Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS , DEVICES , AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise TEXTUAL EXERCISES|11 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS , DEVICES , AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise ADDITIONAL EXERCISES|8 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS , DEVICES , AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|16 VideosRAY OPTICAL AND INSTRUMENTS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise TEXTUAL EXERCISES|60 VideosTELANGANA MARCH-2019
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise SECTION -B|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)-SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS , DEVICES , AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS -LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
- What is a junction diode ? Explain the formation of depletion region a...
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between half-wave and full-wave rectifiers.
Text Solution
|
- What is a Zener diode ? Explain how it is used as a voltage regulator ...
Text Solution
|
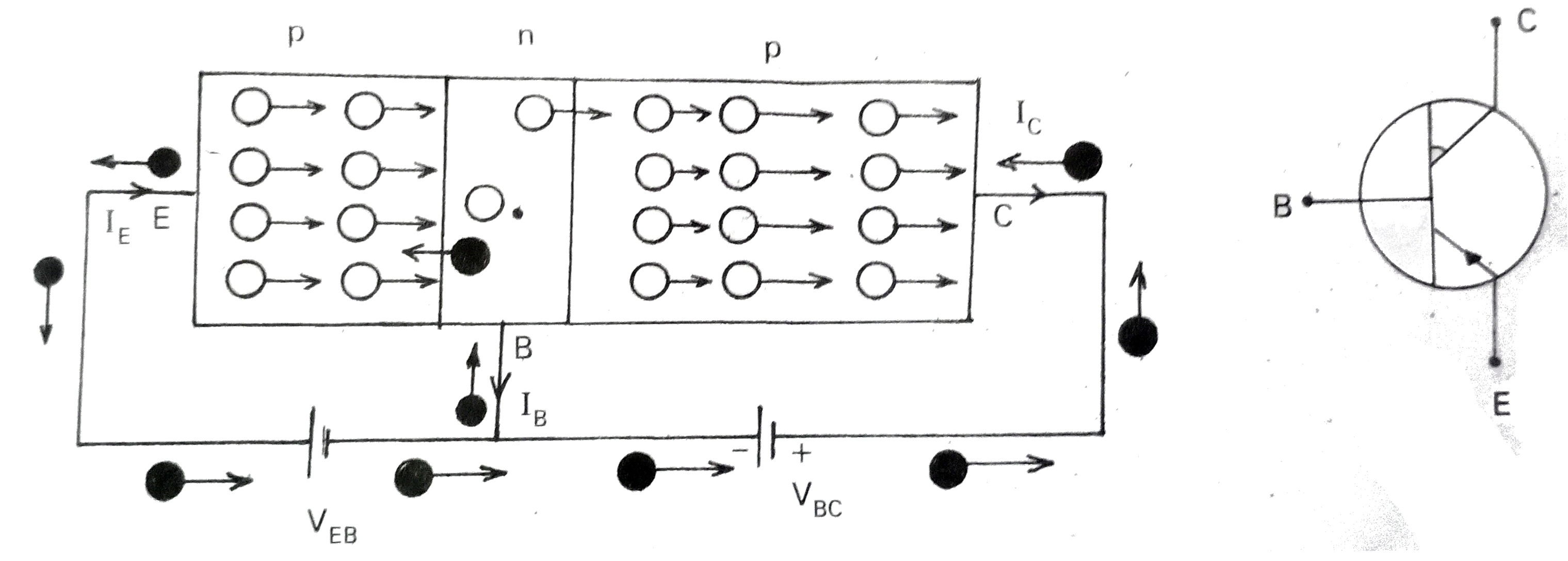
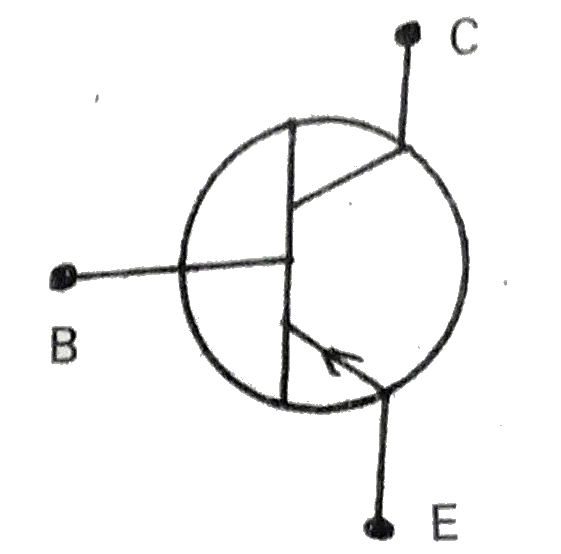
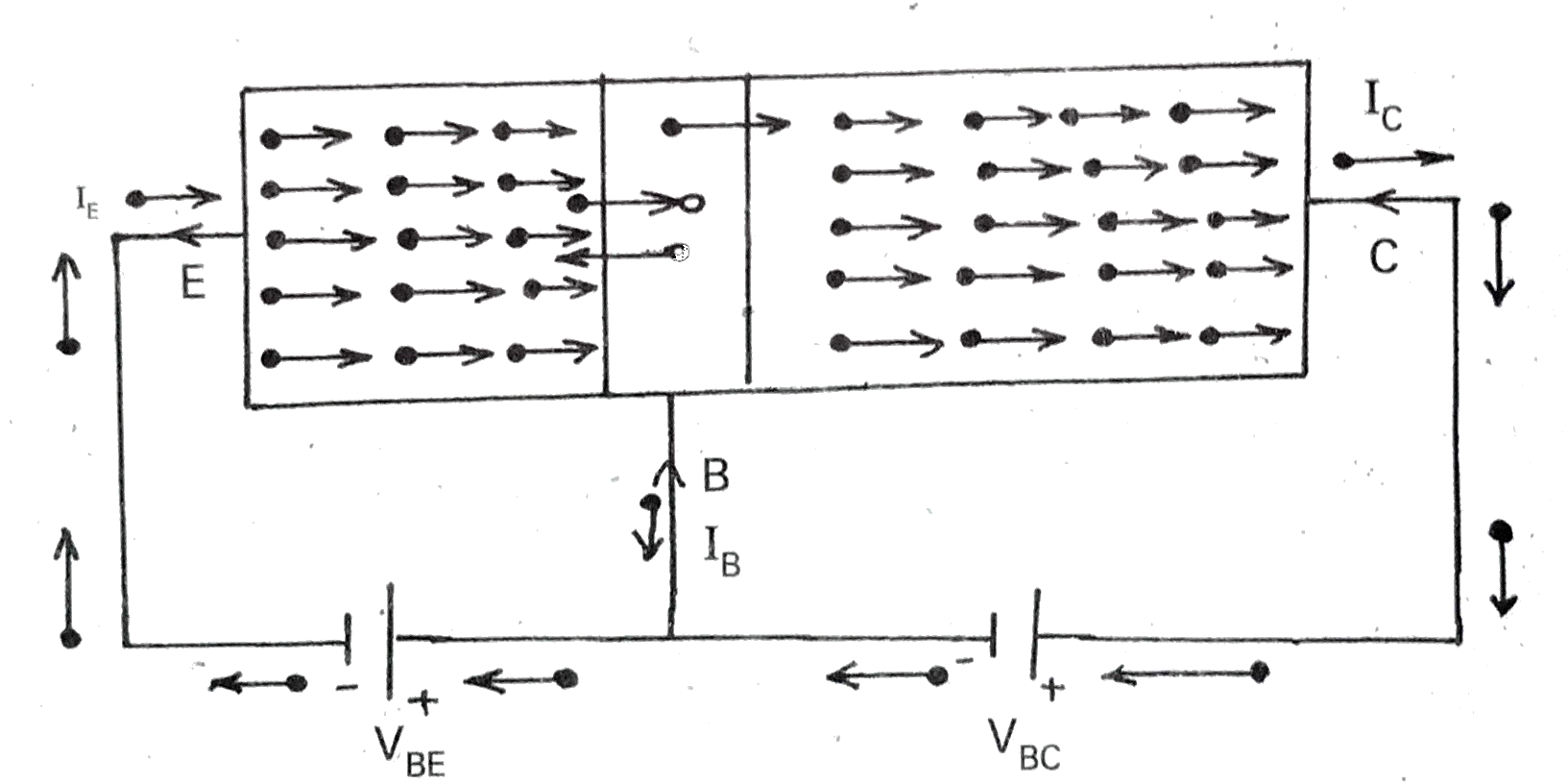
- Describe a transistor and explain its working.
Text Solution
|
- What is amplification ? Explain the working of a common emitter amplif...
Text Solution
|
- Draw an OR gate using two diode and explain its operation. Write the t...
Text Solution
|
- Sketch a basic AND circuit with two diodes and explain its operation....
Text Solution
|