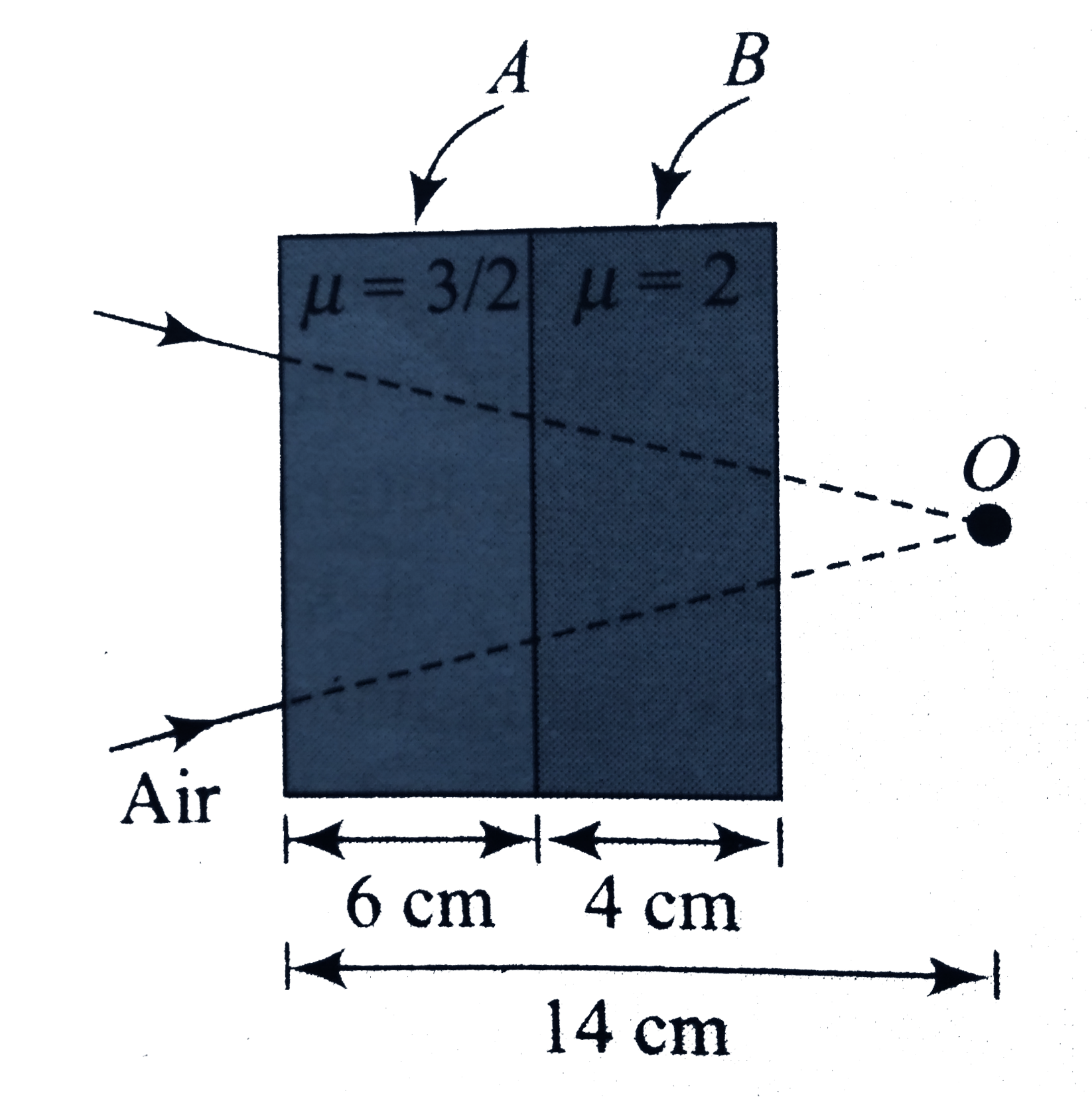
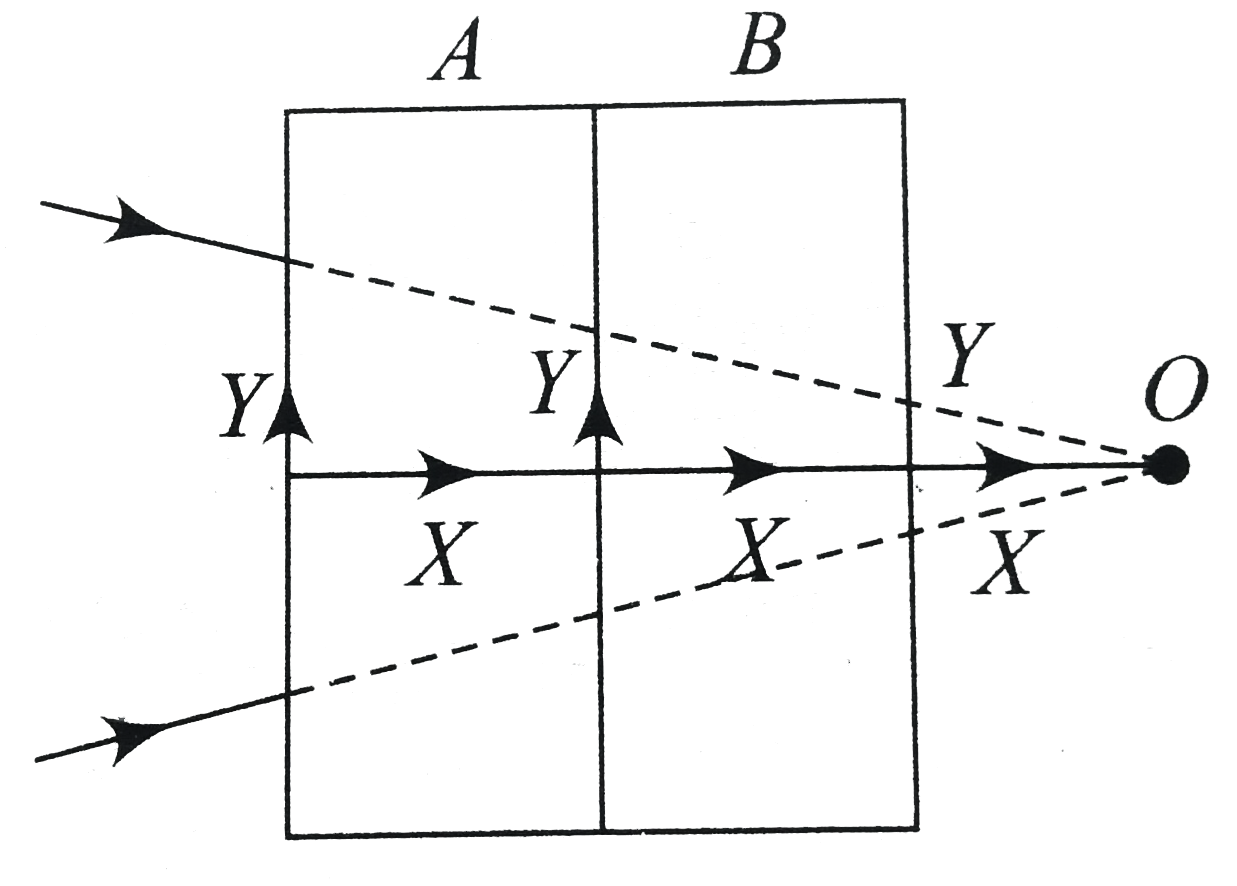
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise1.4|12 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise1.5|22 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise1.2|20 VideosFRICTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|1 VideosGRAVITATION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Question Bank|39 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Exercise1.3
- A converging set of ray, traveling from water to air, is incident on a...
Text Solution
|
- A tank contains three layers of immiscible liquids. The first layer is...
Text Solution
|
- A convergent beam is incident on two slabs placed in contact as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A slab of water is on the top of a glass slab of refractive index 2. A...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light ravels from a liquid of refractive index mu to air. If ...
Text Solution
|
- What should be the value of refractive index n of a glass rod placed ...
Text Solution
|
- An object is placed on the principle axis of a concave mirror of focal...
Text Solution
|
- The image of an object kept at a distance of 30 cm in front of a conca...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, a fish watcher watches a fish through a 3.0 cm thick glass ...
Text Solution
|
- An observer can see through a pin-hole the top end of a thin rod of he...
Text Solution
|
- A vesserl contains a slab of glass 8cm thick and of refractive index 1...
Text Solution
|
- An object O is placed at 8cm in front of a glass slab, whose one face ...
Text Solution
|
- x-y plane separates two media, zge0 contains a medium of refractive i...
Text Solution
|
- The n transparent slabs of refractive index1.5 each having thickness 1...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror with its optic axis vertical and mirror facinig upwar...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in Figure. A plane mirror is fixed at a h...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror of radius 40 cm lies on a horizontla tale and wateis ...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror of radius R is kept on a horizontal table. Water (ref...
Text Solution
|
- The refractive index of an anisotropic medium varies as mu=mu(0)sqrt((...
Text Solution
|
- A light beam of diameter sqrt(3R) is incident symmetrically on a glass...
Text Solution
|