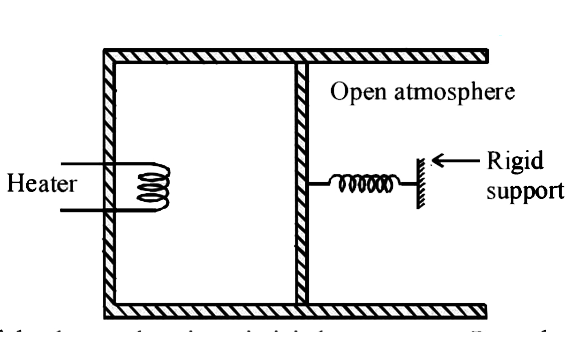
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Corrects|29 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion-Reasoning|6 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|22 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Compression|2 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct Answer Type|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS-Single Correct
- The expansion of an ideal gas of mass m at a constant pressure P is gi...
Text Solution
|
- Two containers of equal volume contain the same gas at pressure P(1) a...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a cylinder by a spring-loaded p...
Text Solution
|
- A box contains N molecules of a perfect gas at temperature T(1) and te...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is filled in the cylinder shown in fig. The two pistons are join...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure of a gas filled in a closed vessel increase by 0.4% when ...
Text Solution
|
- Pressure versus temperature graph of an ideal gas of equal number of m...
Text Solution
|
- The capacity of a vessel is 3 L. It contains 6 g oxygen, 8 g nitrogen ...
Text Solution
|
- Two gases occupy two containers A and B then gas in A, of volume 0.10 ...
Text Solution
|
- A closed vessel contains 8 g of oxygen and 7 g of nitrogen. The total...
Text Solution
|
- Energy of all molecules of a monatomic gas having a volume V and press...
Text Solution
|
- Forty calories of heat is needed to raise the temperature of 1 mol of ...
Text Solution
|
- For a gas the differce between the two specific heat is 4150 J//kg K. ...
Text Solution
|
- The sepific heat at constant volume for the monatomic argon is 0.075 k...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of 5 mol of gas which was held at constant volume was ...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is heated at a constant pressure. The fraction of heat supplied ...
Text Solution
|
- A monatomic gas expands at constant pressure on heating. The percentag...
Text Solution
|
- The average degrees of freedom per molecule for a gas are 6. The gas p...
Text Solution
|
- Certain amount of an ideal gas is contained in a closed vessel. The ve...
Text Solution
|