A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct Answers Type|8 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion-Reasoninig Type|2 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise True/False|5 VideosFRICTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|1 VideosGRAVITATION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Question Bank|39 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Single Correct Answer Type
- A point source of light B is placed at a distance L in front of the ce...
Text Solution
|
- A diverging beam of light from a point source S having divergence ang...
Text Solution
|
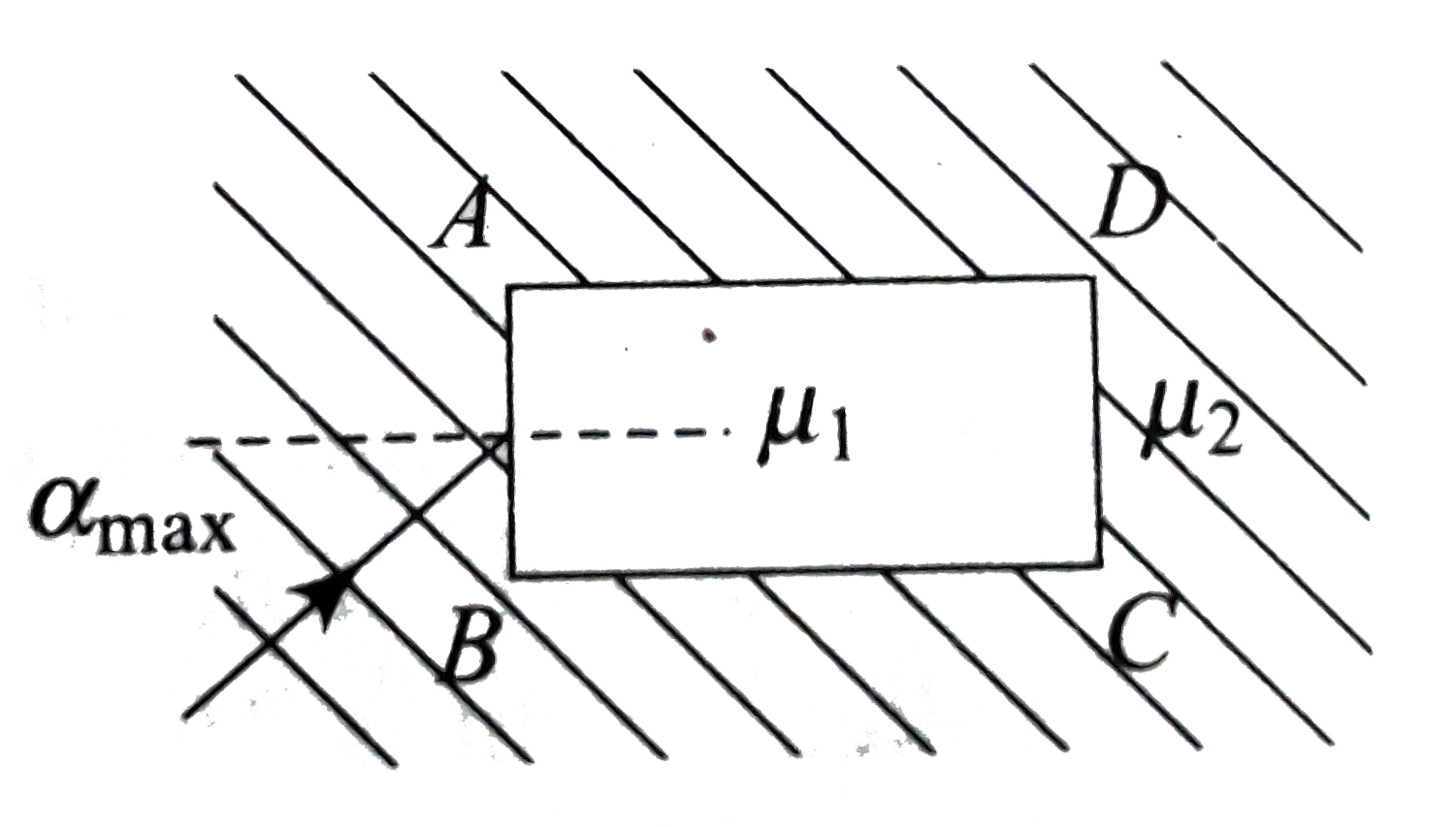
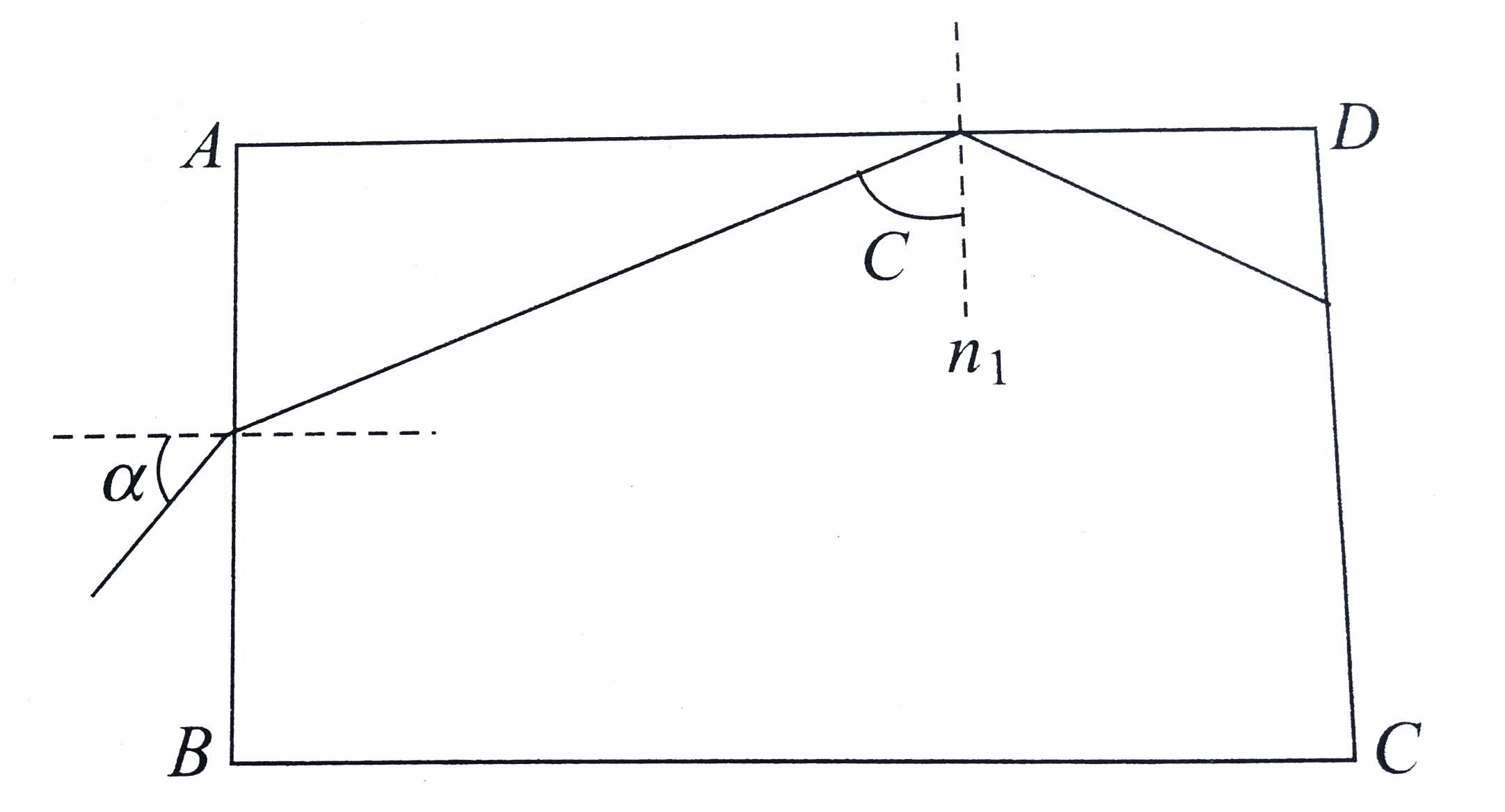
- A rectangular glass slab ABCD of refractive index n(1) is immersed in ...
Text Solution
|
- In a compound microscope, the intermediate image is
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light passes through four transparent media with refractive i...
Text Solution
|
- A given ray of light suffers minimum deviation in an equilateral prism...
Text Solution
|
- An observer can see through a pin-hole the top end of a thin of height...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following sperical lenses does not exhibit dispersion...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane mirros A and B are aligned parallel to each other, as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- The size of the image of an object, which is at infinity, as formed by...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident at the glass-water interface at an angle i....
Text Solution
|
- A beam of white light is incident on the glass-air interface from glas...
Text Solution
|
- An equilateral prism is placed on a horizontal surface. A ray PQ is in...
Text Solution
|
- A point object is placed at the center of a glass sphere of radius 6cm...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens is in contact with a concave lens. The magnitude of the...
Text Solution
|
- A container is filled with water (mu=1.33) upto a height of 33.25cm. A...
Text Solution
|
- Focal length of the plano-convex lens is 15cm. A small object is place...
Text Solution
|
- The graph shown relationship between object distance and image distanc...
Text Solution
|
- A biconvex lens of focal length f forms a circular image of radius r o...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in water is incident on its surface open to ...
Text Solution
|