Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-CALORIMETRY-Solved Example
- A colorimeter contains 400 g of water at a temperature of 5^(@)C. Then...
Text Solution
|
- In an insulated vessel, 25g of ice at 0^(@)C is added to 600g of water...
Text Solution
|
- A solar cooker consists of a curved reflecting surface that concentrat...
Text Solution
|
- An iron wire AB of length 3 m at 0^(@)C is stretched between the oppso...
Text Solution
|
- A composite rod is made by joining a copper rod, end to end, with a se...
Text Solution
|
- How should 1 kg of water at 50^(@)C be divided in two parts such that ...
Text Solution
|
- A layer of ice of 0^(@)C of thickness x(1) is floating on a pond. If t...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical rod of heat capacity 120 J//K in a room temperature 27^(...
Text Solution
|
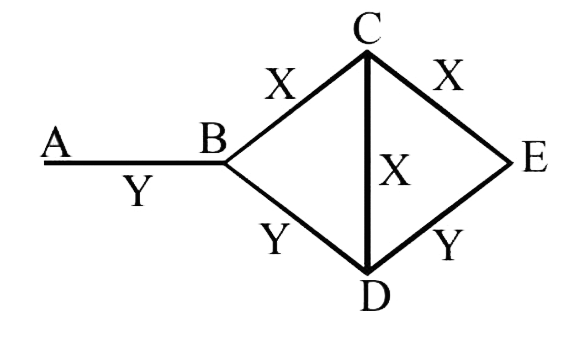
- Three rods of material X and three rods of material Y are connected as...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical block of co-efficient of linear expansion alphas is submerge...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a rod of length L and crosssectional area A is kept in a fu...
Text Solution
|
- A metal of mass 1 kg at constant atmospheric pressure and at initial t...
Text Solution
|
- In a insulated vessel, 0.05 kg steam at 373 K and 0.45 kg of ice at 25...
Text Solution
|