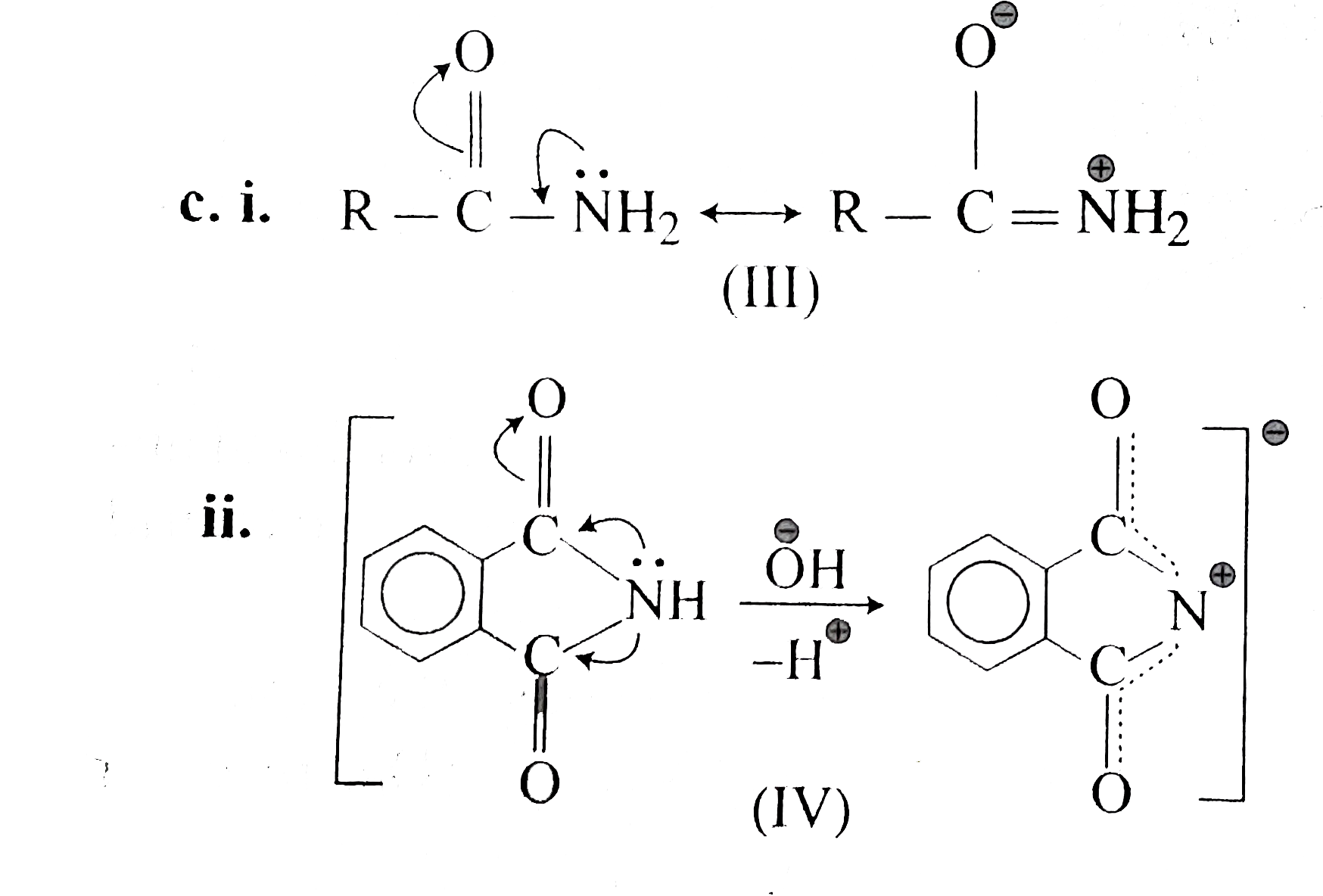
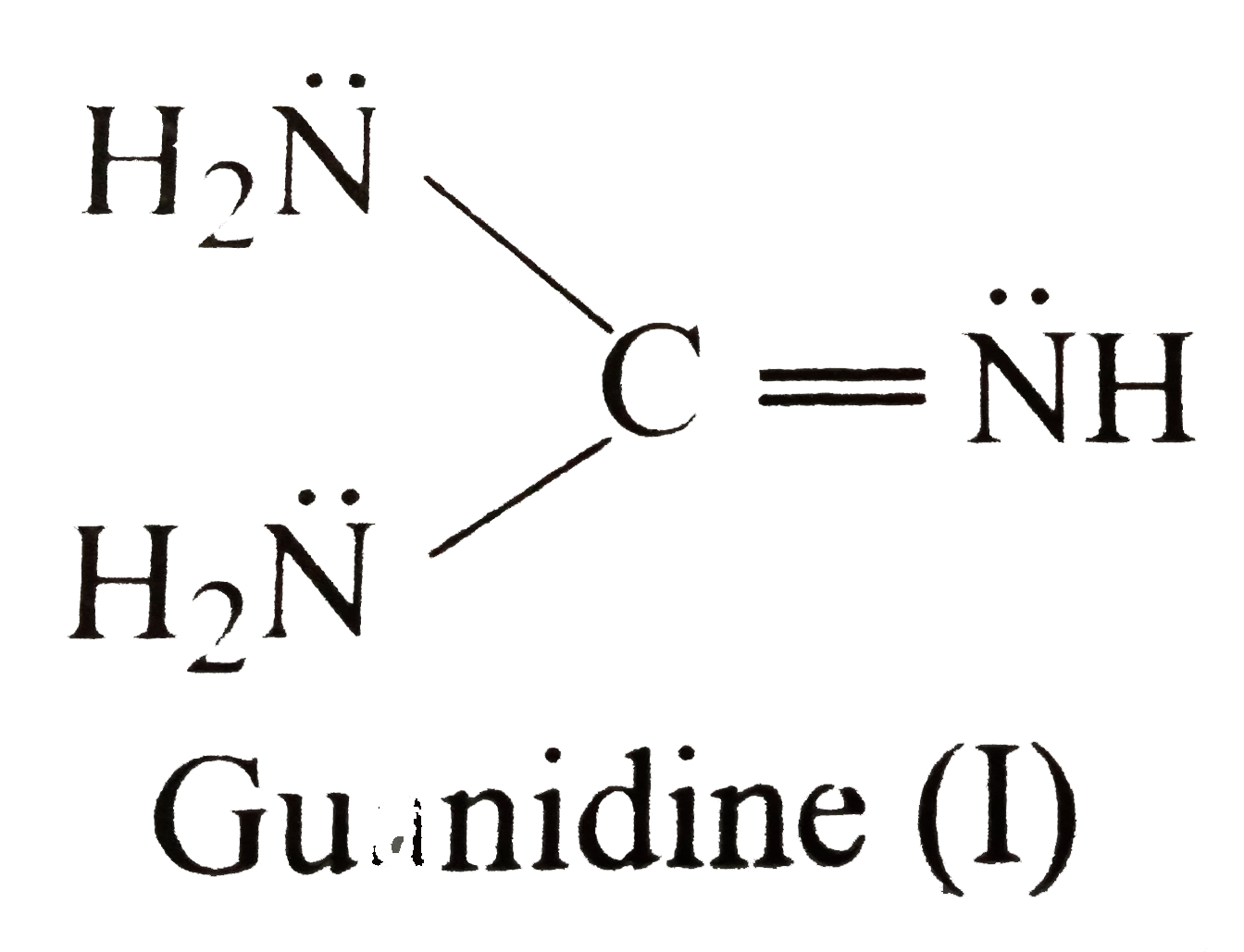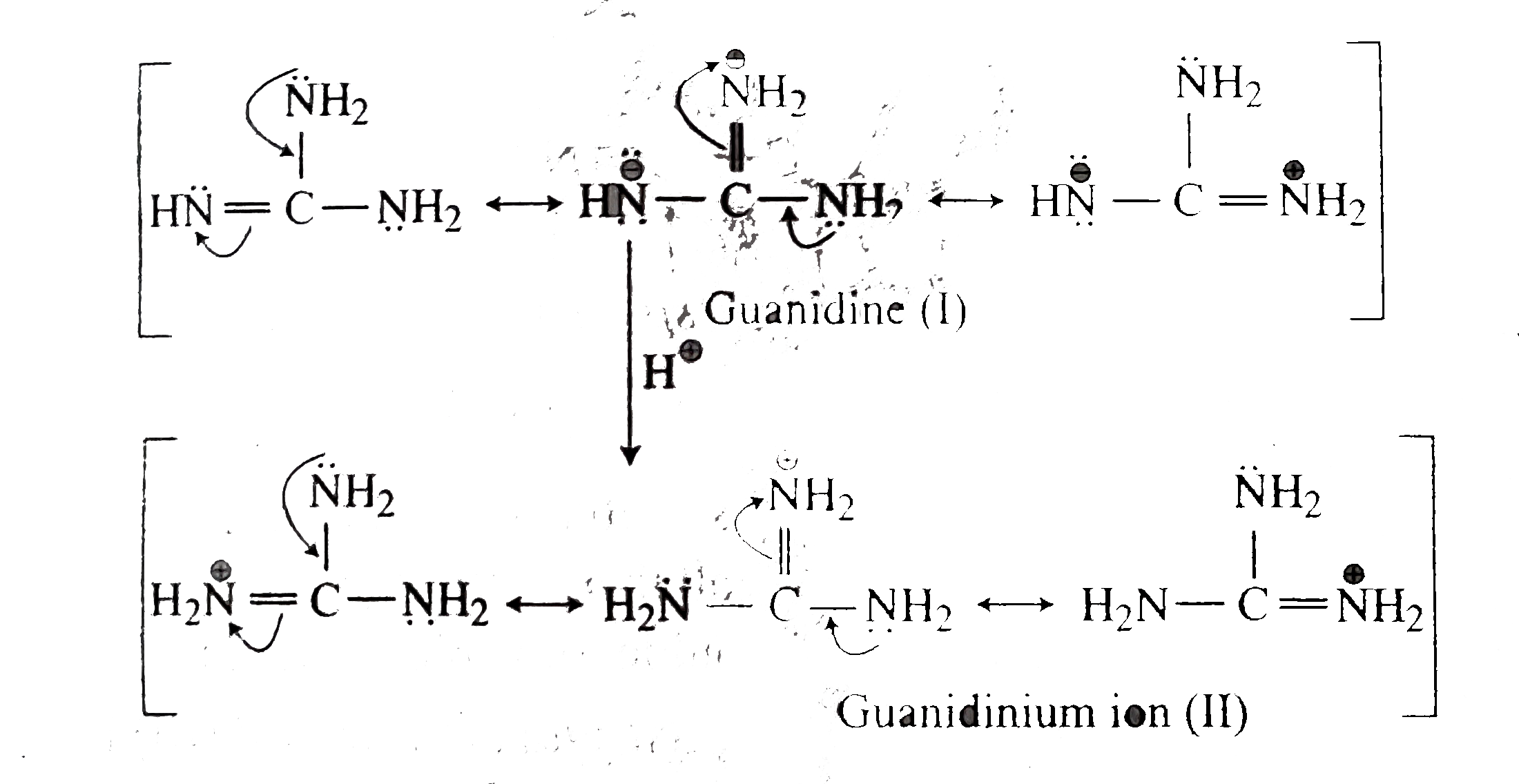Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Solved Example|18 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Subjective|11 VideosCLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Analytical and Descriptive Type|3 VideosHYDROGEN, WATER AND HYDROGEN PEROXIDE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Subjective Archive (Subjective)|3 Videos