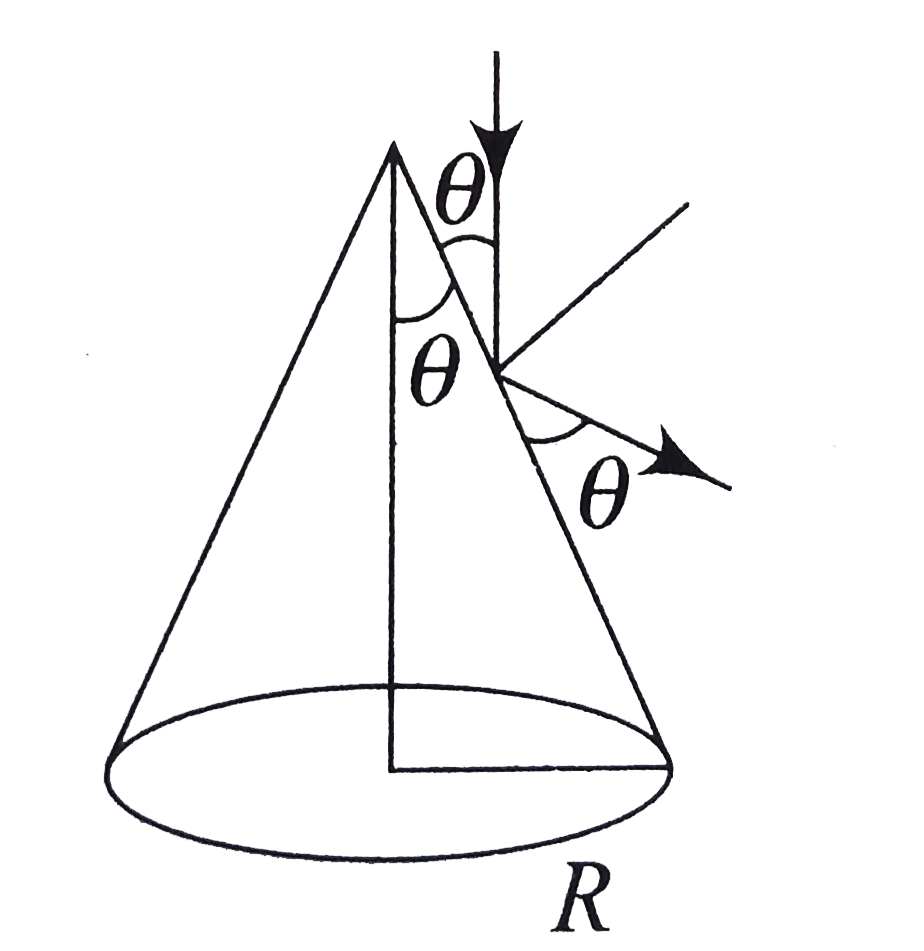
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|9 VideosPHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct Answer Type|7 VideosPHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|10 VideosNUCLEI
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|59 VideosRAY OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise DPP 1.6|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT-Linked Comprehension
- The incident intensity on a horizontal surface at sea level from the s...
Text Solution
|
- The incident intensity on a horizontal surface at sea level from the s...
Text Solution
|
- Light of intensity I falls along the axis on a perfectly refleccting r...
Text Solution
|
- Light of intensity I falls along the axis on a perfectly refleccting r...
Text Solution
|
- An experimental setup of verification of photoelectric effect is shown...
Text Solution
|
- An experimental setup of verification of photoelectric effect is shown...
Text Solution
|
- An experimental setup of verification of photoelectric effect is shown...
Text Solution
|
- An experimental setup of verification of photoelectric effect is shown...
Text Solution
|
- An experimental setup of verification of photoelectric effect is shown...
Text Solution
|
- Light having photon energy hupsilon is incident on a metallic plate ha...
Text Solution
|
- Light having photon energy hupsilon is incident on a metallic plate ha...
Text Solution
|
- Light having photon energy hupsilon is incident on a metallic plate ha...
Text Solution
|
- When light of sufficiently high frequency is incident on a metallic su...
Text Solution
|
- When light of sufficiently high frequency is incident on a metallic su...
Text Solution
|
- When light of sufficiently high frequency is incident on a metallic su...
Text Solution
|
- The energy reveived from the sun by the earth and surrounding atmosphe...
Text Solution
|
- The energy reveived from the sun by the earth and surrounding atmosphe...
Text Solution
|
- The energy reveived from the sun by the earth and surrounding atmosphe...
Text Solution
|
- When a high frequency electromagnetic radiation is incident on a metal...
Text Solution
|
- When a high frequency electromagnetic radiation is incident on a metal...
Text Solution
|