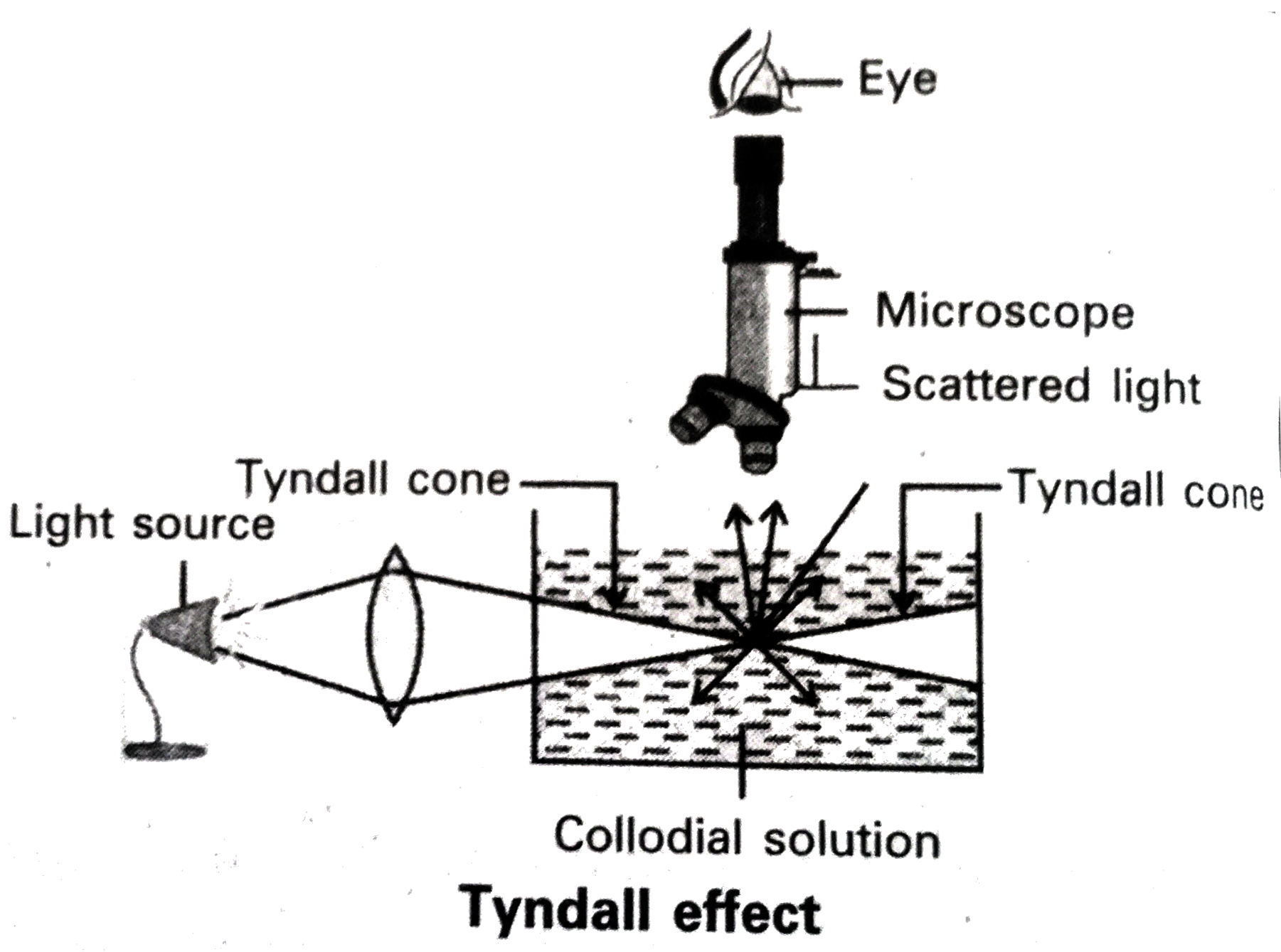
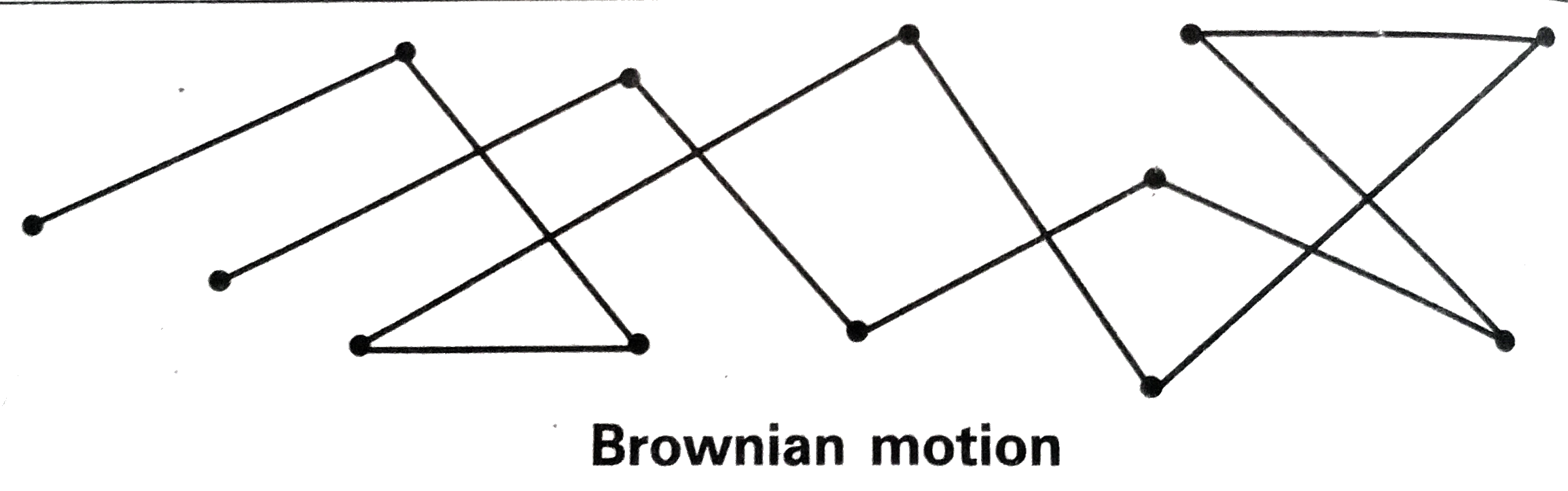
- Describe the properties of colloids with necessary diagrams wherever n...
Text Solution
|
- How emulsions are classified ? Give one example for each type of emuls...
Text Solution
|