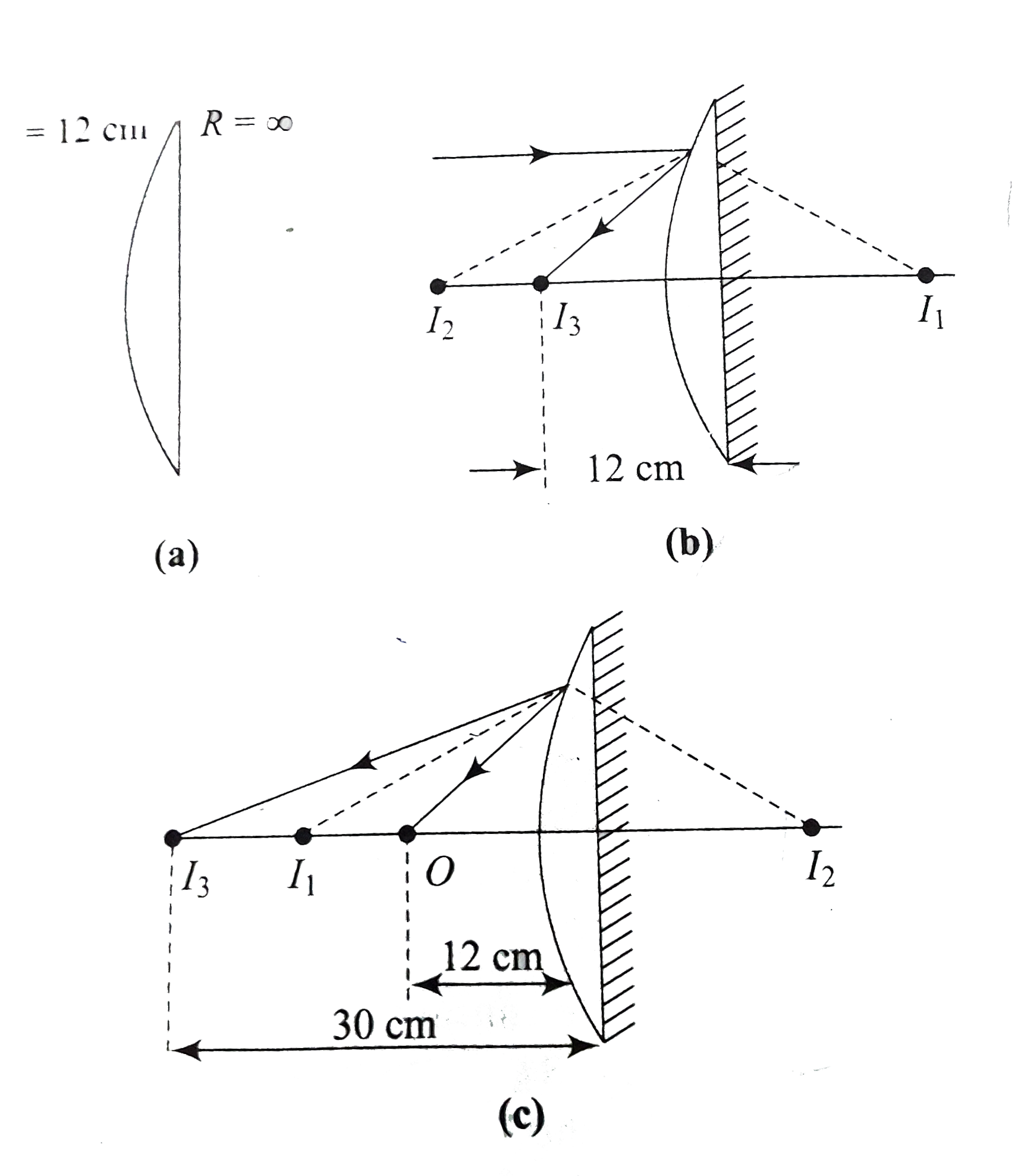
a. As far a lens, by a lensmarker's formula,
`(1)/(f)=(mu_1)[(1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(1))]`
Here `mu=(1.5-1),R_(1)=12cm, and R_(2)=oo`
So, `(1)/(f) =(1.5-1)[(1)/(12)-(1)/(-oo)]` i.e., `f=24cm`
i.e., the lens is convergent with focal length 24cm
b. As light after passing through the lens will be incident on the mirror which will reflect it back throught the lens again, so
`P=P_(L)+P_(M)+P_(L)=2P_(L)+P_(M)`
But `P_(L)=(1)/(f_(L))=(1)/(0.24) and P_(M)=-(1)/(oo)=0` `[f_(M)=(R)/(2)=oo]`
So, `P=2xx(1)/(0.24)+0=(1)/(0.12)D`
The system is equibalent to a concave mirror of focal length F.
`P=-(1)/(F)`i.e.,
`F=-(1)/(P)=-0.12m=-12cm`
i.e., the system will behave as a concave mirror of focal length 12cm . So, as for parallel incident rays `u=-oo`, from mirror formula `(1)/(v)+(1)/(u)=(1)/(f)` we have
`(1)/(v)+(1)/(-oo)=(1)/(12)rArrv=-12cm`
i.e., parallel incident rays will focus at a distance of 12cm in front of the lens as shown in Figure. When object is at 20 cm in front of the given silvered lens, which behaves as a concave mirror of focal length
12 cm, from mirror formula `(1)/(v)+(1)/(u)=(1)/(12)rArrv=-12cm`
`(1)/(v)+(1)/(-20)=(1)/(-12)rArrv=-30cm `
i.e., the silvered lens will form an image at a distance of 30cm in front of it as shown in Figure.