A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-WAVE OPTICS-Linked Comprehension
- In the arrangement shown in figure, light of wavelength 6000 Å is inci...
Text Solution
|
- A lens of focal length f is cut along the diameter into two identical ...
Text Solution
|
- A lens of focal length f is cut along the diameter into two identical ...
Text Solution
|
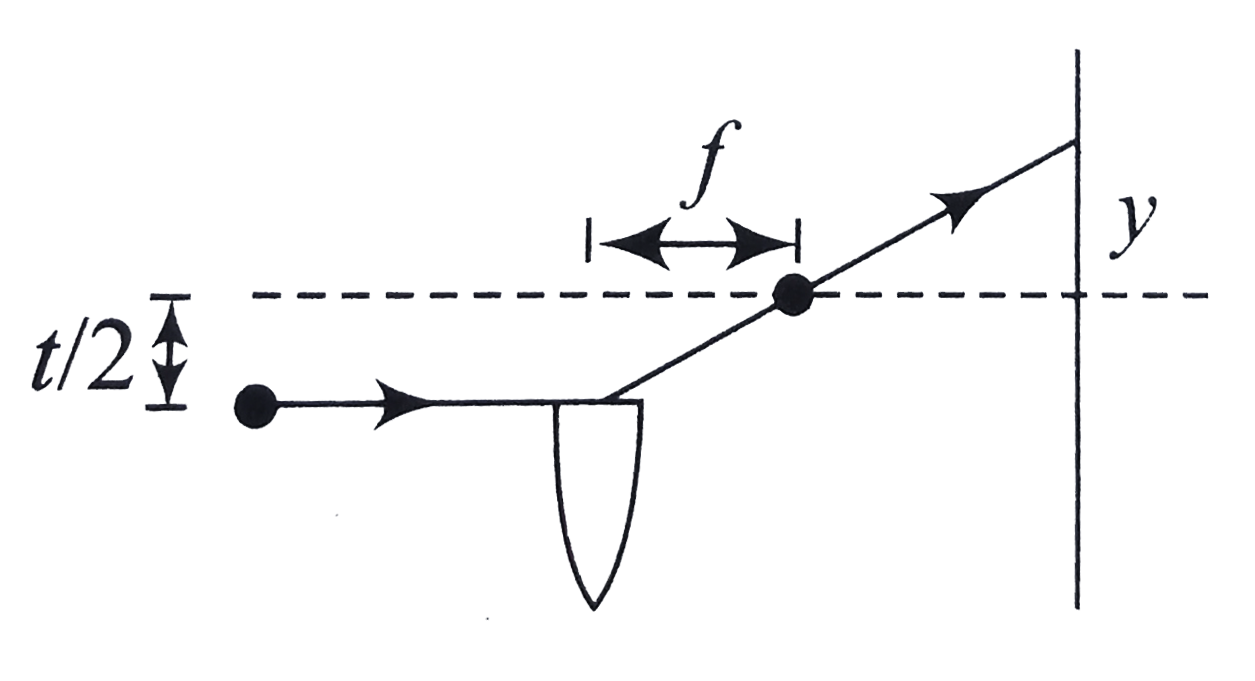
- In the arrangment shown in fin. For what minimum value of d is th...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangment shown in fin. Find the distance x at which the n...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangment shown in fin. Find the fringe width.
