Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.1|20 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.2|28 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger|11 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Compression|2 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct Answer Type|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS-Solved Examples
- A vessel containing 1 g of oxygen at a pressure of 10 atm a temperatur...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas (2.0 moles) is carried round a cycle as shown. If the pro...
Text Solution
|
- Figure. Shows three processes for an ideal gas. The temperature at 'a'...
Text Solution
|
- N molecules each of mass m of gas A and 2 N molecules each of mass 2m ...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas is taken through a cycle ABCA as ...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth vertical tube having two different cross sections is open fro...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of helium gas(lambda=5//3) are initially at temperature 27^@...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a cylinder by a spring-loaded p...
Text Solution
|
- Three moles of an ideal gas (Cp=7/2R) at pressure, PA and temperature ...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of helium gas undergo a cyclic process as shown in Fig. Assu...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through the cycle shown in...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of 2 kg of monatomic helium (assumed ideal) is taken through ...
Text Solution
|
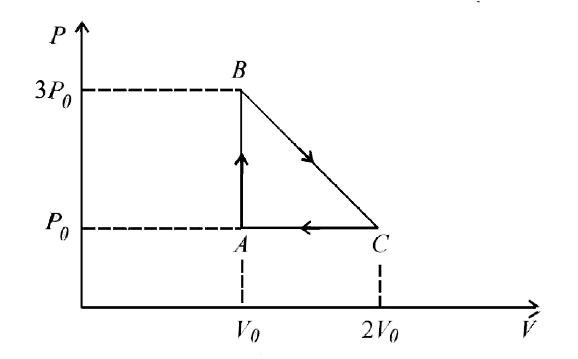
- One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is taken round the cyclic process A...
Text Solution
|
- A masslesss piston divides a closed thermallyy insulated cylinder into...
Text Solution
|