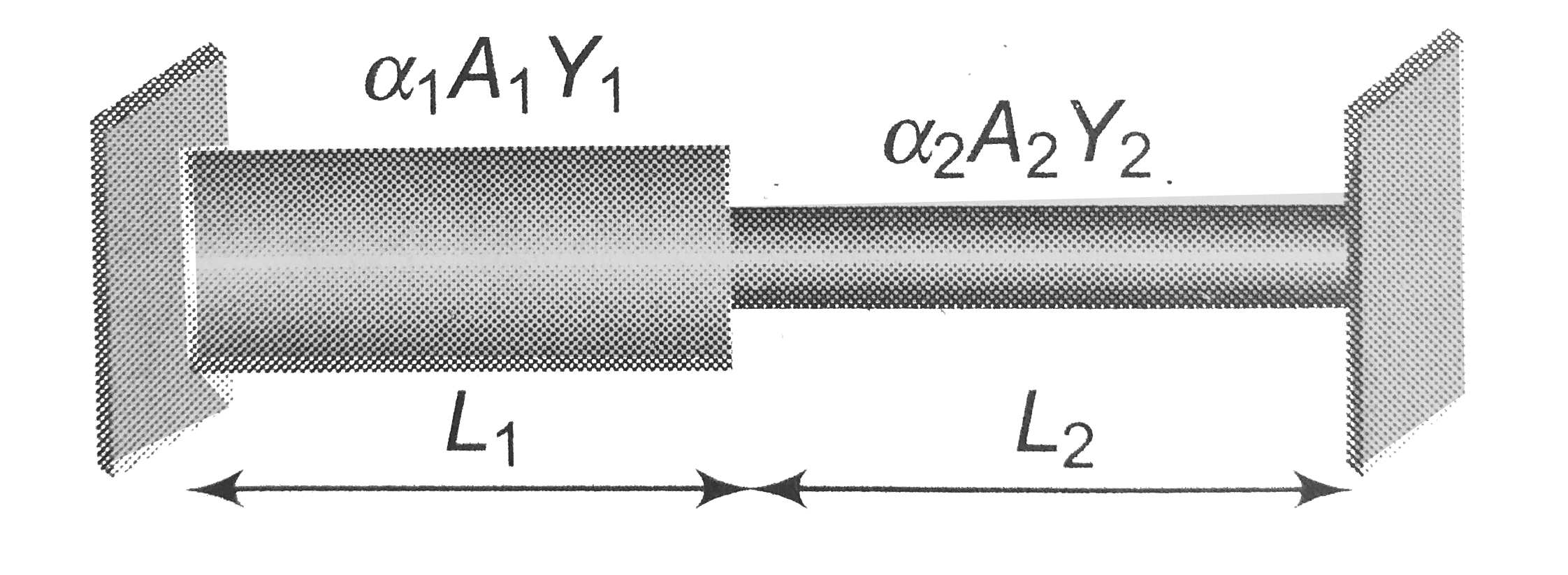
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|25 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Comprehension|30 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|25 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.6|20 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-CALORIMETRY-Single Correct
- There are two thin spheres A and B of the same material and same thick...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in Fig. AB is rod of length 30 cm and area of cross section 1...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods are joined between fixed supports as shown in the figure. Con...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l and cross sectional area A has a variable conductivi...
Text Solution
|
- A black body emits radiation at the rate P when its temperature is T. ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid metallic sphere of diameter 20 cm and mass 10 kg is heated to ...
Text Solution
|
- The coefficient of linear expansion of an in homogeneous rod change li...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is made by attaching two segments together end to end. One segm...
Text Solution
|
- Heat is required to change 1 kg of ice at -20^@C into steam. Q1 is the...
Text Solution
|
- A block of wood is floating in water at 0^@ C. The temperature of wate...
Text Solution
|
- An incandescent lamp consumint P=54W is immersed into a transparent ca...
Text Solution
|
- A thread of liquid is in a uniform capillary tube of length L. As meas...
Text Solution
|
- A brass wire 2 m long at 27^@C is held taut with negligible tension be...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m of lead shot is placed at the bottom of a vertical cardboard ...
Text Solution
|
- An iron rocket fragment initially at -100^@C enters the earth's atmosp...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid of density 0.85 g//cm^(3) flows through a calorimeter at the ...
Text Solution
|
- An iron ball (coefficient of linear expansion=1.2xx(10^(-5)//^(@)C) ha...
Text Solution
|
- A flask of mercury is sealed off at 20^@C and is completely filled wit...
Text Solution
|
- The densities of wood and benzene at 0^(@)C are 880 kg//m^(3) and 900 ...
Text Solution
|
- An iron rod and another of brass, both at 27^@C differ in length by 10...
Text Solution
|