Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|221 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion-Reasoninig|2 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise1.7|21 VideosFRICTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|1 VideosGRAVITATION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Question Bank|39 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Subjective
- A direct-vision prism is made out of three prisms, each with a refract...
Text Solution
|
- A person wants to see AB part of his image. His eye level is at 1.8m a...
Text Solution
|
- The internal surface of the walls of a sphere is specular. The radius...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in Figure,. And object O is at the position (-10,2) with resp...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, AB is the principal axis of the concave mirror. A point ob...
Text Solution
|
- If an observer sees the bottom of the vessel shown in Figure., at 8cm,...
Text Solution
|
- O is a point object kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror M o...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure ., L is a converging lens of focal length 10cm and M Iis a c...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary observer O looking at a fish F in water (mu(w)=4//3) thro...
Text Solution
|
- The back wall of an aqaurium is a mirror that is 30 cm away from the f...
Text Solution
|
- An object is placed 20cm to the left of a converging lens having focal...
Text Solution
|
- A composite slab consisting of different media is placed in front of a...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls on the surface of a convex lens whose r...
Text Solution
|
- A thin biconvex lens of refractive index 3//2 and radius of curvature...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length f(1) is placed in front of a luminous po...
Text Solution
|
- A lens is made of three thin different mediums. Radius of curvature an...
Text Solution
|
- An equiconvex lens, f(1)=10cm, is placed 40 cm in front of a concave ...
Text Solution
|
- A biconvex lens, f(1)=20cm , is placed 5cm in front of a convex mirror...
Text Solution
|
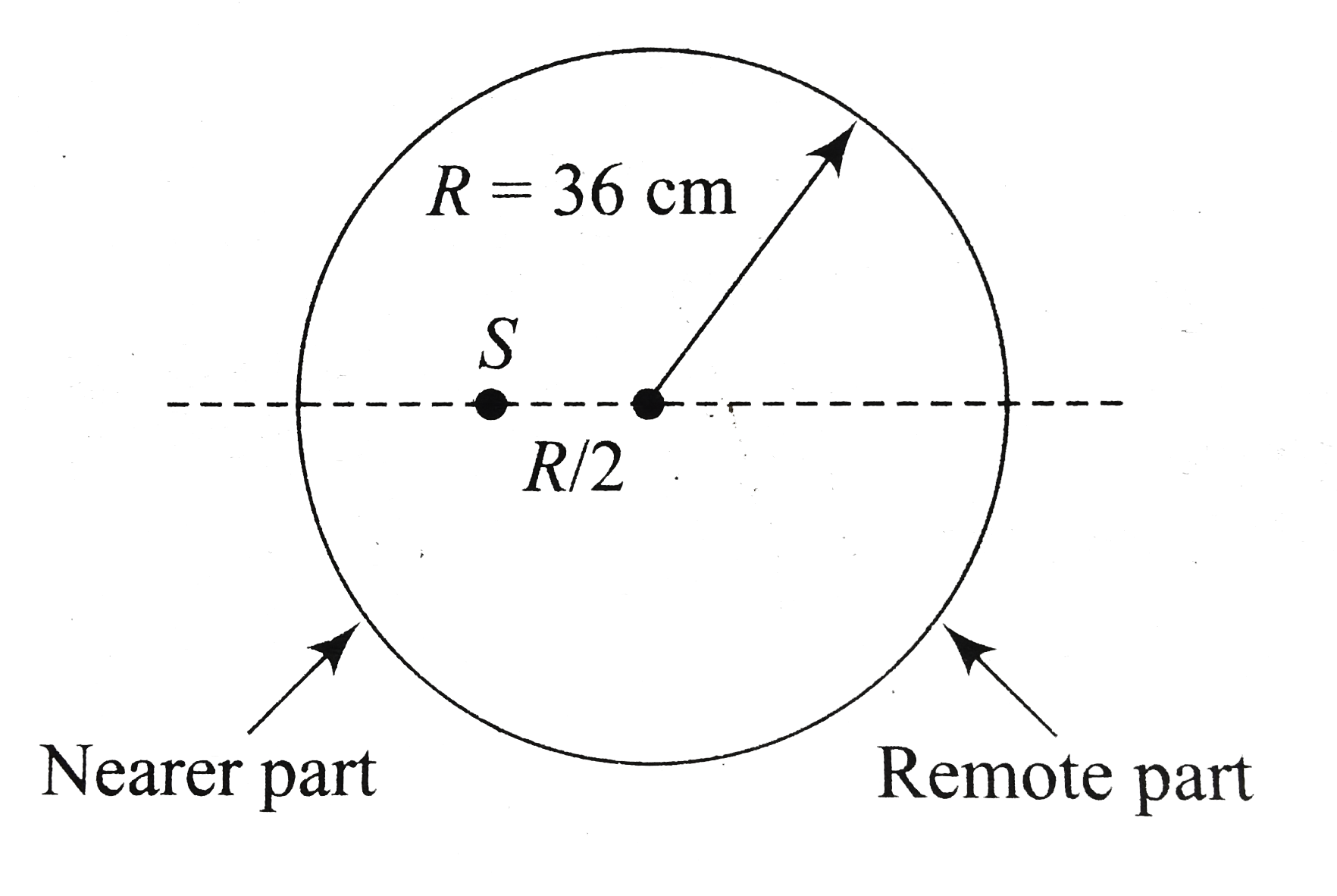
- A transparent sphere of radius R ahs a cavity of radius R//2 as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary observer O looking at a fish F in water (mu(w)=4//3) thro...
Text Solution
|