Text Solution
|
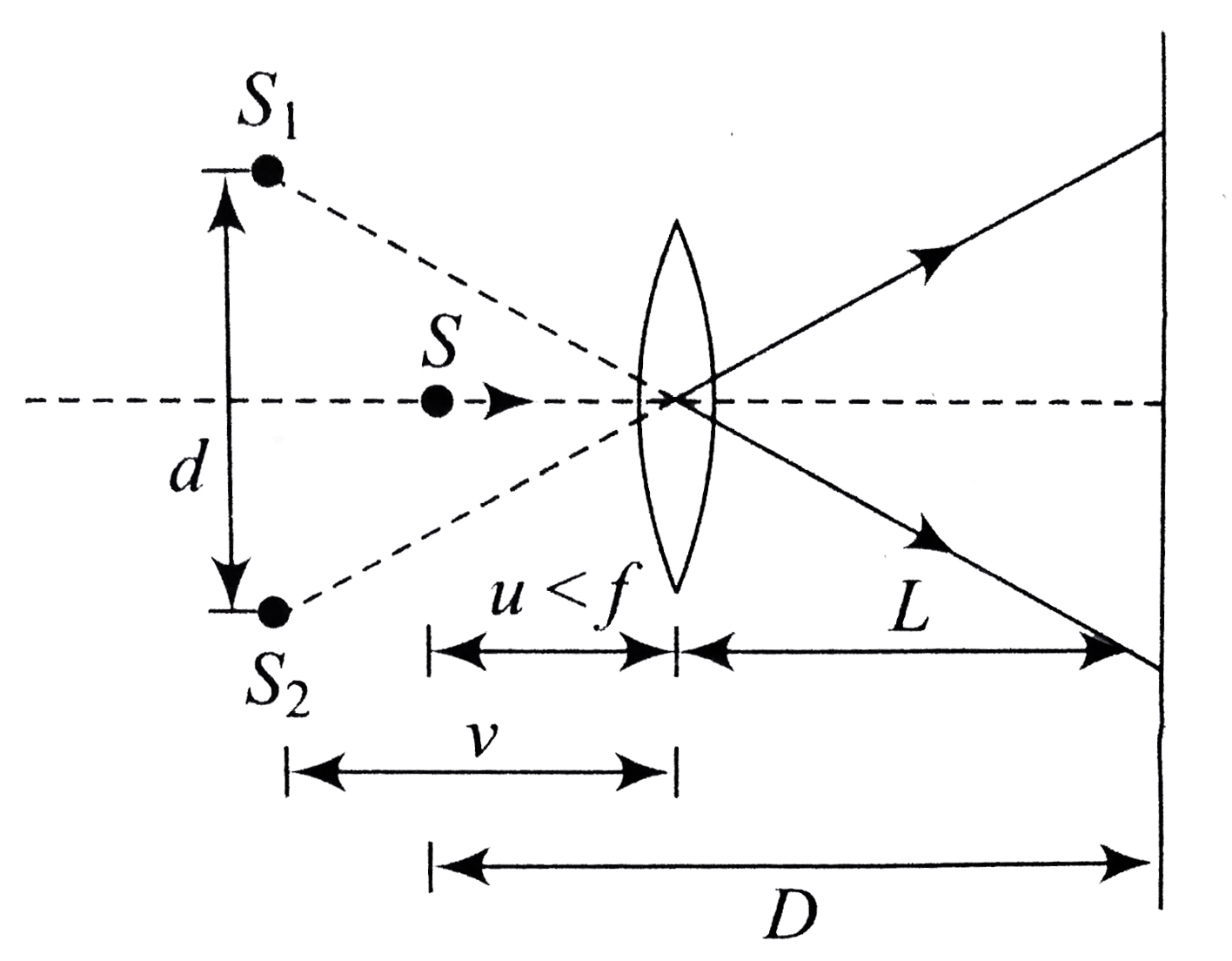
- Consider the situation shown in fig. The two slits S(1) and S(2) place...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in fig. The two slits S(1) and S(2) place...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in fig. The two slits S(1) and S(2) place...
Text Solution
|
- The arrangement for a mirror experiment is shown in figure. S is a poi...
Text Solution
|
- The arrangement for a mirror experiment is shown in figure. S is a poi...
Text Solution
|
- The arrangement for a mirror experiment is shown in figure. S is a poi...
Text Solution
|
- Young's double-slit experiment setup with ligth of wavelength lambda =...
Text Solution
|
- Young's double-slit experiment setup with ligth of wavelength lambda =...
Text Solution
|
- Young's double-slit experiment setup with ligth of wavelength lambda =...
Text Solution
|
- An interference is observed due to two coherent sources S(1) placed at...
Text Solution
|
- An interference is observed due to two coherent sources S(1) placed at...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows the interfernece pattern obtained in double slit expe...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows the interfernece pattern obtained in double slit expe...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows the interfernece pattern obtained in double slit expe...
Text Solution
|
 .
.