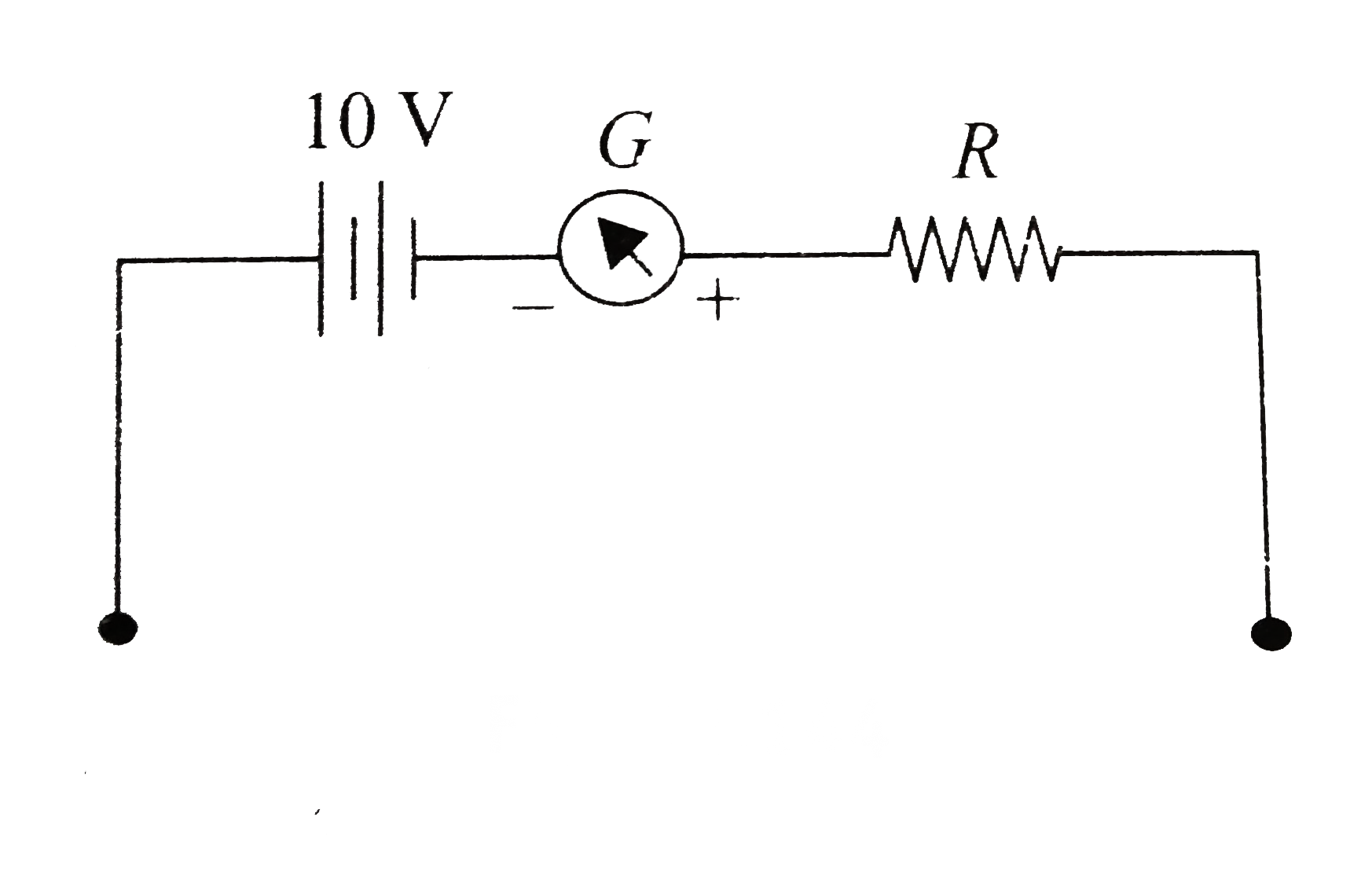A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger Answer type|20 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Fill in the blanks|10 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion and Reason Type|8 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Question Bank|4 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3-Comprehension Type
- In the connection shown in the figure, initially the switch K is open ...
Text Solution
|
- In the connection shown in the figure, initially the switch K is open ...
Text Solution
|
- In the connection shown in the figure, initially the switch K is open ...
Text Solution
|
- The value of resistance of an unknown resistor is calculated using the...
Text Solution
|
- The value of resistance of an unknown resistor is calculated using the...
Text Solution
|
- The value of resistance of an unknown resistor is calculated using the...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit given in the figure, both batteries are ideal . Emf E1 ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit given in the figure, both batteries are ideal . Emf E1 ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit given in the figure, both batteries are ideal . Emf E1 ...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit is in a steady state. The charge in capacitor C1 is
Text Solution
|
- The circuit is in a steady state. The charge in capacitor C2 is
Text Solution
|
- The circuit is in a steady state. The charge in capacitor C3 is
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit as shown, it is given that R1//R2 = 1//2 and potential ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit as shown, it is given that R1//R2 = 1//2 and potential ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit as shown, it is given that R1//R2 = 1//2 and potential ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in the figure . The value of current I1 is
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in the figure . The value of current I4 is
Text Solution
|
- An ohm meter measures the resistance placed between its leads. This re...
Text Solution
|
- An ohm meter measures the resistance placed between its leads. This re...
Text Solution
|
- An ohm meter measures the resistance placed between its leads. This re...
Text Solution
|