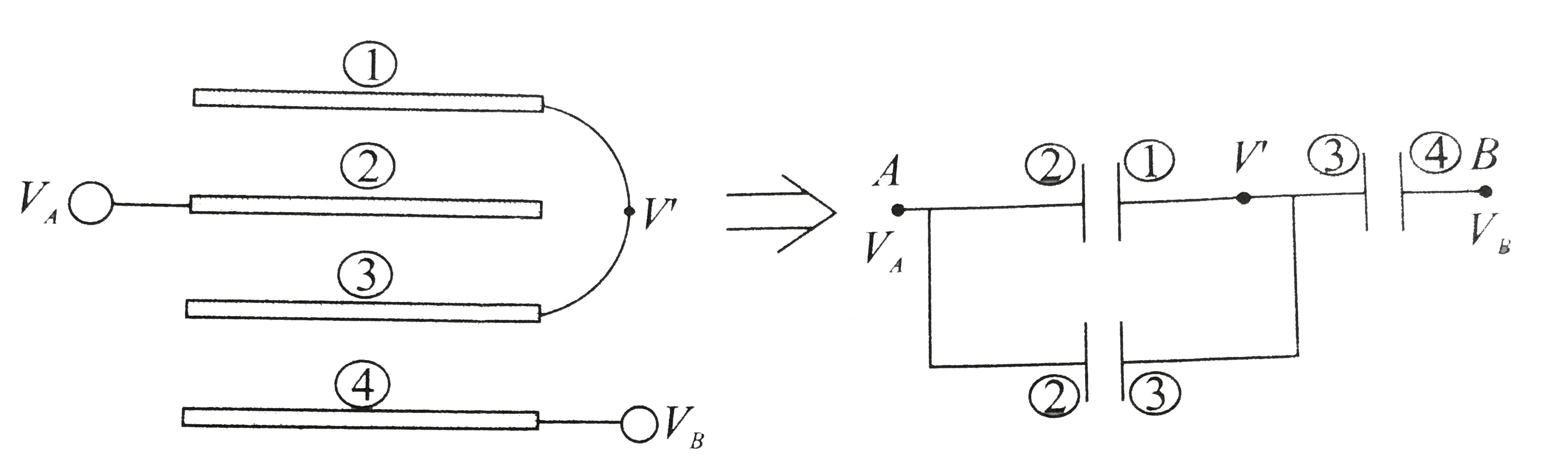Method 1 : Let the potentials of plates `A` and `B` be `V_(A)` and `V_(B)` respectively. As the plates (1) and (2) are comected together, they will have a common potential, say (V'). Now we will make an equivalent circuit digram by connecting the different plates across the assumed potential defference.
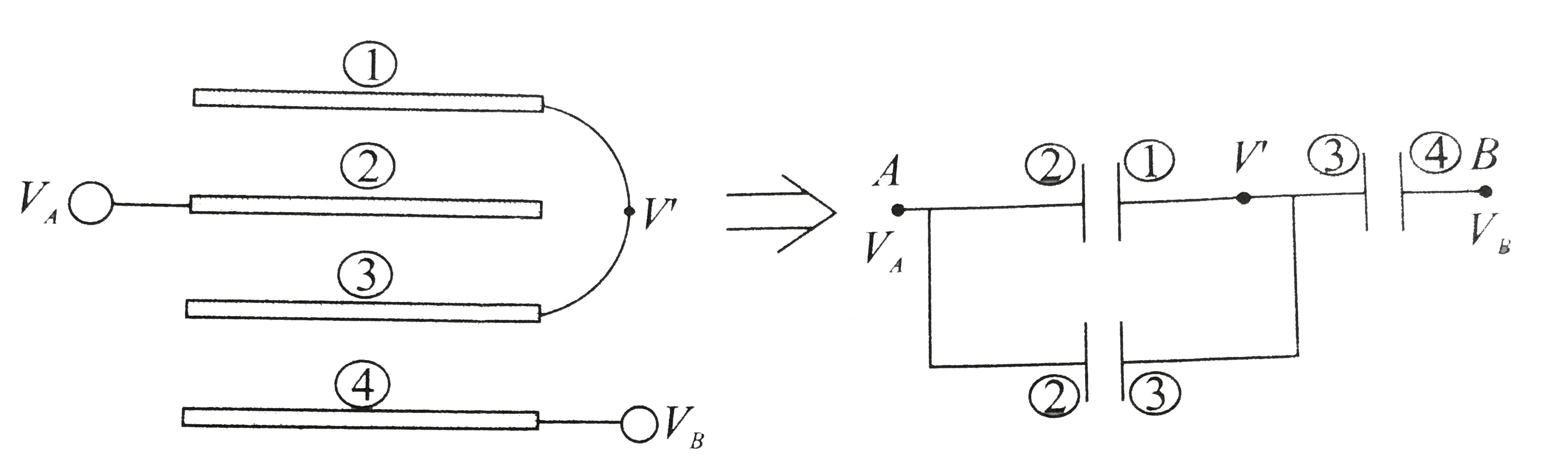
The equivalent capcitance between `A` and `B` can easily be calculated as follows:
`C_(eq)=2/3 C=2/3 (epsilon_(0)A)/d`
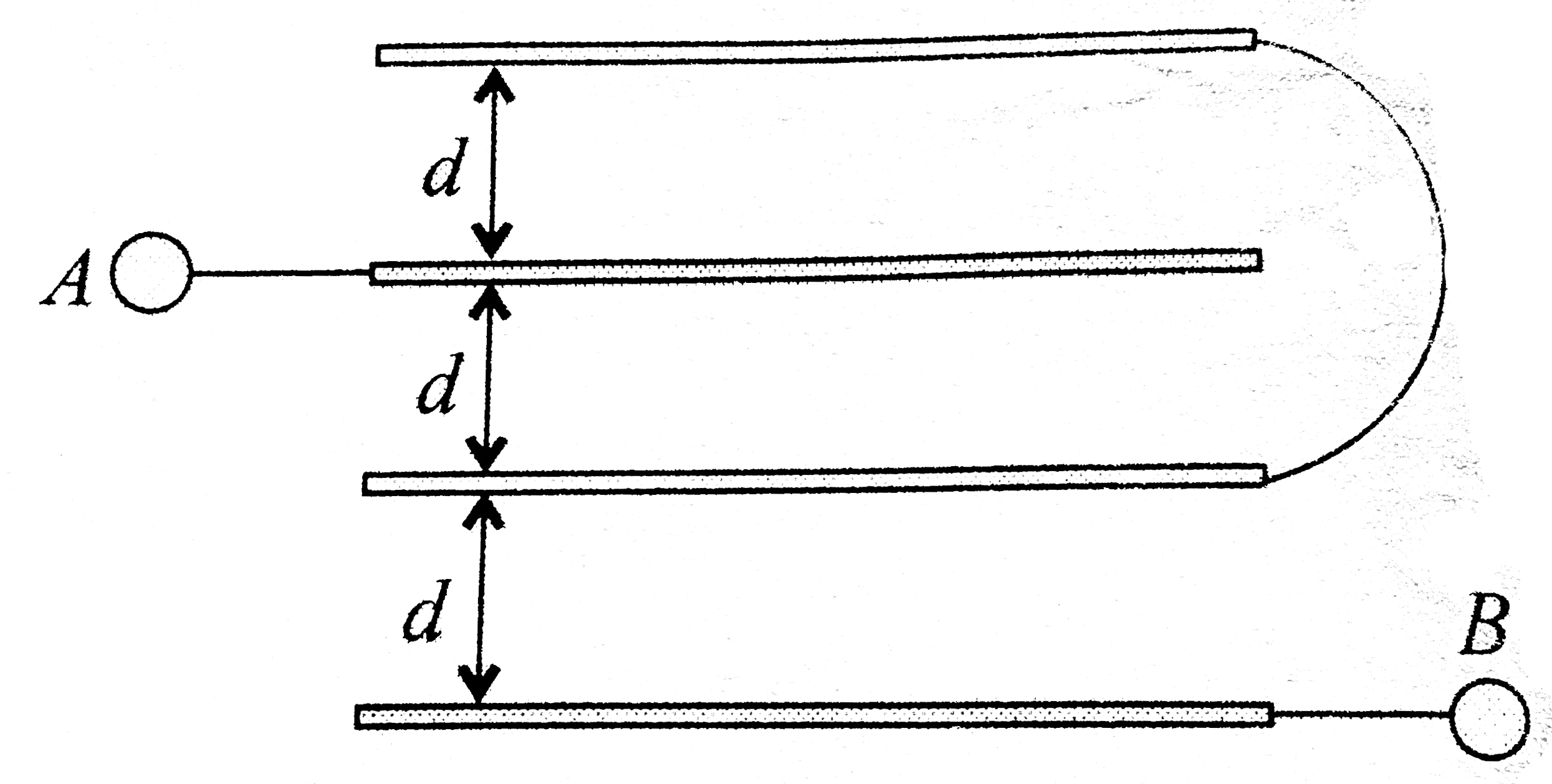
Method 2: Let us assume that battery is connected between `A` and `B` Let potentials of `A` and `B` be `V` and `0`. plates (1) and (2) are connceted together and both have the same potential `(V')`. The charge supplied by the positive terminal og the battery to plate (1) be (Q), same charge will come out from plate (4). The outermost surface of the plates will carry no charge . Hence, `-Q` charge will appear on the inner surface of plate (4). The charge distribution on different surfaces of the paltes can be done by using conservation of charge. The charge appearing on the facing surfaces should be equal and opposite. The equal and opposite. The charges appearing on difference surfaces are shown in. The capacitance of the system of plates can be given by
`C=Q/(V-0)` (i)
Between plates (i) and (2),
`(Q-x)=C(V-V')` (ii)
Between plates `(2)` and `(3)`,
`x=C(V-V')` (iii)
Between plates (3) and (4).
`Q=C(V'-0)` (iv)
From `(ii)` and `(iii), (iv)`
`(Q-x)=x` or `x=Q/2` (v)
Adding Eqs. (iii) and (iv), we get (v)
`V=x/C+Q/C=(3Q)/(2C)` or `Q/C=2/3 C=2/3(2epsilon_(0)A)/d=C_(eq)`.
 .
.