Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW-MCQ s
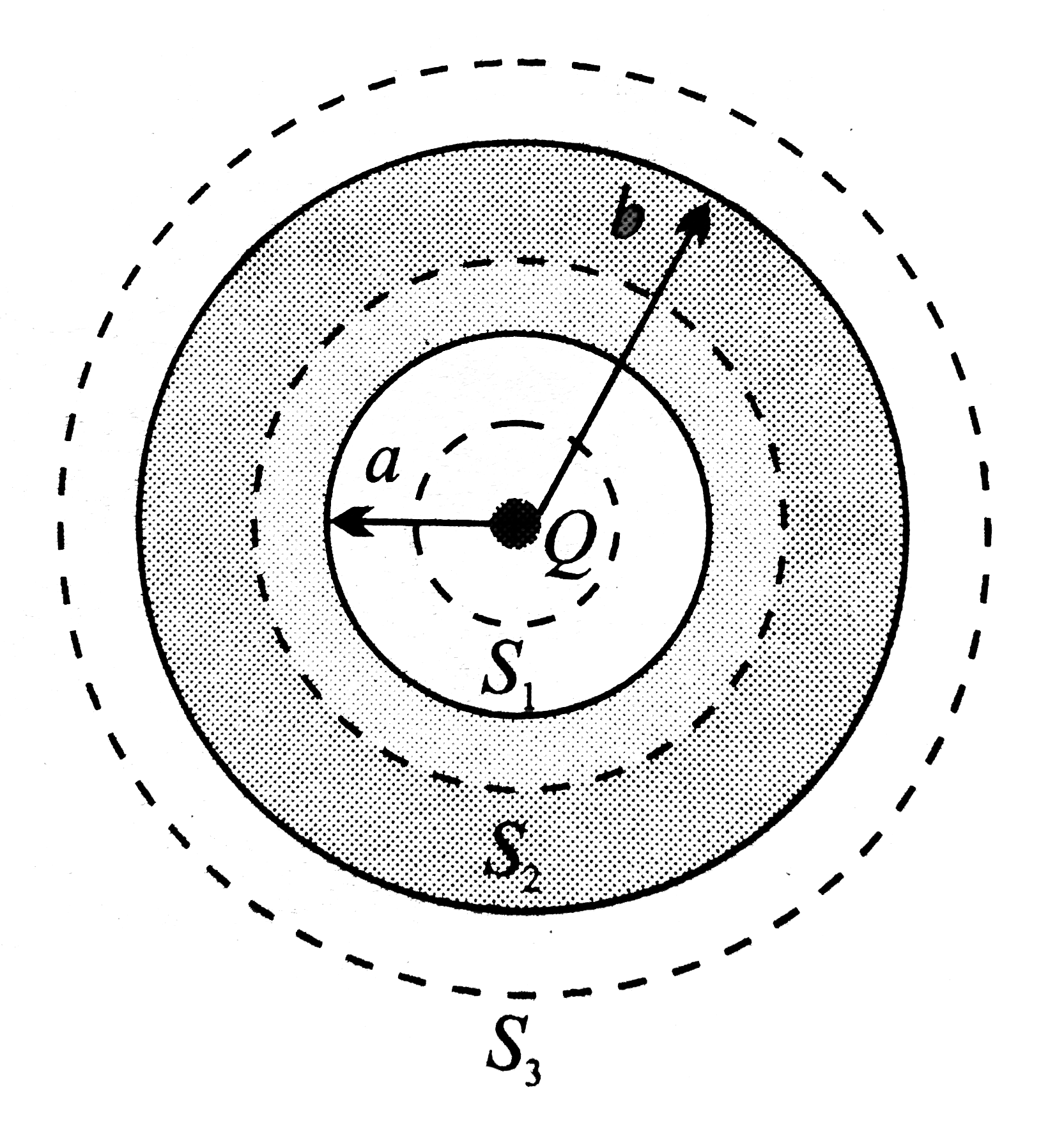
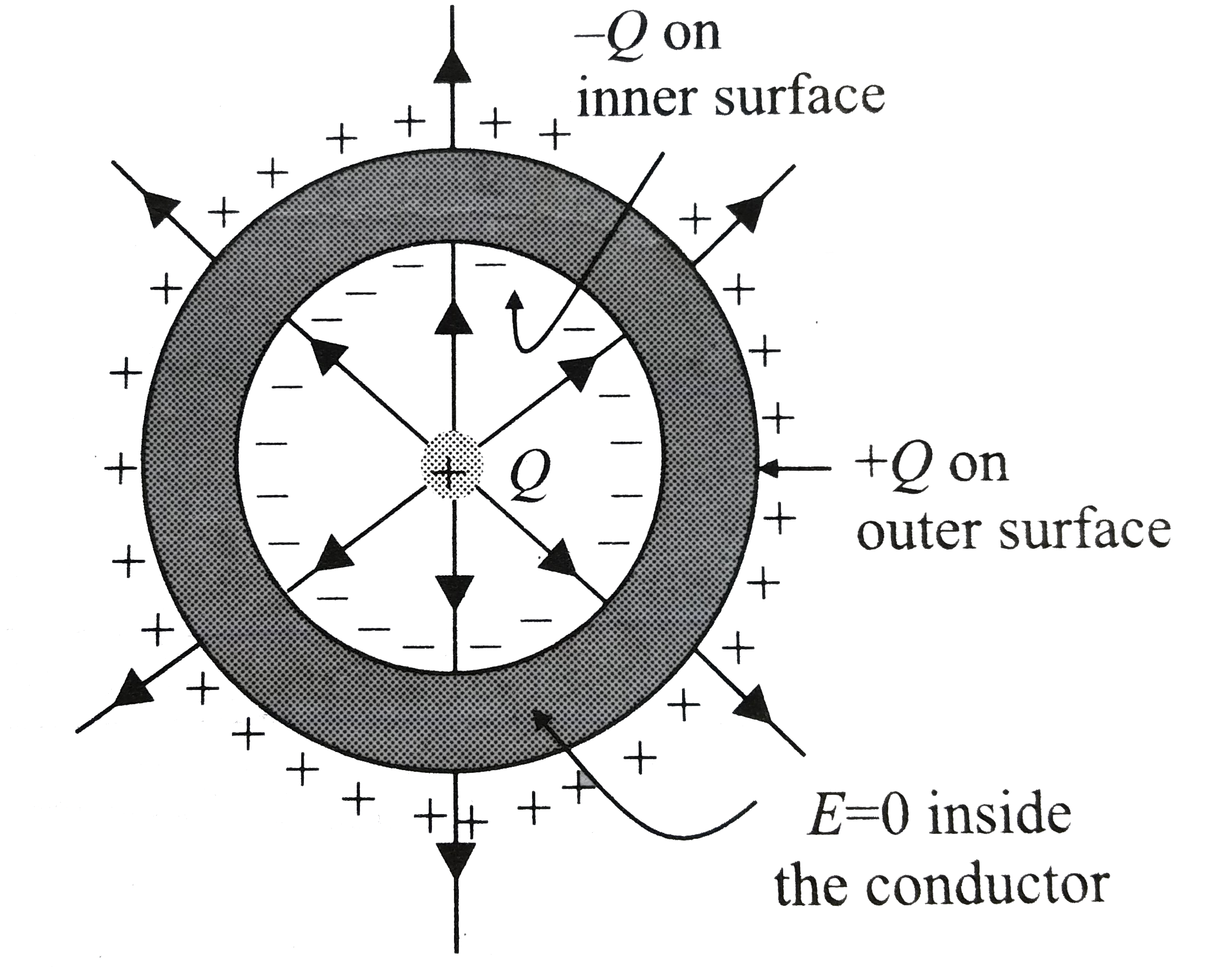
- A point charge +Q is placed at the centre of an uncharged spherical co...
Text Solution
|
- Electric flux through a surface area 10 m^(2) lying in the xy plane in...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of radius R and length L is placed in a uniform electric fi...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge q is placed near hemisperical suface without base, cyli...
Text Solution
|
- A linear charge having linear charge density lambda pentrates a cube d...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius R is placed in the plane its centre at origin and its...
Text Solution
|
- A position charge q is placed at a distance of 4R above the centre of ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows. In cross section m three solid cylinders, each of length...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown four solid spheres, each with charge Q uniformly distribu...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure a hemispherical bowl of bowl of radius R is shown Electr...
Text Solution
|
- figure shows, in cross section, two Gaussian spheres and two Gaussian ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows four Gaussian surfaces consisting of identical cylindrica...
Text Solution
|
- In figure , a solid sphere of radius a = 2.00cm is concentric with a s...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform charge density of 500 nC//m^(3) is distributed throughout a ...
Text Solution
|
- the net electric flux through each face of a die (singular of dice) ha...
Text Solution
|
- A Gaussian surface S encloses two charges q(1)= q and q(2) = -q the fi...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field in a region is radially outward with magnitude E=A...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of a cylindrical ve...
Text Solution
|
- Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a along straight wire o...
Text Solution
|
- In a region of space having a spherical symmetric distribution of cha...
Text Solution
|
- In a region of space the electric field in the x-direction and proport...
Text Solution
|