(a) (i)
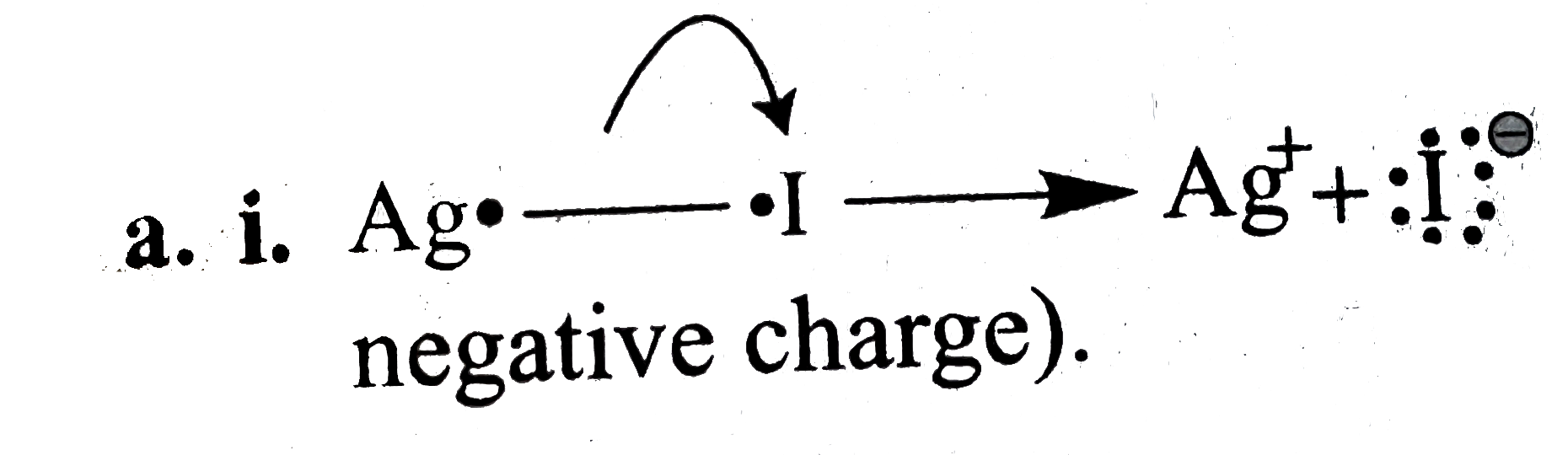
(More `EN` atoms acquire negative charge).
(ii) `H_3 N^(oplus) overset (Ө)B F_3 rarr H_3 N : B F_3` (Bonded atoms with formal charges give uncharged products.)
(iii) `[Cu( :ddotOH_(2))_(4)]^(2+) rarr Cu^(2+) +4H_(2)ddotO:`
(b) Coordinate convalent bonding.
( c) `H_3 C CO .. COCH_3 rarr 2 CH_3 CO. (A radical)`
(d) Triplet carbene has lower energy because with two `overline e^, s` in different orbitials there is less electrostatic repulsion then when both are in the same orbital.
( c) `X_2 C` : singlet is more stable. because lone pair of `overline e^, s` on `X` can overlap laterally with the empty orbitial (lone pair of `overline e^, s`) of the singlet carbene, thereby stabilising the singlet state. The resonance structure are :

(f) `F_2 C` is most stable singlet, since `f` and `C` are in the same period of the periodic table and are about the same size permitting more efficient overlap `(2p(F) - 2p (C)` or `p pi - p pi(bond)`. Moreover, `(F - C)` bond length is the shortest bond length and provides more extensive lateral and provides more extensive lateral overlap.
(g) The `EA` is less than `IE`. When `*CH_3` gains an `overline e` to become carbanion, `C` acquires a stable octet of `overline e^, s`. When it loses an `overline e`, it becomes unstable with only six `overline e^, s`.
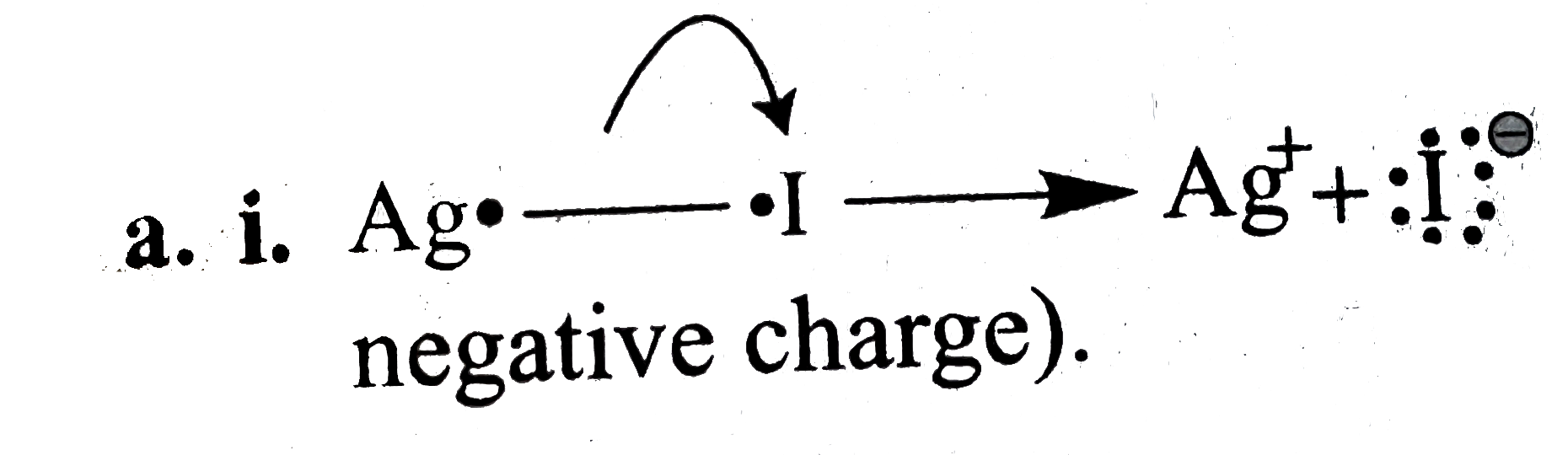 (More `EN` atoms acquire negative charge).
(More `EN` atoms acquire negative charge). 