Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
QUALITATIVE INORGANIC SALT ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Solved Example|11 VideosQUALITATIVE INORGANIC SALT ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Linked Comprehension)|68 VideosP-BLOCK GROUP 18 ELEMENTS - THE INERT GASES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex 5.1 (Objective)|14 VideosREDUCTION AND OXIDATION REACTION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise SUBJECTIVE TYPE|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-QUALITATIVE INORGANIC SALT ANALYSIS-Viva Voce Questions And Part-C (Analysis Of Cations)
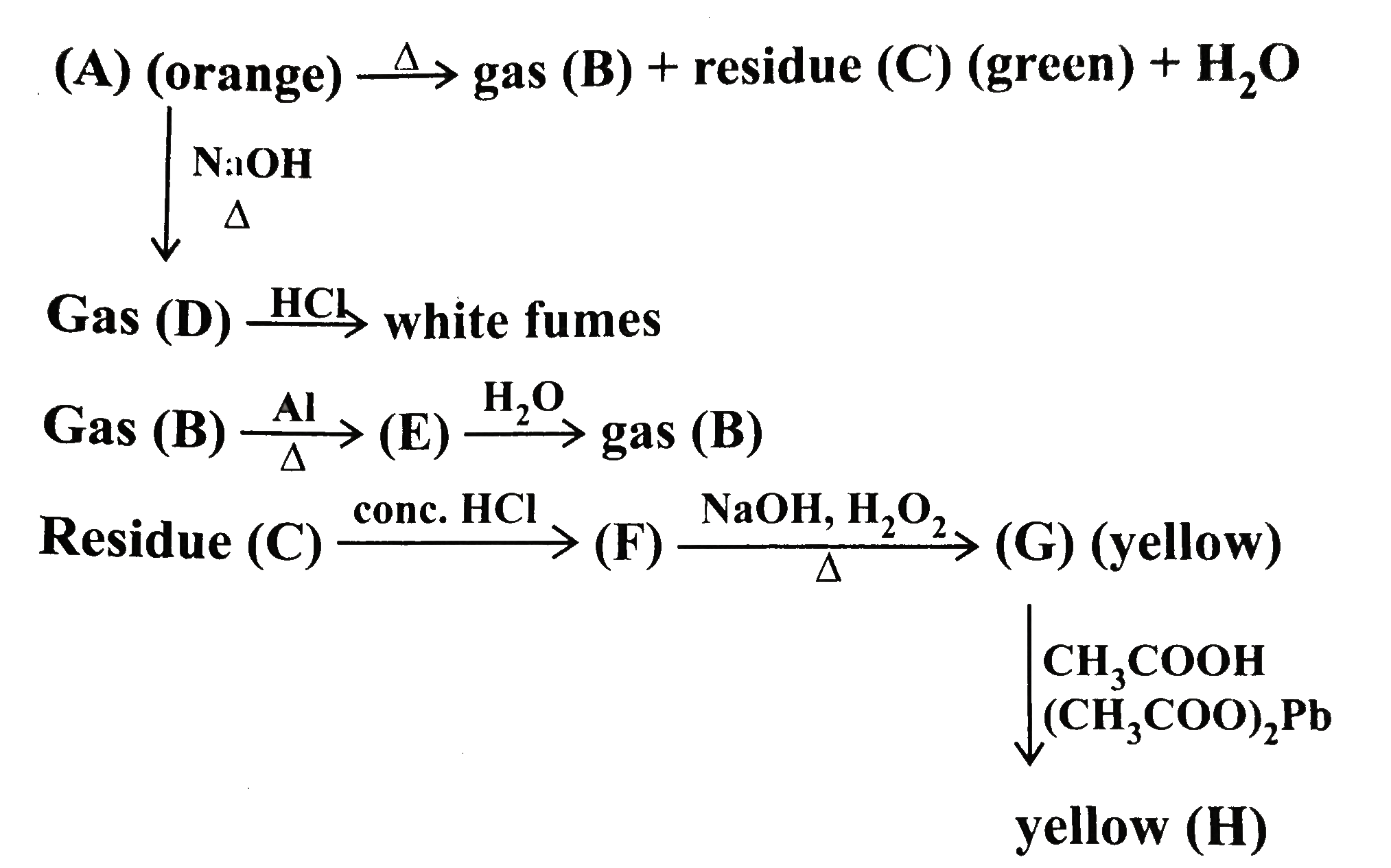
- Gas (D)overset(HCI) to while fumes Gas(B)overset(AI)underset(Delta)to...
Text Solution
|
- Why is it necessary to prepare original solution for the detection of ...
Text Solution
|
- Why do we not prefer to prepare original solution in conc. H(2)SO(4) o...
Text Solution
|
- What is solubility product? Explain its importance in qualitative anal...
Text Solution
|
- What is the basis of classification of cations into different group ?
Text Solution
|
- Why are only Pb^(2+),Ag^(o+) and Hg(2)^(2+) ions precipitated in group...
Text Solution
|
- Why is lead plaed in gourp I as well in II?
Text Solution
|
- Is it necessary to acidify a solution before group II cations are prec...
Text Solution
|
- Give the reason for the formation of a light yellow or white ppt. in t...
Text Solution
|
- Why do we Prefer HCl for preparing solution of cations?
Text Solution
|
- Is it advisable to use conc. HCI in place of dilute HCI for preparing ...
Text Solution
|
- Why is it essential to boil off H(2)S gas before proceeding to group I...
Text Solution
|
- Can the solution be acidified with HNO(3) in group II before passing H...
Text Solution
|
- What can it be, if the precipitate of group I is soluble in hot water ...
Text Solution
|
- Why is H(2)SO(4) never employed for preparing original solution for th...
Text Solution
|
- Group I filtrate is made moderately acidic before proceeding to group ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the
Text Solution
|
- Why do we add excess of NH(4)Cl and NH(4)OH in the precipitation of gr...
Text Solution
|
- Why is it essential to oxidise ferrous salt to ferric salt in group II...
Text Solution
|
- Can NH(4)Cl be replaced by any other ammonium salt for the precipitati...
Text Solution
|
- How will you distinguish between ferrous and ferric salts?
Text Solution
|