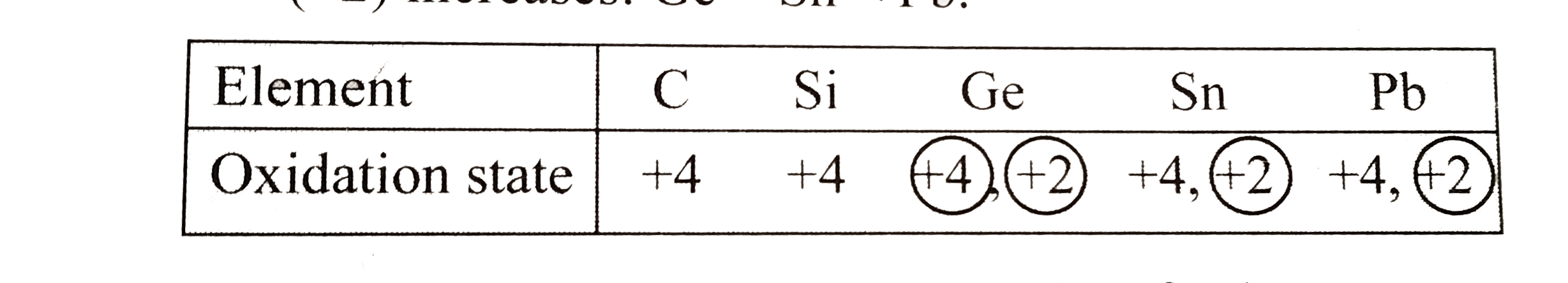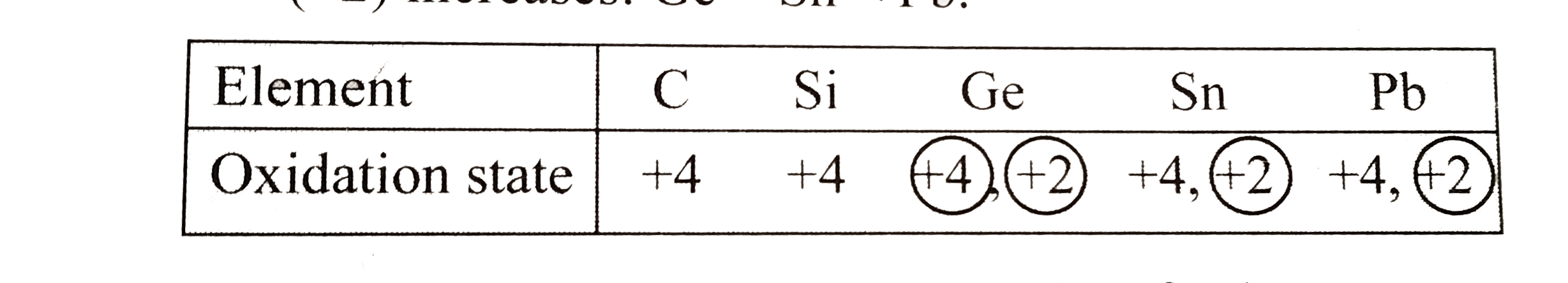a. Electronic configuration of group `13` elements is `ns^(2)np^(2)`. `B` and `Al` have noble gas core beneath the valence shell electron, whereas `Ga, In` and `TI` have fully filled lesser shielding `d-` and or `f`-orbital present in-between the noble gas core and valence electron. Since `d` and `f` orbitals have lesser shielding effect, Ga, in and Ti exhibit inert part effect, whereas `B` and `Al` do not. Hence, `B` and `Al` exhibit only one stable oxidation state, i.e. `+3`, whereas `Ga,In` and `TI` due to inert pair effect shows as oxidation state of `+1` also, besides group oxidation state of `+3`.
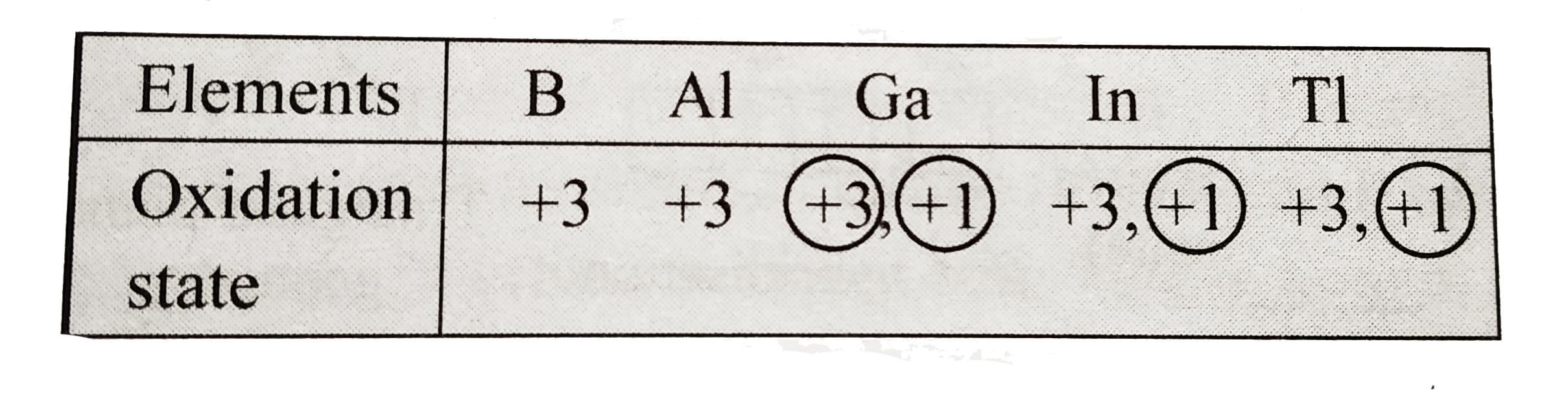
Down the group `(darr)`, stability of lower oxidation state `(+1)` increases, i.e. `GaltTnltTI`, whereas that of higher oxidation state `(+3)` decreases, i.e.`Gagt"In"gtTI`
b. Electronic configuration of group `14` elements in `ns^(2)np^(2)`.`C` and `Si` have noble gas core beneath the valence shell electrons, whereas `Ge,Sn` and `Pb` have fully filled lesser shielding `d`- and or `f`-orbital in between the noble gas core and valence shell electrons.
Shielding effect varies in the order:`nsgtnpgtndgtnf`. Hence,`C` and `Si` do not exhibit inert pair effect, whereas `Ge,Sn` and `Pb` exhibit inert pair effect. Consequently, `C` and `Si` shows as oxidation state, `+4` (group oxidation state), whereas `Ge,Sn` and `Pb`,besides showing group oxidation state of `+4`, also shows an oxidation state of `+2`.Stability of higher oxidation state `(+4)` decreases down the group `(darr)`,`GegtSngtPb`,whereas that of lower oxidation state `(+2)` increases:`GeltSnltPb`.