A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
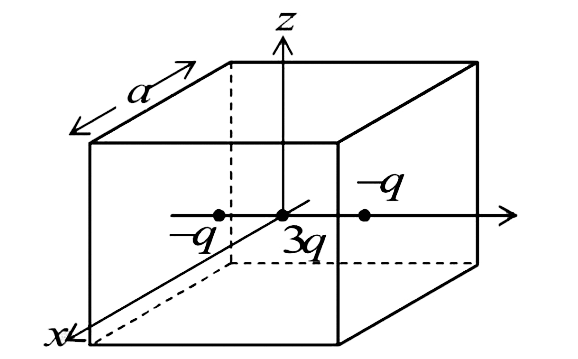
- A cubical region of side a has its centre at the origin. It encloses t...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical region of side a has its centre at the origin. It encloses t...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges+q nd -q are held fixed at (-a,0) and (a,0) respectiv...
Text Solution
|
- Two fixed charges -2Q and +Q are located at points (-3a,0) and (+3a,0)...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges q each are fixed at (a,0) and (-a,0). A third charge...
Text Solution
|
- बिंदु (0, 0, -a) तथा (0, 0, a) पर दो आवेश क्रमशः -q और +q स्थित हैं। ...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges-q and +q are located at points (0, 0,-a) and (0, 0, ...
Text Solution
|
- एक घनाकार क्षेत्र की भुजा a और केन्द्र उद्गम पर है। इसमें तीन बिन्दु आ...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges -q and + q are located at points A (0, 0, -a ) and B(0, 0 ...
Text Solution
|