Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise INTEXT QUESTIONS|22 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise VSAQ|1 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|17 VideosGENERAL PRINCIPLES OF MMETALLURGY
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise DAM SURE SAQ|1 VideosORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING C,H AND O
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise INTEXT QUESTIONS|54 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
- Discuss the physical properties of haloalkanes .
Text Solution
|
- Explain SN^(2) reaction
Text Solution
|
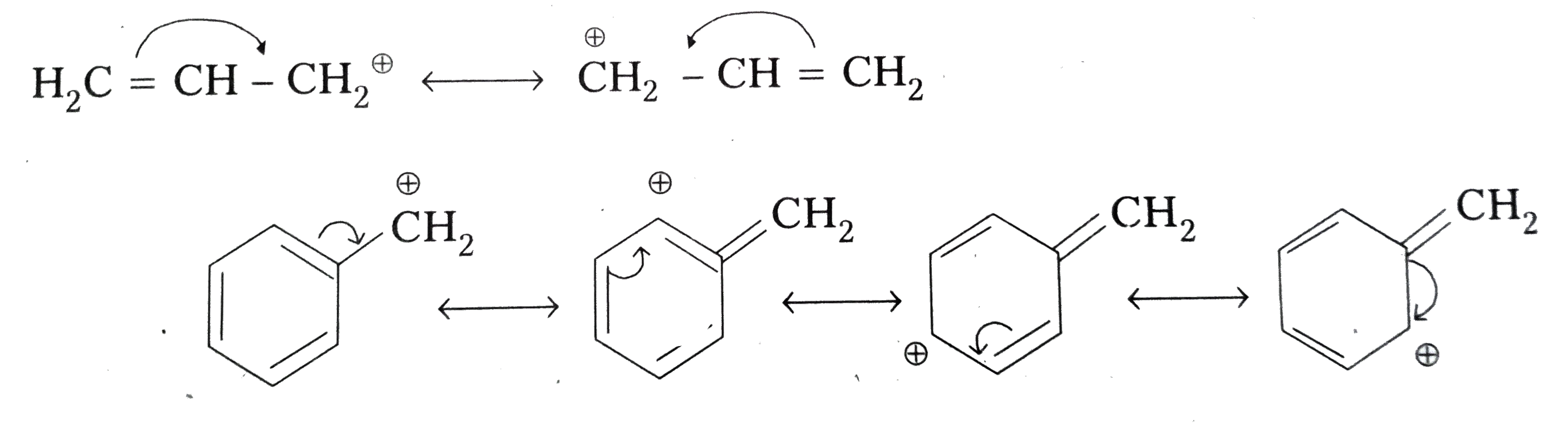
- Explain why allylic and benzylic halides are more reactive towards S(N...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the stereo chemical effect on the hydrolysis of 2-bromobutane...
Text Solution
|
- What is the criteria for optical activity . Give two examples of chira...
Text Solution
|
- Define Racemic mixture
Text Solution
|
- Define Retention of configuration
Text Solution
|
- Define Enantiomers .
Text Solution
|
- Write the mechanism of dehydrohalogenation of 2-bromobutane .
Text Solution
|
- Explain the Grignard reagents preparation and application with suitabl...
Text Solution
|
- A primary alkyl halide C(4)H(9) Br (A) reacted with alcoholic KOH to g...
Text Solution
|
- Account for the statements : Arylhalides are extremely less reactive...
Text Solution
|
- Account for the statements : p-Nitrochlorobenzene and o,p-dinitrochl...
Text Solution
|
- Explain how the conversions are carried out : Propene to Propanol
Text Solution
|
- Explain how the conversions are carried out : Ethanol to But-1-yne
Text Solution
|
- Explain how the conversions are carried out : 1-Bromopropane to 2-Br...
Text Solution
|
- Explain how the conversions are carried out : Aniline to chlorobenze...
Text Solution
|
- What happen when n-butylchloride is treated with alc. KOH.
Text Solution
|
- What happen when Bromobenzene is treated with Mg in presence of dry ...
Text Solution
|
- What happen when Methylbromide is treated with sodium in presence of...
Text Solution
|