Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Solved Example|5 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 3.1|15 VideosELECTROMAGENTIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|40 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 Videos
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-compression type
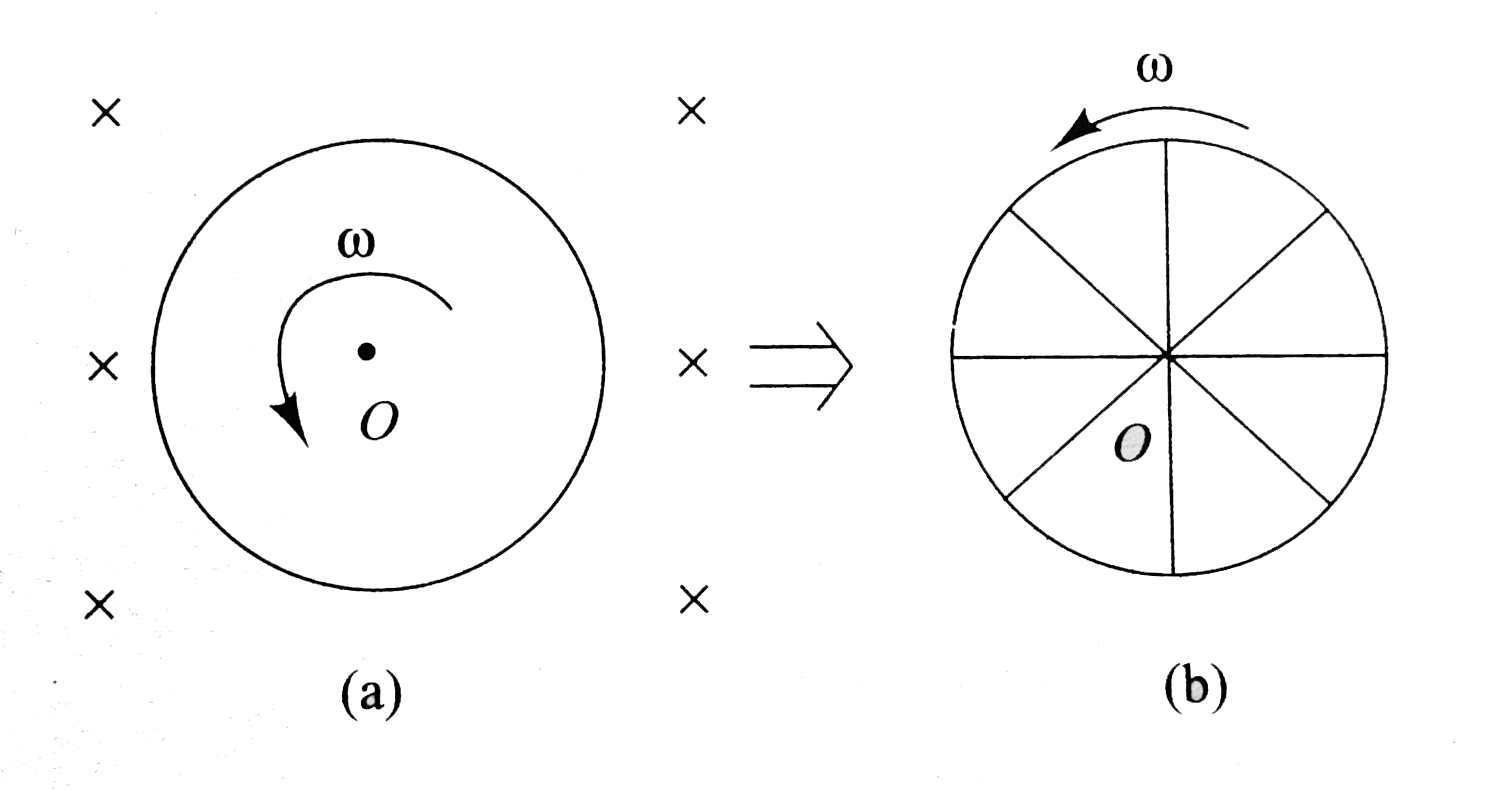
- A metal disc of radius R = 25 cm rotates with a constant angular veloc...
Text Solution
|
- A thin non conducting ring of mass m, radius a carrying a charge q can...
Text Solution
|
- A thin non conducting ring of mass m, radius a carrying a charge q can...
Text Solution
|
- A thin non conducting ring of mass m, radius a carrying a charge q can...
Text Solution
|
- A thin non conducting ring of mass m, radius a carrying a charge q can...
Text Solution
|
- It is known to you that ''whenever the flux of a magnetic field throug...
Text Solution
|
- It is known to you that ''whenever the flux of a magnetic field throug...
Text Solution
|
- It is known to you that ''whenever the flux of a magnetic field throug...
Text Solution
|