Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Solved Examples|24 VideosALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Subjective Type)|31 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Single correct Answer|14 VideosAPPENDIX - INORGANIC VOLUME 1
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise chapter-7 Single correct answer|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ALKYNES-Exercises (Archives - Analytical and Desriptive Type)
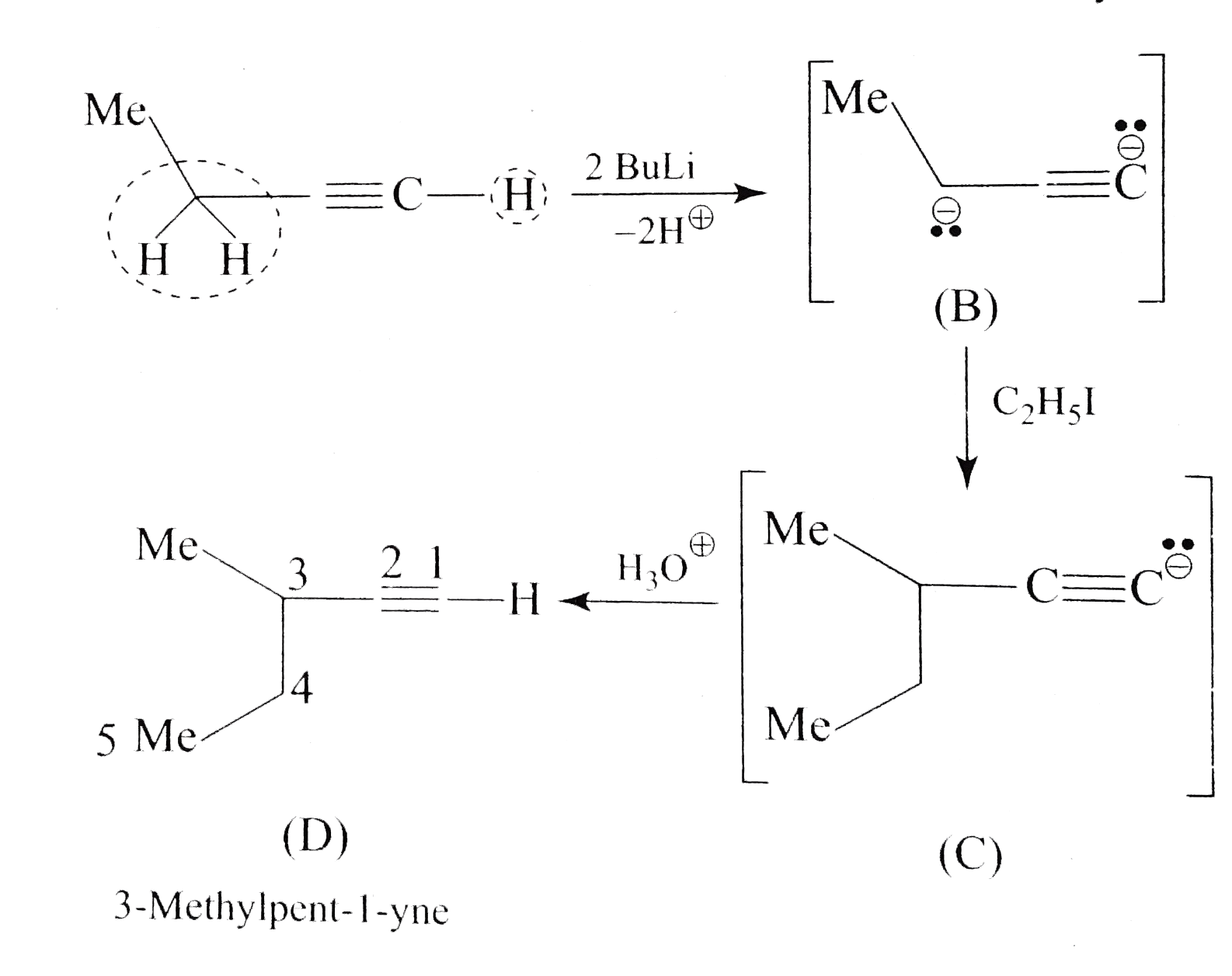
- Explain the formation of products (B), (C), and (D) in the following r...
