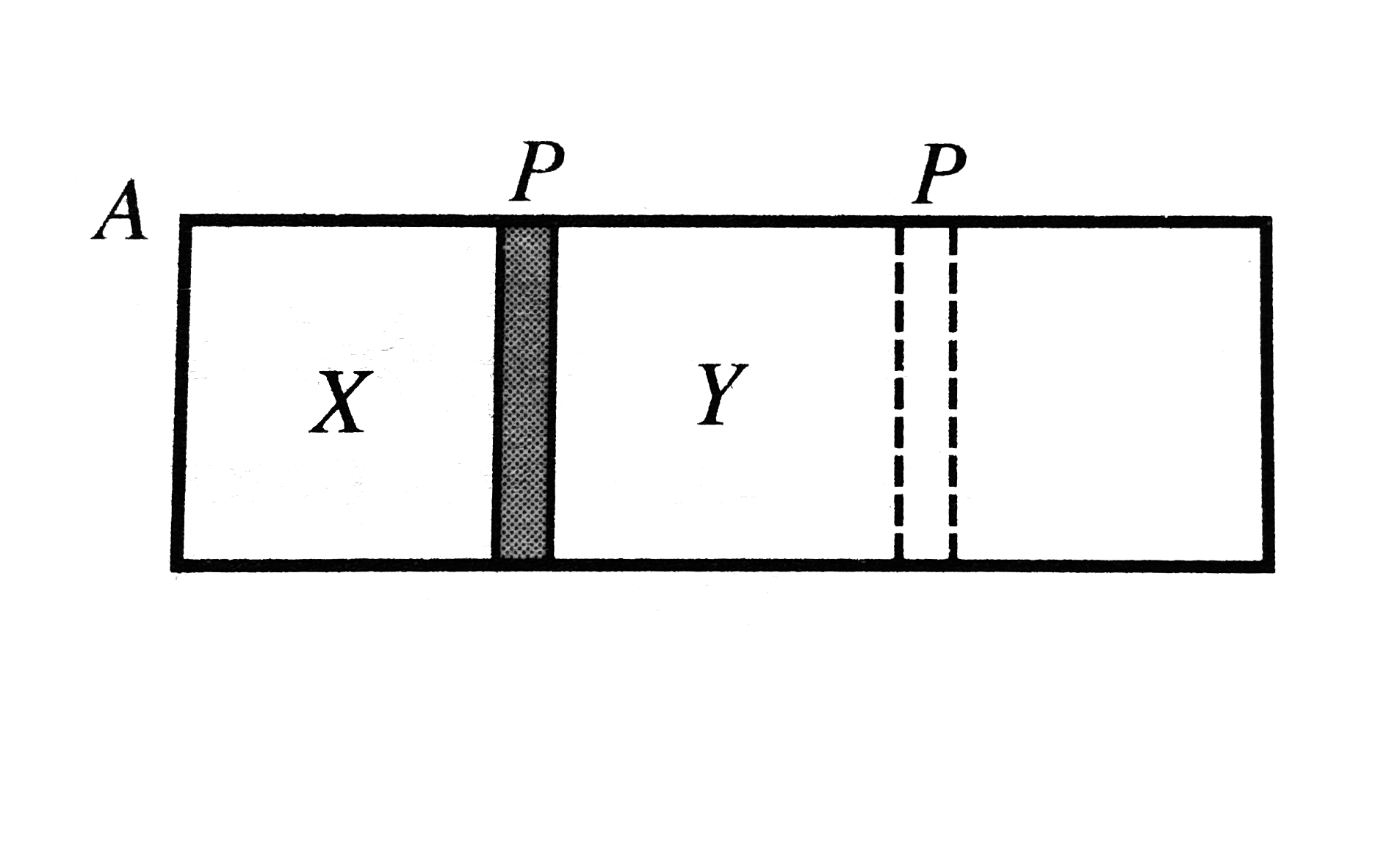A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Corrects|29 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion-Reasoning|6 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|22 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Compression|2 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct Answer Type|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS-Single Correct
- A cylinder of ideal gas is closed by an 8kg movable piston of area 60c...
Text Solution
|
- A certain ideal gas undergoes a polytropic process PV^(n) = constant s...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical chamber A of uniform cross section is divided into two p...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas (1 mol, monatomic) is in the intial state P (see Fig.) on...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an isochore, an isotherm, an adiabatic and two isobars of...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary cylinder of oxygent used in a hospital has the following ...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of ideal gas is expanded to twice its original volume of 1.00...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of air (C(V) = 5R//2) is confined at atmospheric pressure in ...
Text Solution
|
- A thermodynamic process is shown in Fig. The pressures and volumes cor...
Text Solution
|
- Carbon monoxide is carried around a closed cyclic processes abc, in wh...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is taken through a cyclic thermodynamic process through f...
Text Solution
|
- Pressure versus temperature graph of an ideal gas as shown in Fig. C...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is taken through the cycle AtoBtoCtoA, as shown in the fi...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical containers A and B with frictionless pistons contain the...
Text Solution
|
- Argon gas is adiabatically compressed to half its volume. If P, V and ...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed mass of helium gas is made to undergo a process in which its p...
Text Solution
|
- Oxygen gas is made to undergo a process in which its molar heat capaci...
Text Solution
|
- If the ratio of specific heat of a gas of constant pressure to that at...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is at 1 atm pressure with a volume 800 cm^(3). When 100 J of hea...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed mass of a gas is first heated isobarically to double the volum...
Text Solution
|