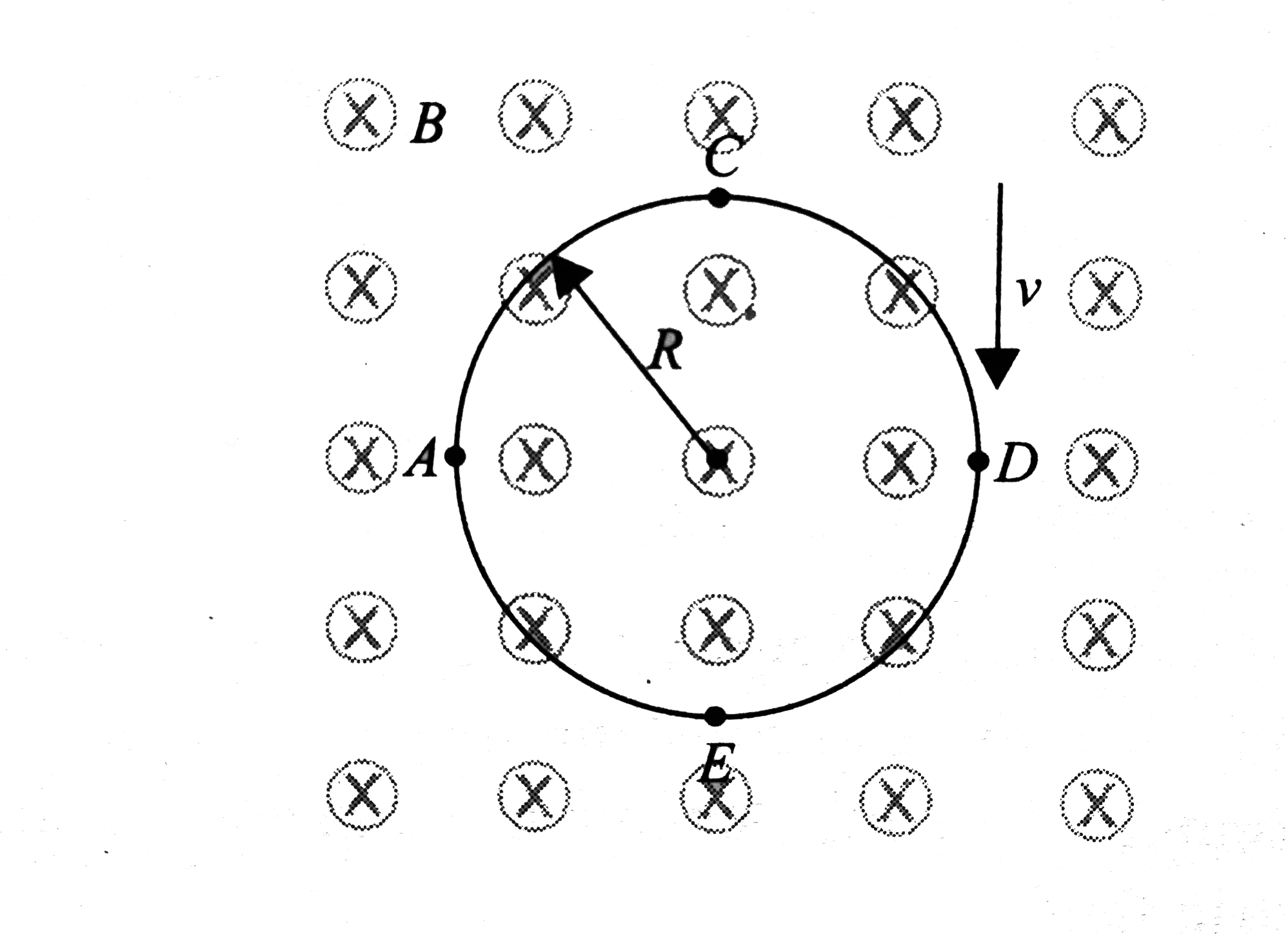
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercises Asserton - Reasoning|8 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercises Linked Comprehension|36 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercises Single Correct|79 VideosELECTROMAGENTIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|40 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Exercises Multiple Correct
- A uniform circular loop of radius a and resistance R palced perpendicu...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire of length l and mass m can slide without friction on...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length l is hinged at point O. It is free to rotat...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length is moved at constant velocity v(0) on two p...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown 'R' is a fixed conducting fixed ring of negligible...
Text Solution
|
- An infinite current-carrying conductor is placed along the z-axis and ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R is rolling without sliding on a horizontal surface ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting loop rotates with constant angular velocity about its fix...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet is moved between two parallel circular loops A and B with...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet moves toward two idential parallel circular loops with a...
Text Solution
|
- A highly conducting ring of radius R is perpendicular to and concentri...
Text Solution
|
- The acceleration of the charge on the gap faces will cease when the to...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown , the wires P(1)Q(1) and P(2)Q(2) are made to slid...
Text Solution
|
- A small magnet M is allowed to fall through a fixed horizontal conduct...
Text Solution
|
- The counductor AD moves to the right in a uniform magnetic field direc...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitude of the earth's magnetic field at the north pole is B(0) ...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical conducting ring ogradius R falls vertically in a horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- A flat coil, C, of n turns, area A and resistance R, is placed in a un...
Text Solution
|
- In the above problem. The plane of the coil is initially kept parallel...
Text Solution
|
- In the above problem, if the coil rotates with a constant angular velo...
Text Solution
|