Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Solved Example|15 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 4.1|23 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger|11 VideosMISCELLANEOUS KINEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger type|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-LINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION-Multiple Correct Answer Type
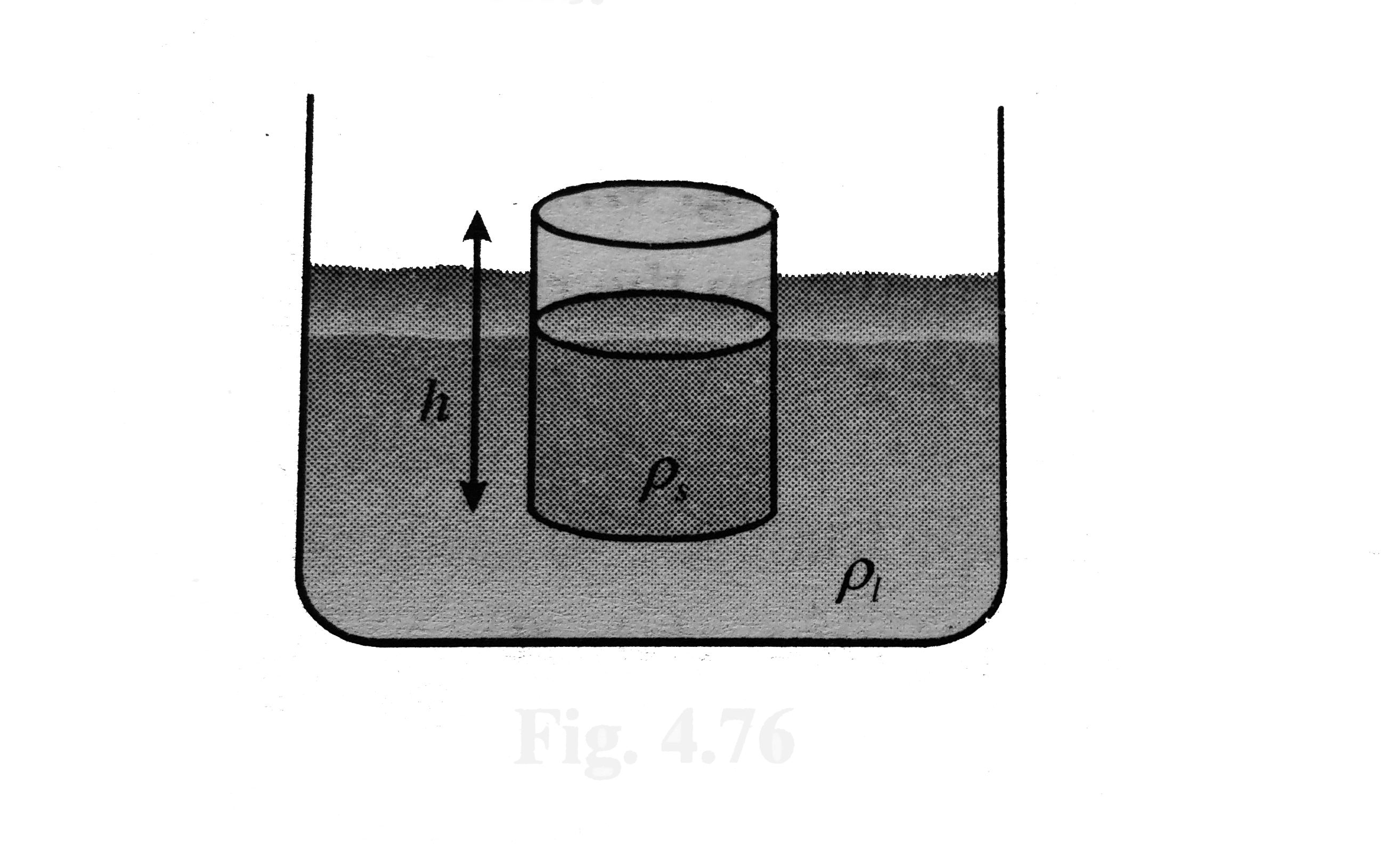
- Consider a solid cylinder of the density rho(s) cross section area A a...
Text Solution
|
- The springs shown in the figure are all upstretched in the beginning w...
Text Solution
|
- A spring has natural length 40 cm and spring constant 500 N//m. A bloc...
Text Solution
|
- A 1kg block is eecuting simpe hrmonic motion of ampliltude 0.1 m m on ...
Text Solution
|
- A mass M is in static equilibrium on a massless vertical spring as sho...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A (5kg) and B (2kg) attached to the ends of a spring consta...
Text Solution
|
- The displacement of a particle varies with time according to the relat...
Text Solution
|
- Three simple harmonic motions in the same direction having each of amp...
Text Solution
|
- Funcation x=A sin^(2) omegat+B cos^(2) omegat+ C sin omegat cos omegat...
Text Solution
|
- The x-coordinate of a particle moving on x-axis is given by x = 3 sin...
Text Solution
|