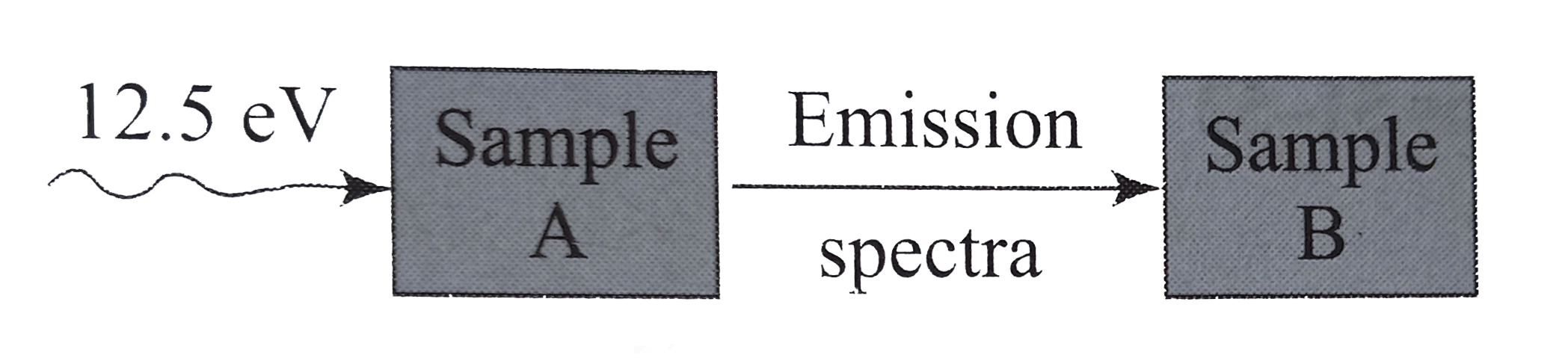A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ATOMIC PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|4 VideosATOMIC PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Fill In The Blanks|8 VideosATOMIC PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|13 VideosALTERNATING CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|65 VideosATOMS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ATOMIC PHYSICS-Linked Comprehension
- Simplified model of electron energy levels for a cartain atom is shown...
Text Solution
|
- Simplified model of electron energy levels for a cartain atom is shown...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic beam of light having photon energy 12.5 eV is incident...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic beam of light having photon energy 12.5 eV is incident...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic beam of light having photon energy 12.5 eV is incident...
Text Solution
|
- A single electron orbits a stationary nucleus of charge + Ze, where Z ...
Text Solution
|
- A single electron orbits a stationary nucleus of charge + Ze, where Z ...
Text Solution
|
- A single electron orbits a stationary nucleus of charge + Ze, where Z ...
Text Solution
|
- When high energetic electron beam , (i.e., cathode rays) strike the he...
Text Solution
|
- When high energetic electron beam , (i.e., cathode rays) strike the he...
Text Solution
|
- Light from a discharge tube containing hydrogen atoms falls on the sur...
Text Solution
|
- Light form a dicharge tube containing hydrogen atoms falls on the surf...
Text Solution
|
- Light from a discharge tube containing hydrogen atoms falls on the sur...
Text Solution
|
- The electron in a Li^(+ +) ion is the nth shell , n being very large. ...
Text Solution
|
- The electron in a Li^(+ +) ion is the nth shell , n being very large. ...
Text Solution
|
- The electron in a Li^(+ +) ion is the nth shell , n being very large. ...
Text Solution
|
- Two hydrogen-like atoms A and B are of different masses and each atom ...
Text Solution
|
- Two hydrogen-like atoms A and B are of different masses and each atom ...
Text Solution
|
- 1.8 g of hydrogen is excite by irradiation. The study of spectra indic...
Text Solution
|
- 1.8 g of hydrogen is excite by irradiation. The study of spectra indic...
Text Solution
|