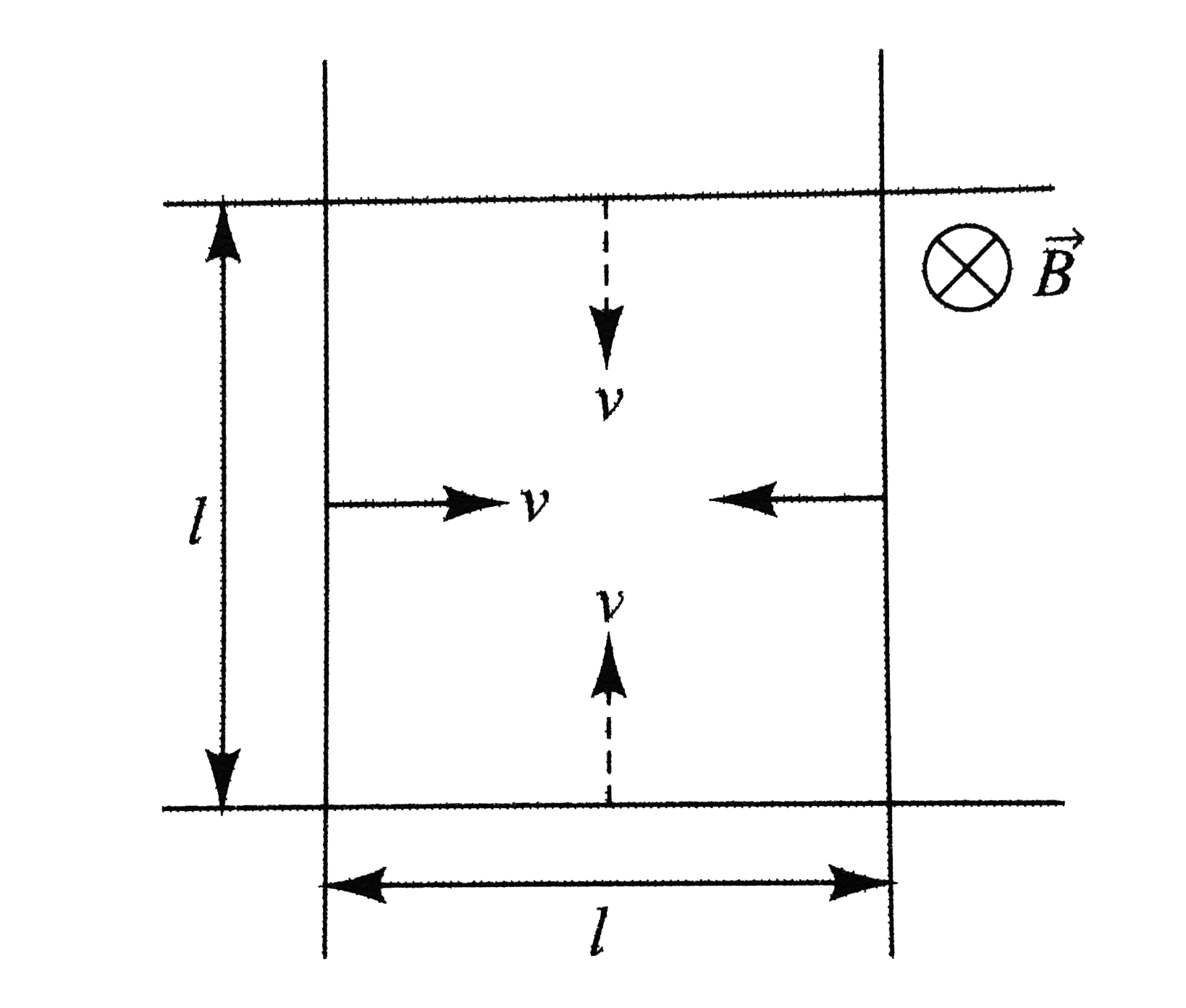
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 3.1|15 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 3.2|27 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise compression type|7 VideosELECTROMAGENTIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|40 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Solved Example
- A square loop of side 'a' with a capacitor of capacitance C is located...
Text Solution
|
- A thermocol vessel contains 0.5kg of distilled water at 30^(@)C. A me...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel vertical metellic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A pair of parallel horizontal conducting rails of negligible resistanc...
Text Solution
|
- in fig. The four rods have lambda resistance per unit length. The arre...
Text Solution
|