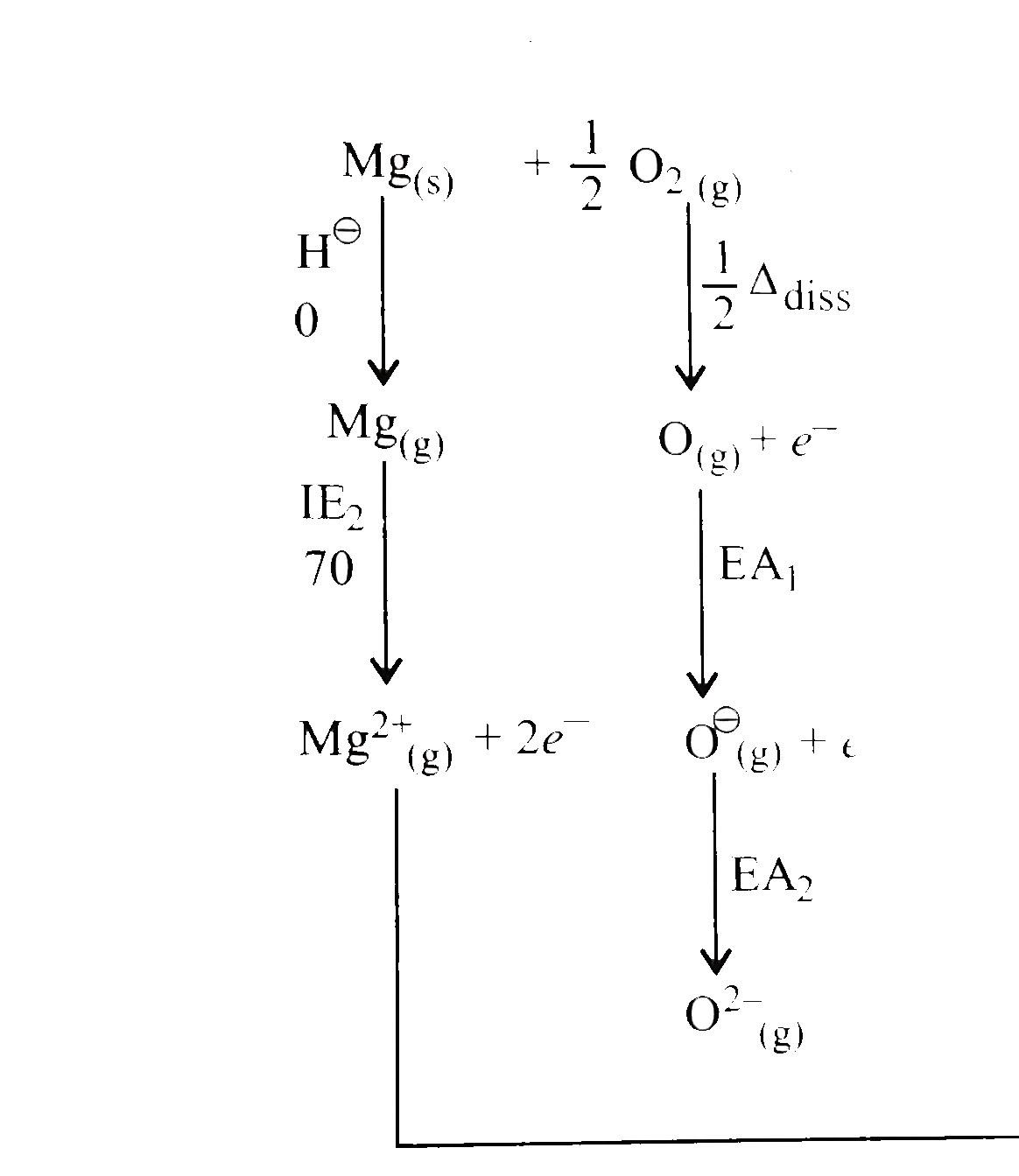A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Single Correct)Miscellaneous|10 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Assertion Reasoning)|11 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Single Correct) Bond Angle|4 VideosP-BLOCK GROUP 14 - CARBON FAMILY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Archives (Subjective)|9 VideosPURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Assertion Reasoning Type|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Exercises (Single Correct) Lattice And Hydration Energy
- Decreasing order of hydration energy of the following is
Text Solution
|
- Extent of hydrolysis of the following is
Text Solution
|
- Give the decreasing order of thermal stability of the following .
Text Solution
|
- Lattice energy of an ionic compound depedns upon :
Text Solution
|
- Na(2)SO(4) is soluble in water while BaSO(4) is insoluble. Which of th...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the lattice energy from the following data (given 1 eV = 23....
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the EA of O atom to O^(2-) ion from the following data: i....
Text Solution
|