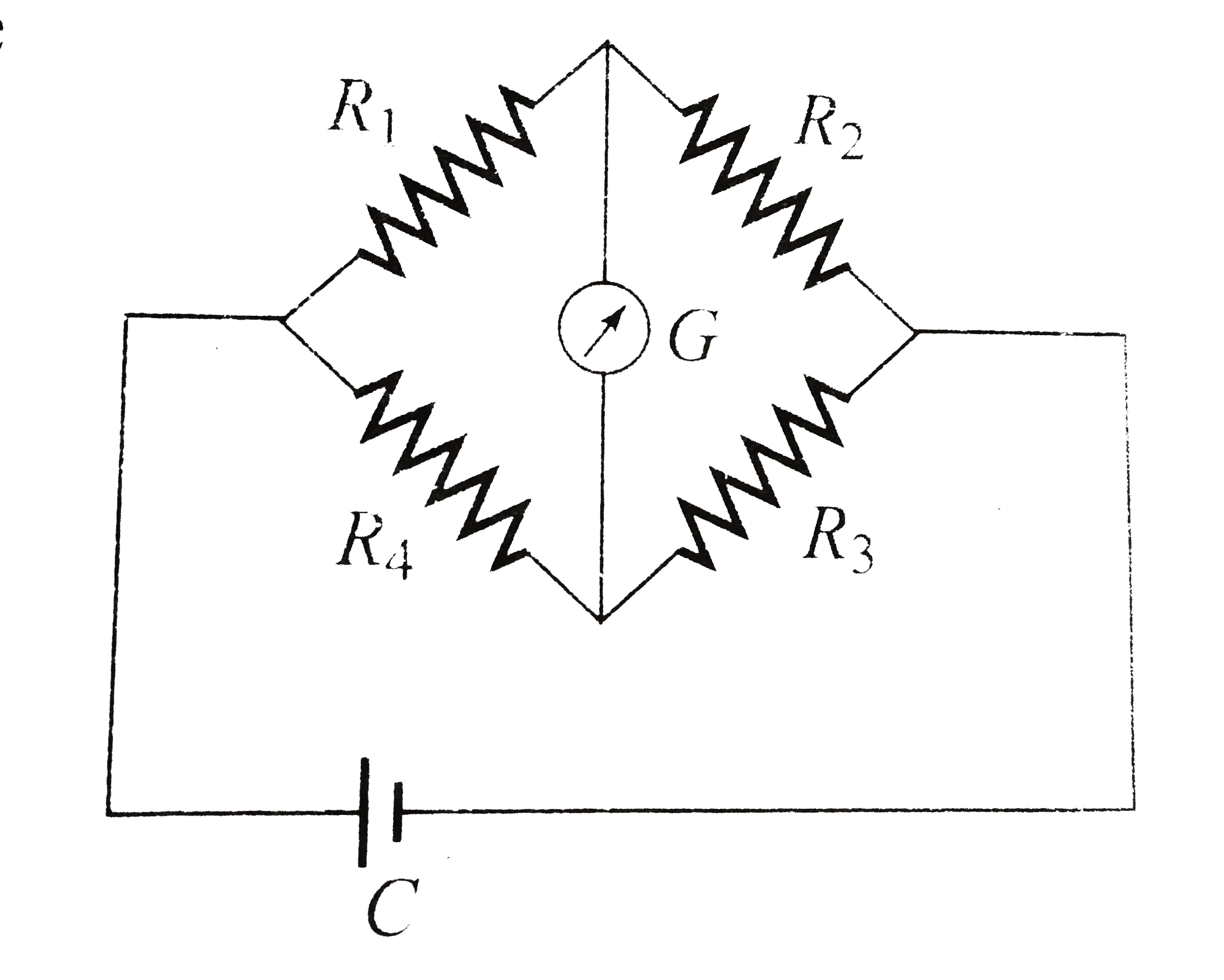
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The Wheatstone's bridge shown in the Fig. A2.5 is balanced. If the pos...
Text Solution
|
- The Wheatstone's bridge shown in the Fig. A2.5 is balanced. If the pos...
Text Solution
|
- If in the experiment of Wheatstone's bridge, the positions of cells an...
Text Solution
|
- The balanced position of meter bridge is …… interchangeing the positio...
Text Solution
|
- Figure (a) below shows a wheat stone bridge in which P, Q, R, S are fi...
Text Solution
|
- The Wheatstone bridge shown in the above figure is balanced. If the po...
Text Solution
|
- In a wheatstone bridge if the battery and galvanometer are interchange...
Text Solution
|
- In a balanced Wheatstone's network, galvanometer and cell are intercha...
Text Solution
|
- A meterbridge is in balance condition. Now if galvanometer and cell ar...
Text Solution
|