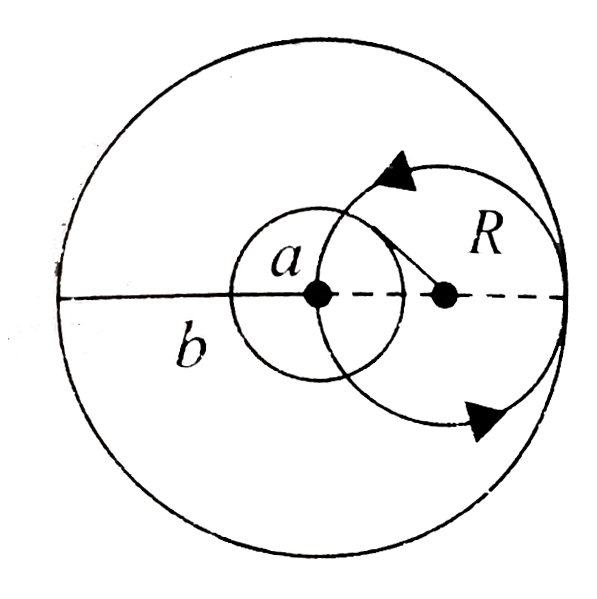
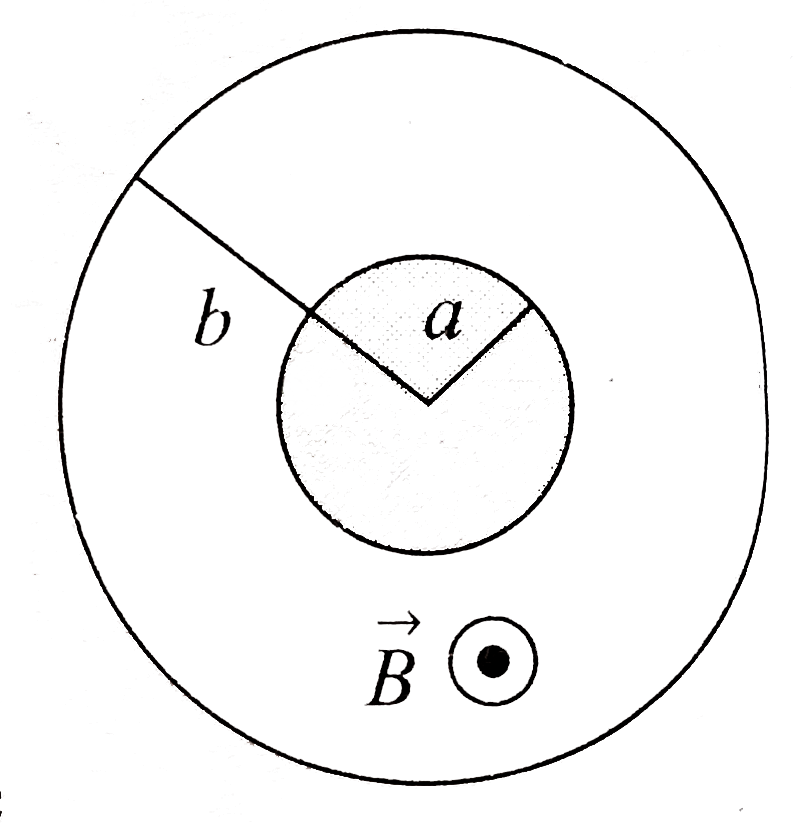A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5-Linked Comprehension
- In the given arrangement, the space between a pair of co-axial cylindr...
Text Solution
|
- In the given arrangement, the space between a pair of co-axial cylindr...
Text Solution
|
- In the given arrangement, the space between a pair of co-axial cylindr...
Text Solution
|
- The path of a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field depends on ...
Text Solution
|
- The path of a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field depends on ...
Text Solution
|
- The path of a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field depends on ...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic force on a charged particle is given by vec F(m) = q(vec(v) x...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic force on a charged particle is given by vec F(m) = q(vec(v) x...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic force on a charged particle is given by vec F(m) = q(vec(v) x...
Text Solution
|
- Following experiment was performed by J.J. Thomson in order to measure...
Text Solution
|
- Following experiment was performed by J.J. Thomson in order to measure...
Text Solution
|
- Following experiment was performed by J.J. Thomson in order to measure...
Text Solution
|
- In uniform magnetic field, if angle between vec(v) and vec(B) is 0^(@)...
Text Solution
|
- In uniform magnetic field, if angle between vec(v) and vec(B) is 0^(@)...
Text Solution
|
- In uniform magnetic field, if angle between vec(v) and vec(B) is 0^(@)...
Text Solution
|
- A straight segment OC(of length L meter) of a circuit carrying a curre...
Text Solution
|
- A straight segment OC(of length L meter) of a circuit carrying a curre...
Text Solution
|
- Four long wires each carrying current I as shown in Fig. are placed a...
Text Solution
|
- Four long wires each carrying current I as shown in Fig. are placed a...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown Fig. There present a magnetic field B = 1...
Text Solution
|