Text Solution
|
- Outline the reaction sequence of the conversion of ethene to ethyne (t...
Text Solution
|
- Identify a reagent from the following list which can easily distinguis...
Text Solution
|
- How would you convert acetylene to acetone?
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons for the following: CH2=CH^(Θ) is more basic than HC-=C^...
Text Solution
|

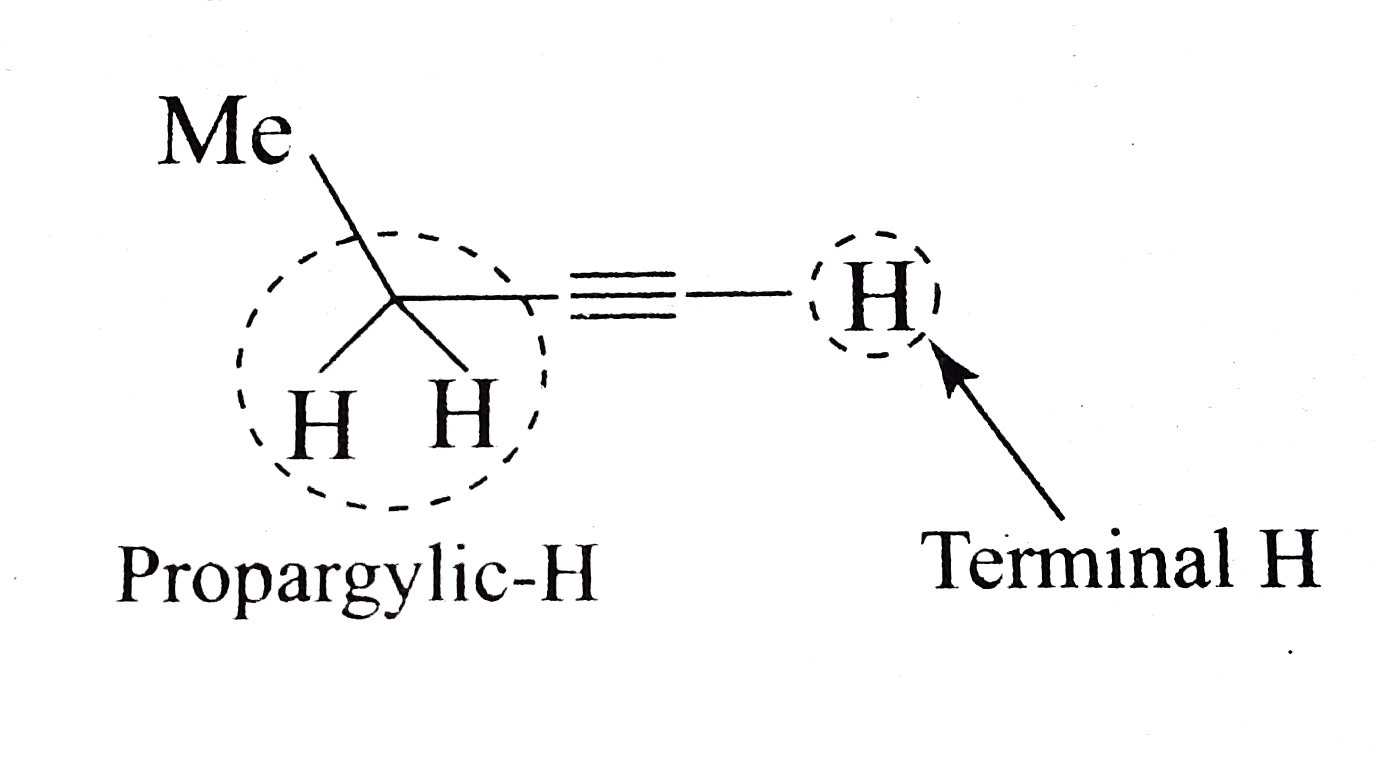
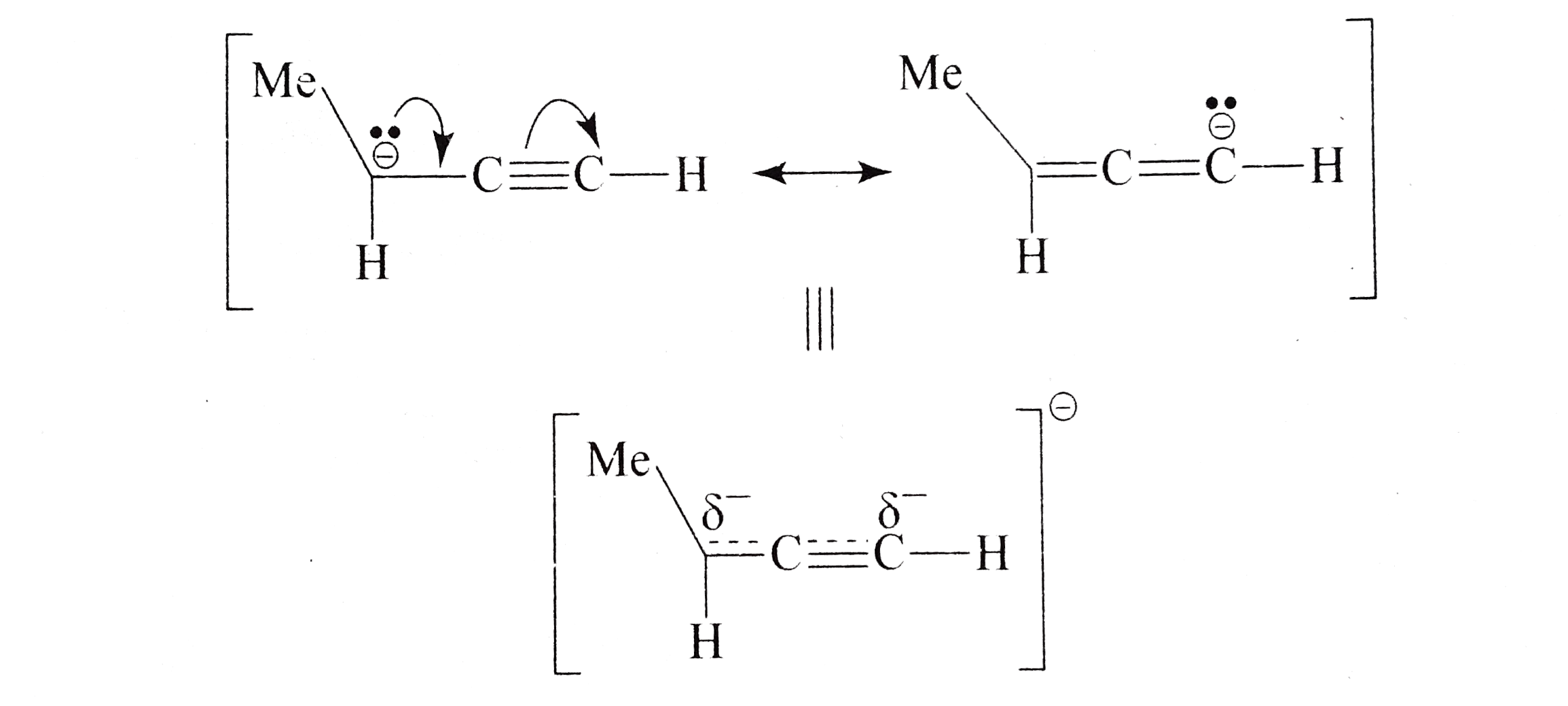
 Propargylic H is acidic due to resonance stabilisation (extended delocalisation) of the negative charge, as shown:
Propargylic H is acidic due to resonance stabilisation (extended delocalisation) of the negative charge, as shown: