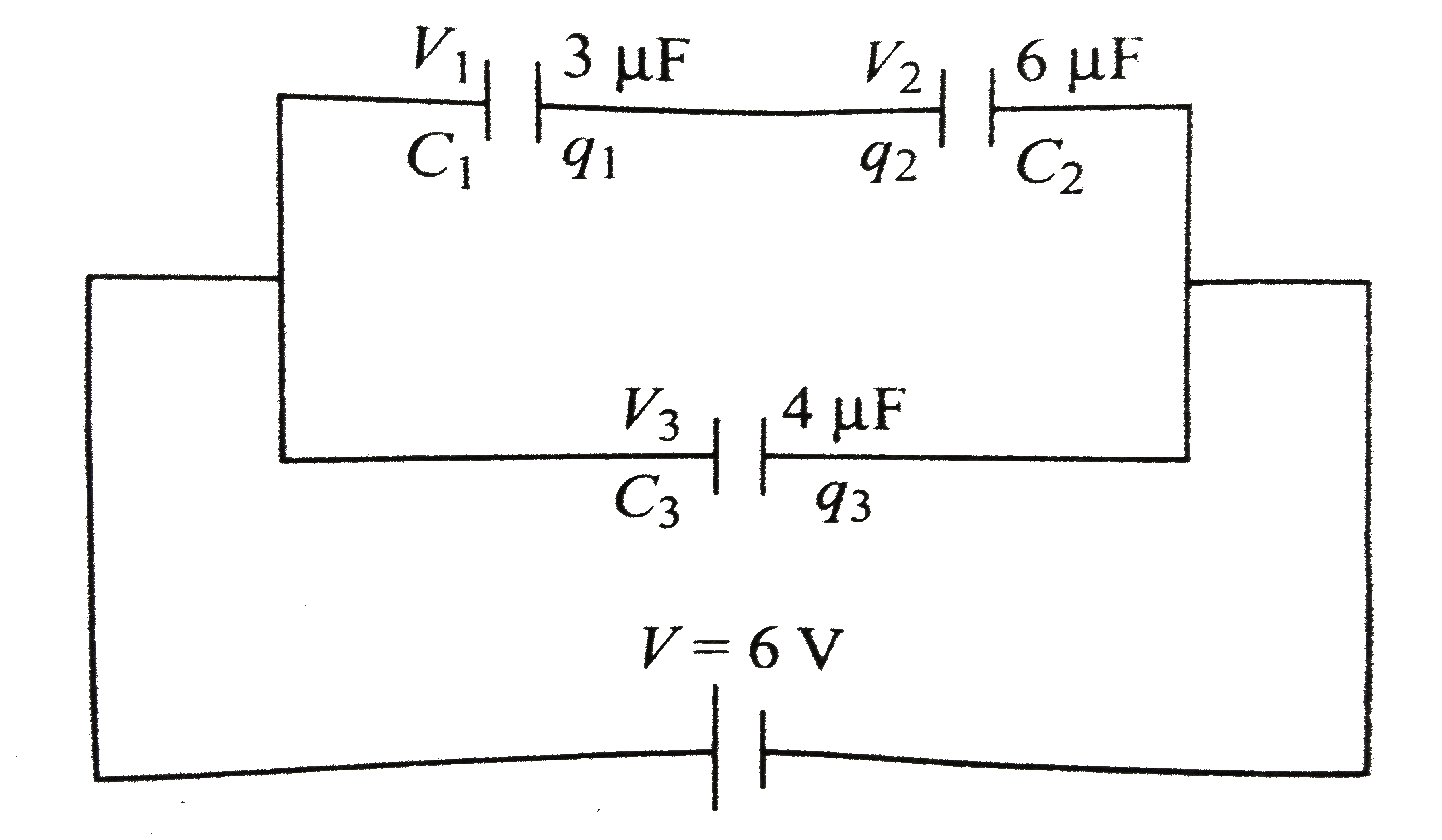
i. `C_(1)` and `C_(2)` are in series, so their equivalent capacitance is
`C=(C_(1)C_(2))/(C_(1)+C_(2))=(3xx6)/(3+6)=2 muF`
This `C'` will be in parallel `C_(3), So
`C_(eq)=C'+ C_(3)=2+4=6 muF`
ii. `6 V` will be in parallel across `C_(1)` and `C_(2)` in the inverse ratio of the capacitances. So potential defference across `C_(1)` is
`V_(1)=(C_(2)V)/(C_(1)+C_(2))=(6xx6)/(3+6)=4 V`.
and potential differnce across `C_(2)` is `V_(2)=(C_(1)V)/(C_(1)+C_(2))=(3xx6)/(3+6)=2 V`
Because `C_(3)` is connected directly aross the battery without any other capacitor in between , so potential difference across `C_(3)` is `V_(3) =V=6 V`. Also charge on `C_(1)` is
`q_(1)=C_(1)V_(1)=3xx4=12 muC`
and charge on `C_(2)` is
`1q_(2)=C_(2)V_(2)=6xx2-12 muC`
We see that `q_(1)q_(2)`, because is series, charge is the same.
chaege on `C_(3)` is
`q_(3)=C_(3)V_(3)=4xx6=24 muC`.
Alternative methode to find charge.
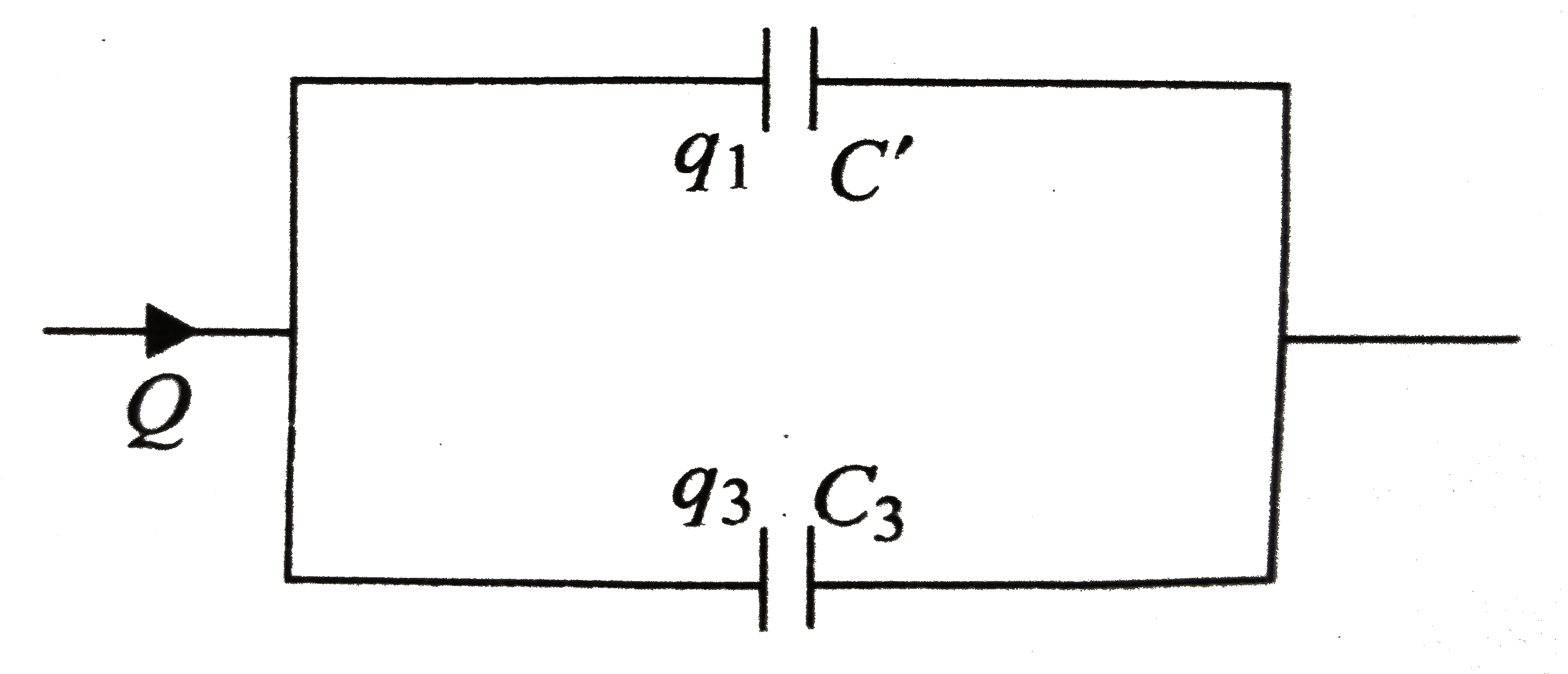
Total charge that will flow through the battery is
`Q = C_(eq)V = 6 xx 6 = 36 muC`
It will be divided inthe direct ratio of `C'` and `C_(3)`, so
`q_(1) = (C'Q)/(C'+C_(3)) = (2 xx 36)/(2+4) = 12 muC`
`q_(3) = (C'Q)/(C'+C_(3)) = (4 xx 36)/(2+4) = 24 muC`
Energy in `C_(1)` is
`U_(1) = (1)/(2)C_(1)V_(1)^(2) = (1)/(2)xx3xx4 = 24mu J`
Energy in `C_(2)` is
`U_(2) = (1)/(2)C_(2)V_(2)^(2) = (1)/(2)xx6xx2^(2) = 12mu J`
Energy is `C_(3)` is
`U_(3) = (1)/(2)C_(3)V_(3)^(2) = (1)/(2)xx4xx6 = 72mu J`
Total energy is
`U = U_(1) + U_(2) + U_(3) = 24 + 12 + 72 = 108 mu J`
Alternatively
`U = (1)/(2) xx 6 xx 6^(2) = 108 muJ`
 .
. 