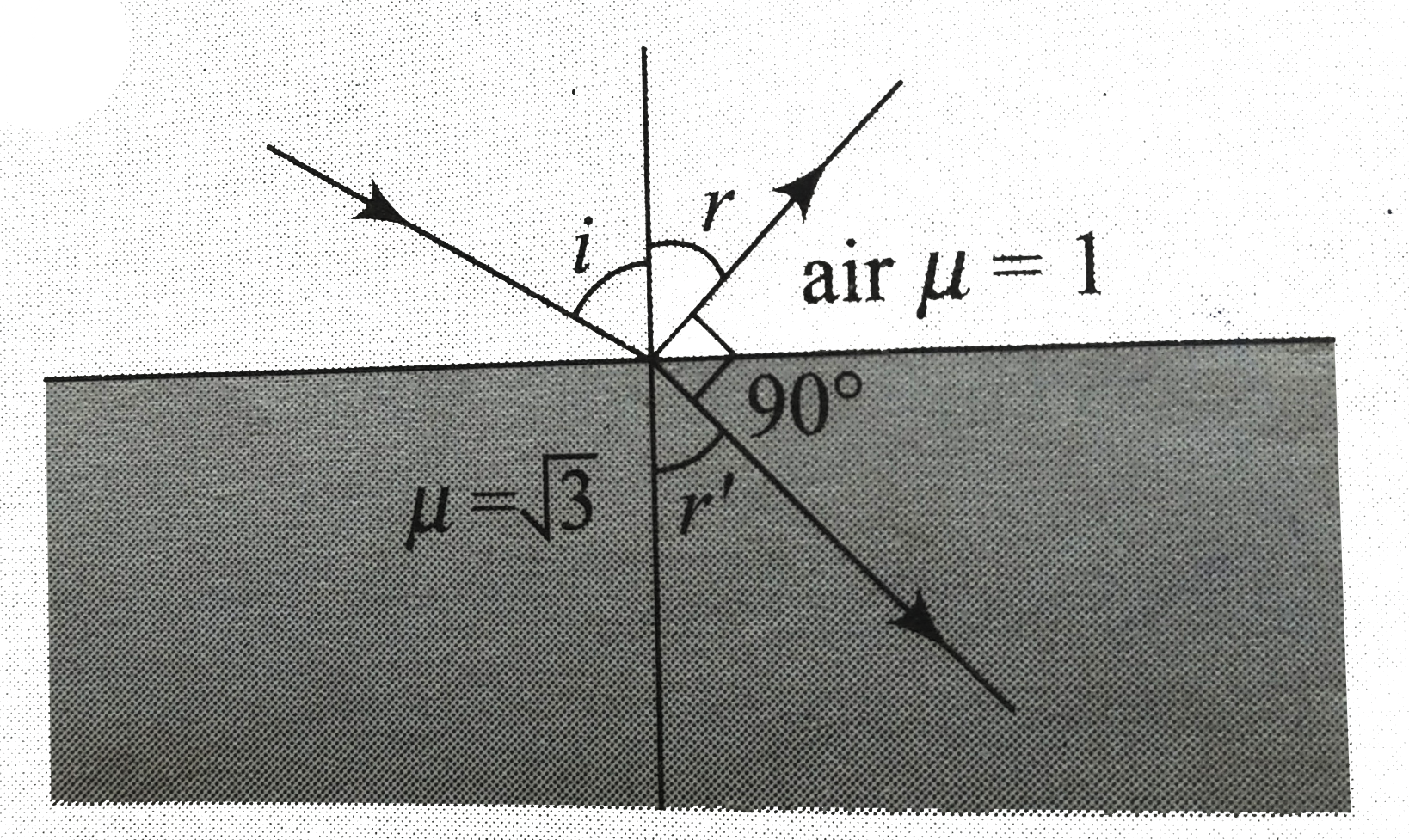Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Integer Type
- A ray of light is incident on a transparent glass slab of refractive i...
Text Solution
|
- The focal length of a thin biconvex lens is 20cm. When an object is mo...
Text Solution
|
- A large glass slabe (mu=5//3) of thickness 8cm is placed over a point ...
Text Solution
|
- Image of an object approaching a convex mirror of radius of curvature ...
Text Solution
|
- Water (with refractive index =4//3) in a tank is 18cm deep. Oil of ref...
Text Solution
|