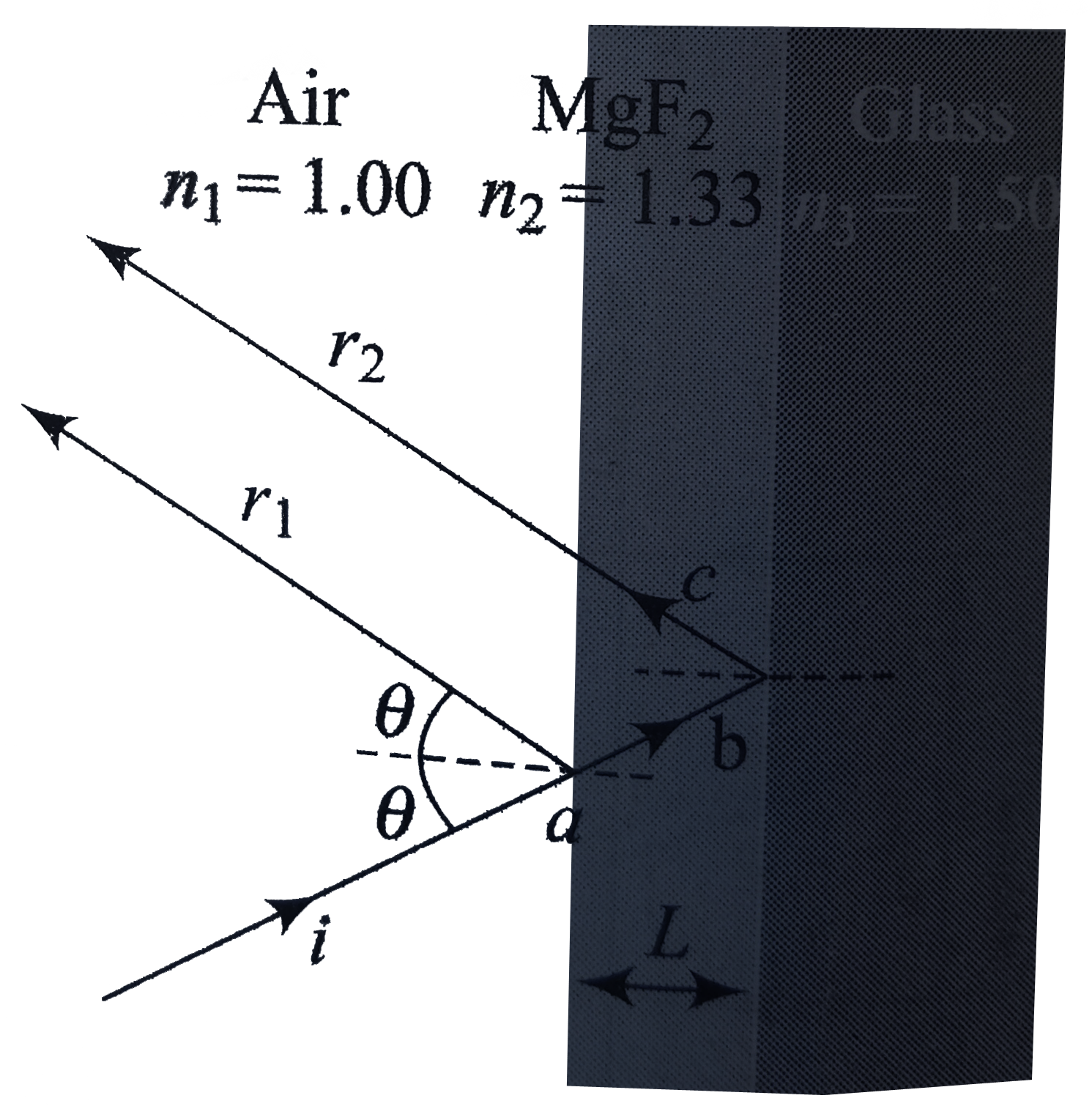Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-WAVE OPTICS-QUESTION BANK
- A glass lens is coated on one side with a thin film of magnesium fluor...
Text Solution
|
- In a single slit diftion, slit width is 0.6mm and distance of first mi...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of resolving powers of an optical microscope for two wavelen...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light of lambda=600 nm from a.distant sourcé falls on a sing...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment, the slits are 2 mm apart and are il...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment the spacing between the slits is 0...
Text Solution
|
- A slit of size 0.15m is placed at 2.1m from a screen. On illuminated i...
Text Solution
|
- In the Young's double-slit experiment, the intensity of light at a poi...
Text Solution
|
- In YDSE distance between slits and screen is 1.5 m. When light of wave...
Text Solution
|
- Two Polaroids P(1) and P(2) are placed with their axis perpendicular t...
Text Solution
|
- In an YDSE, the fringes are formed at a distance of 1 m from double sl...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment the separation d between the slits i...
Text Solution
|
- A single slit is of width 0.5mm. Distance of screen from slit is 1 m. ...
Text Solution
|
- In YDSE distance between slits is 0.2 mm, distance between slit & scre...
Text Solution
|
- In an interference pattern the (n+4)^(th) blue bright fringe and n^(th...
Text Solution
|
- In double slit experiment, the angular width of the fringes is 0.20^(c...
Text Solution
|
- A light has amplitude A and angle between analyser and polariser is 60...
Text Solution
|
- A unpolarised light is passing through three polaroids as shown. If fi...
Text Solution
|
- In YDSE, if sources are incoherent, the intensity on screen is 13 I(0^...
Text Solution
|
- An unpolarized light passes through three polarizing sheets whose pola...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment, 60 fringes were seen in the field...
Text Solution
|