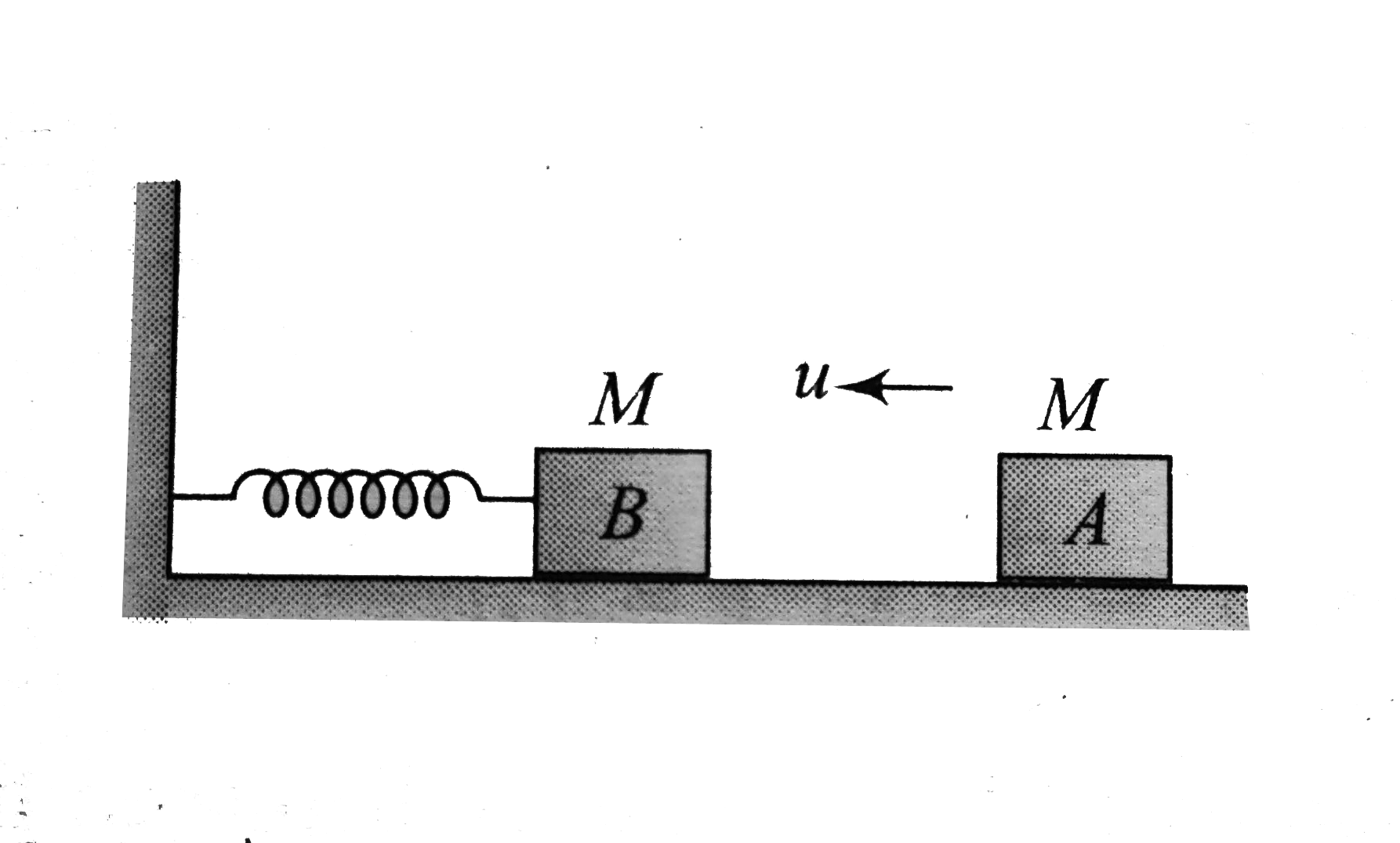Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|21 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|107 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 4.1|23 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger|11 VideosMISCELLANEOUS KINEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger type|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-LINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION-Exercise 4.2
- A mass M attached to a spring oscillation with a period of 2 s. If the...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal rod of mass m and length L is pivoted at one end The rod'...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum has a period T for small oscillations. An obstacle is place...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal spring block system of mass M executes simple harmonic mo...
Text Solution
|
- A spring of spring constant 200 N//m has a block of mass 1 kg hanging ...
Text Solution
|
- With the assumption of no slipping, determine the mass m of the block ...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of length l swings from a small angle theta . Its sw...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length l is pivoted distance x from the top of the ro...
Text Solution
|
- The period of oscillation of a spring pendulum is T. If the spring is ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform stick of length l is hinged so as to rotated about a harmoni...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is released in a smooth dimetrical tunnel of earth a. After ...
Text Solution
|
- A body is in SHM with period T when oscillated from a freely suspended...
Text Solution
|
- A point mass m is suspended at the end of a massless wire of length l ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, the block A of mass m collides with the identical...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a block P of mass m resting on a smooth floor at a distan...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a block P of mass m resting on a smooth horizontal ground...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a spring block system hanging in equilibrium. If a veloci...
Text Solution
|
- Find the amplitude of the harmonic motion obtained by combining the mo...
Text Solution
|
- x(1) = 3 sin omega t,x(2) = 4 cos omega t Find (i) amplitude of resu...
Text Solution
|
- A partical is subjucted to two simple harmonic motions x(1) = A(1) ...
Text Solution
|