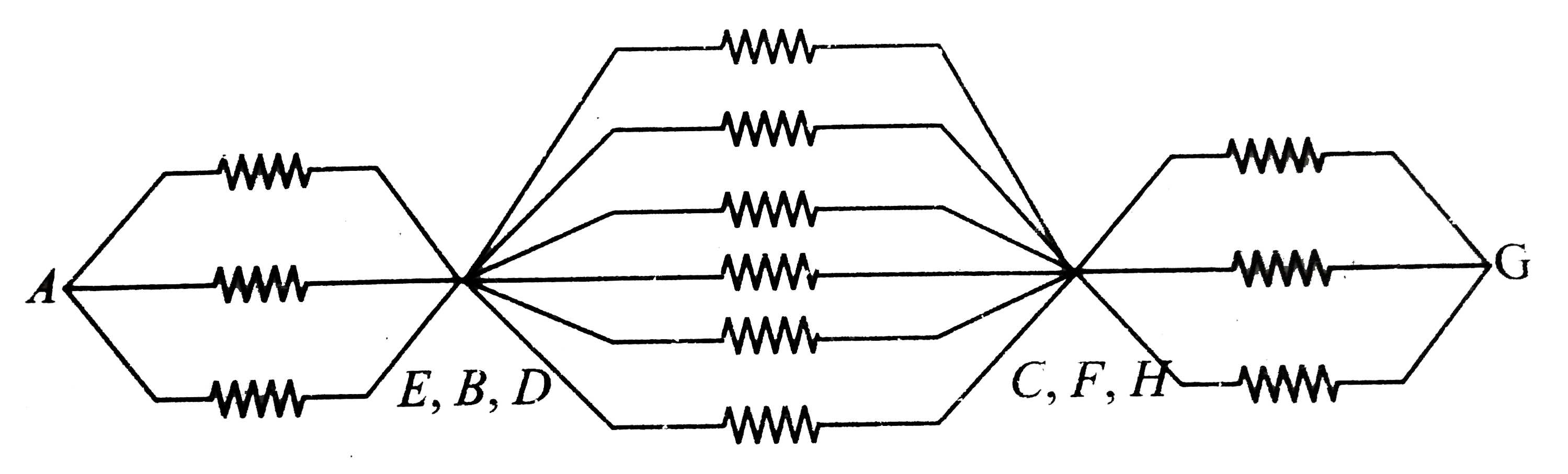
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger|8 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|16 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT & CIRCUITS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Kirchhoff s law and simple circuits|15 VideosELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise MCQ s|38 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT-Comprehension
- Consider the circuit shwon in fig. The circuit is in steady state. ...
Text Solution
|
- In the netwrok shown in fig. each resistance is R. The equivalent...
Text Solution
|
- In the netwrok shown in fig. each resistance is R. The equivalent...
Text Solution
|
- In the netwrok shown in fig. each resistance is R. The equivalent...
Text Solution
|
- A resistor circuit is constructed such that 12 resistor are arranged t...
Text Solution
|
- A resistor circuit is constructed such that 12 resistor are arranged t...
Text Solution
|
- A resistor circuit is constructed such that 12 resistor are arranged t...
Text Solution
|
- Consider 12 resistor arranged symmetrically in shape of bipyraimd ABCD...
Text Solution
|
- Consider 12 resistor arranged symmetrically in shape of bipyraimd ABCD...
Text Solution
|
- Consider 12 resistor arranged symmetrically in shape of bipyraimd ABCD...
Text Solution
|
- shown a network of four resistance and three batteries Choose the...
Text Solution
|
- shown a network of four resistance and three batteries Mark the i...
Text Solution
|
- shown a network of four resistance and three batteries Which of t...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement, 11 wires each of resistance 5Omega are used as sid...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement, 11 wires each of resistance 5Omega are used as sid...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement, 11 wires each of resistance 5Omega are used as sid...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the circuit shown in fig. Current through R2 is zero if ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the circuit shown in fig. Assuming R1 = 2Omega, current ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the circuit shown in fig. Assuming R1 =2Omega = R4, R3 =...
Text Solution
|
- The following two questions refer to the circuit shown. Assume that th...
Text Solution
|