A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Comprehension|35 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger|8 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|72 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT & CIRCUITS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Kirchhoff s law and simple circuits|15 VideosELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise MCQ s|38 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT-Multiple Correct
- In the network shown in fig. , points A, B, and C are at potentials of...
Text Solution
|
- When some potential differece is maintained between A and B, current I...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in fig. the cell has emf 10V and internal resista...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in fig. some potential difference is applied betw...
Text Solution
|
- A battery of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a res...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit.
Text Solution
|
- For the batteries shown in fig. R1, R2 and R3 are the internal resista...
Text Solution
|
- A single battery is connected to three resistances as shown in fig. 5....
Text Solution
|
- The charge flowing in a conductor varies with times as Q = at - bt^2. ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference between points A and B in the circuit shown i...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in fig. mark the correct options.
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit (as shown in fig. 5.319).
Text Solution
|
- Study the following circuit diagram in fig. 5.320 and mark the correct...
Text Solution
|
- The capacitor C is initially without charge. X is now joined to Y for ...
Text Solution
|
- Two circuits are called circuit A and Circuit B. The equivalent resist...
Text Solution
|
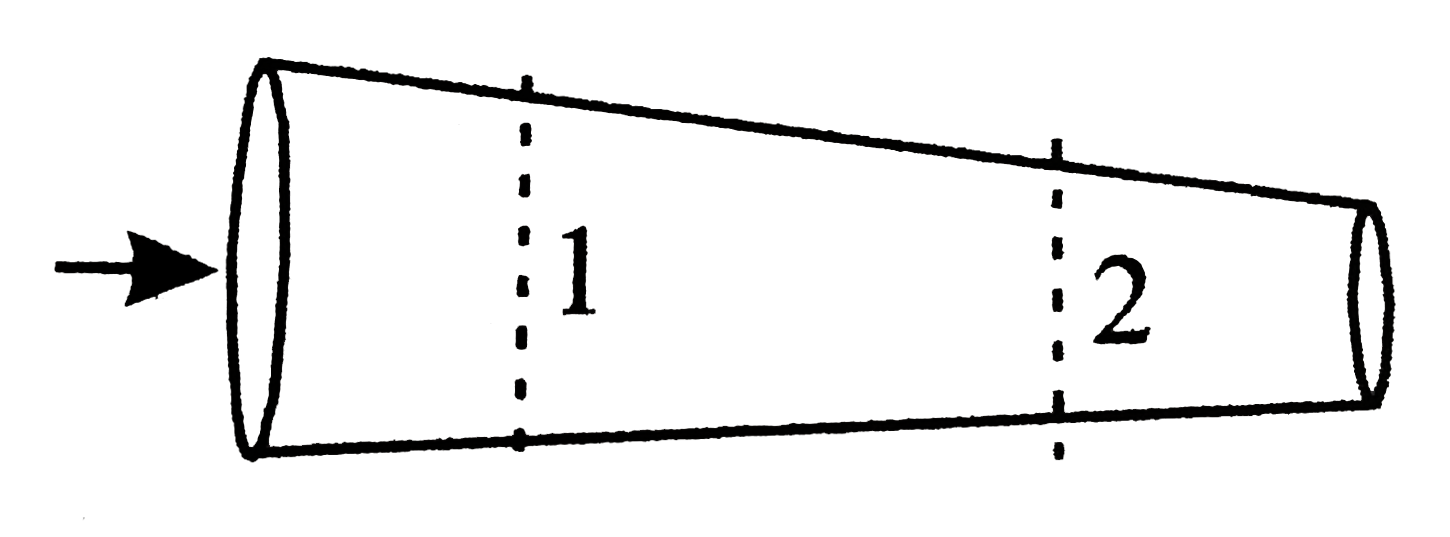
- Consider a conductor of variable cross section in which current is fl...
Text Solution
|