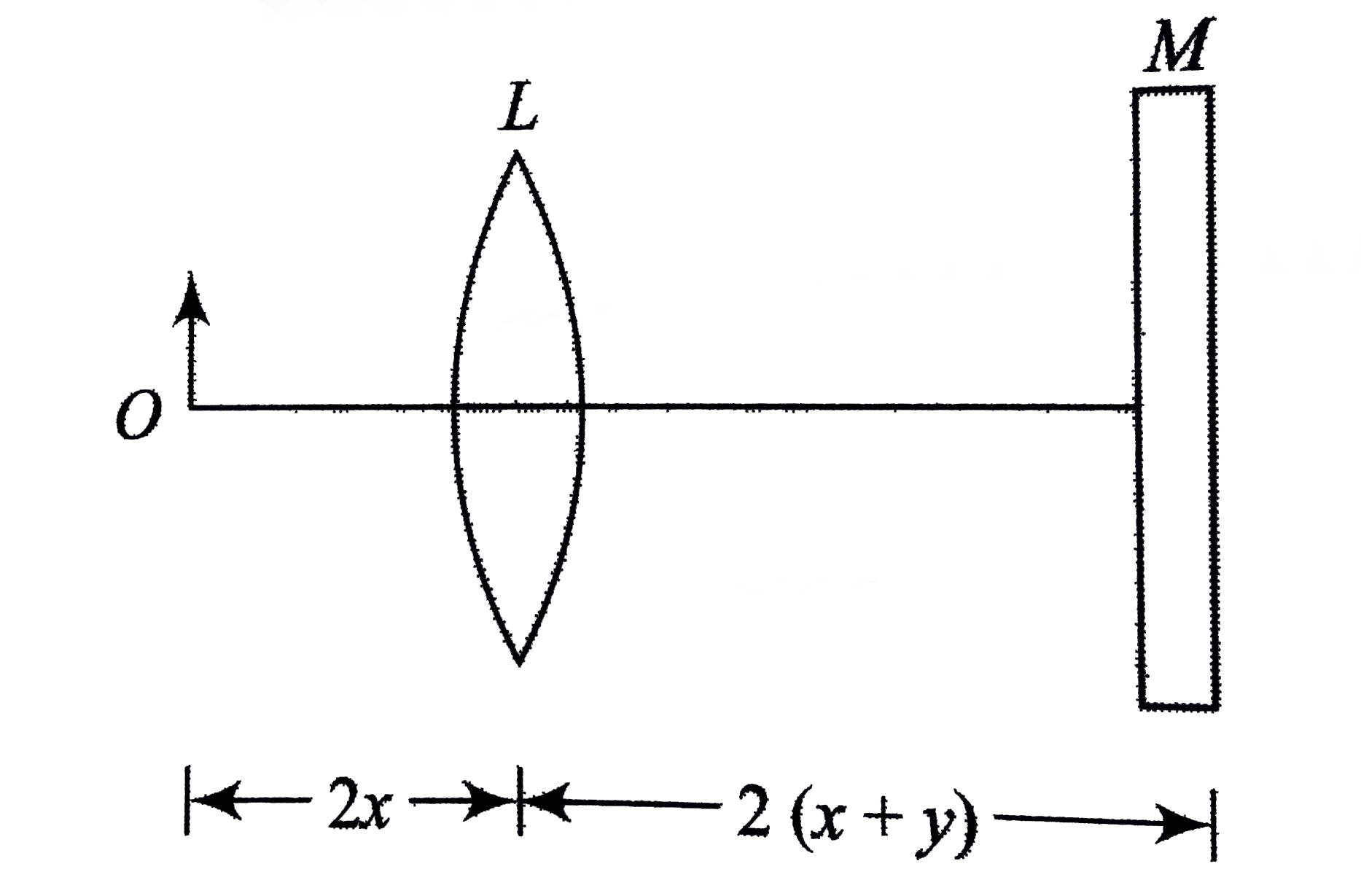It is given that a parallel beam incident on the lens, after refraction, converges to a point at a distance x from the lens. This implies that the focal length of the lens is x.
It is also given that a parallel beam incident on the mirror, after reflectino, converges to a point at a distance y from it. This implies that the mirror is a concave mirror of focal length y.
Obviously, object O is kept at 2F of lens L. Hence, its image `I_(1)` forms on the other side oat 2F , i.e., at distance 2x to the right of the lens. The image will be real, inverted, and magnification of this image `m_(1)=(v)/(u)=(2x)/(-2x)=-1` .
Image `I_(1)` of O formed by lens L acts as object for the mirror. Its distance from the pole of mirror will `2(x+y)-2x=2y` . This implies that it will be at the center of curvature of the concave mirror (y being the focal length of the mirror). Therefore, the concave mirror forms a real, inverted (relative to `I_(1)`) image `I_(2)` at the same position.
Magnification of `I_(2)` (relative to `I_(1)` ), ` m_(2)=-1` . Finally, `I_(2)` acts as object for the lens. Its distance from thelens is 2x. Hence, it is at 2F of the lens (x being the focal length of the lens). Therefore, the lens will form a real and inverted image of `I_(2)` at 2F on the other side, i.e., to its left. Obviously, `I_(3)` will be at the same position as of the object.
Magnification of `I_(3)` (relative oto `I_(2))=-1`
Total magnification `= m_(1)xxm_(2)xxm_(3)=-1xx-1xx-1=-1`
Thus, the final image is real and inverted and of the same size (2cm).
Complete reay diagram is shown in Figure.