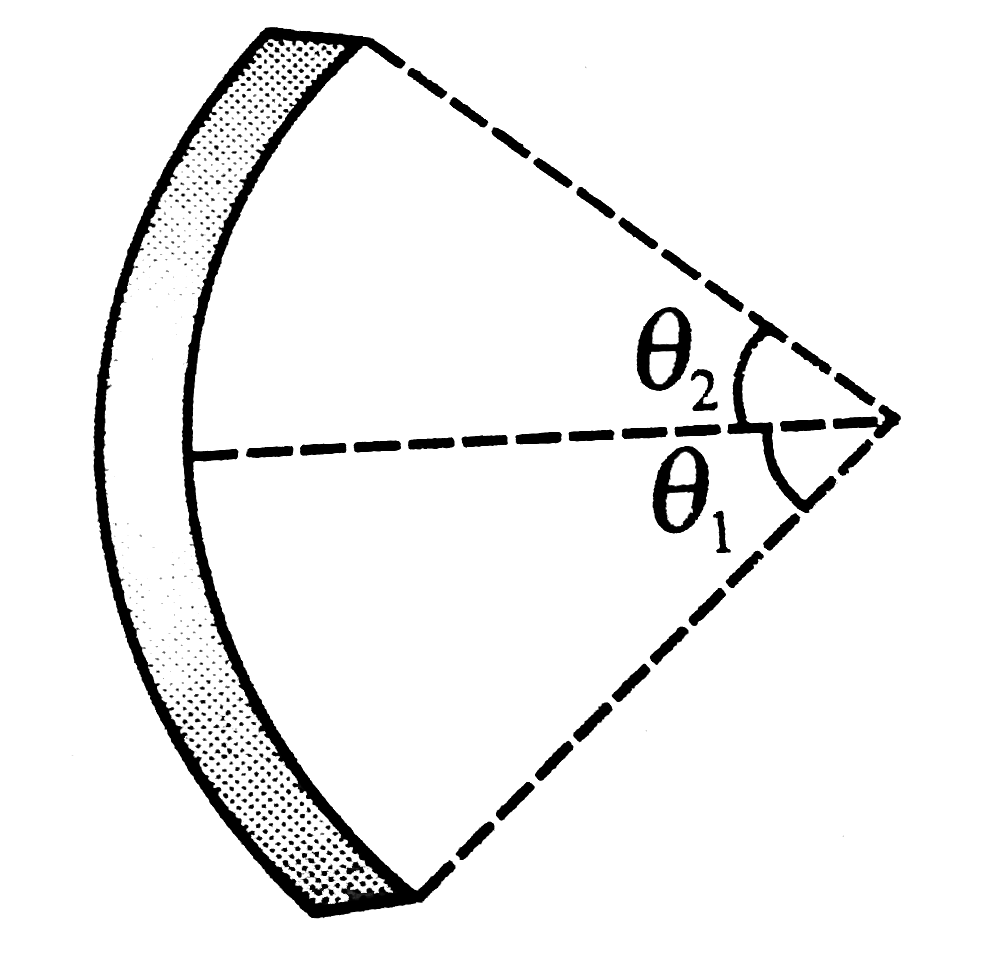A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD-Single Answer Correct Type
- Find the electric field at the centre of a uniformly charged semicircu...
Text Solution
|
- The given figure gives electric line of force due to two charges q(1) ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the four field patterns shown. Assuming there are no charge i...
Text Solution
|
- A charge Q is fixed at a distance d in front of an infinite metal plat...
Text Solution
|
- The lines of force of the electric field due to two charges q and Q ar...
Text Solution
|
- Two ideantical point charges are placed at a separation of d. P is a p...
Text Solution
|
- The bob of a pendulum of mass 8 mu g carries an electric charge of 39....
Text Solution
|
- Two charges each equal to eta q(eta^(-1) lt sqrt(3)) are placed at the...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges (+Q) and (-2Q) are fixed on the X-axis at positions ...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical shell is uniformly charge positively .the electric fie...
Text Solution
|
- An electron falls through a small distance in a uniform electric field...
Text Solution
|
- There is a uniform electric field of strength 10^(3)V//m along y-axis....
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown there is a large sheet of charge of uniform surfac...
Text Solution
|
- Three charges of (+2q), (-q) and (-q) are placed at the corners A,B an...
Text Solution
|
- An electric dipole is placed along the x-axis at the origin O.A point ...
Text Solution
|
- An electric dipole is placed at the origin O and is directed along the...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical dipoles are arranged as shown below. What will be the ...
Text Solution
|
- Two electric dipoles of moment P and 64P are placed in opposite direct...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges (+Q) and (-2Q) are fixed on the X-axis at positions ...
Text Solution
|
- An electric dipole is kept on the axis of a uniformly charged ring at ...
Text Solution
|
- Two short dipoles phat(k) and P/2 hat(k) are located at (0,0,0) & (1m,...
Text Solution
|