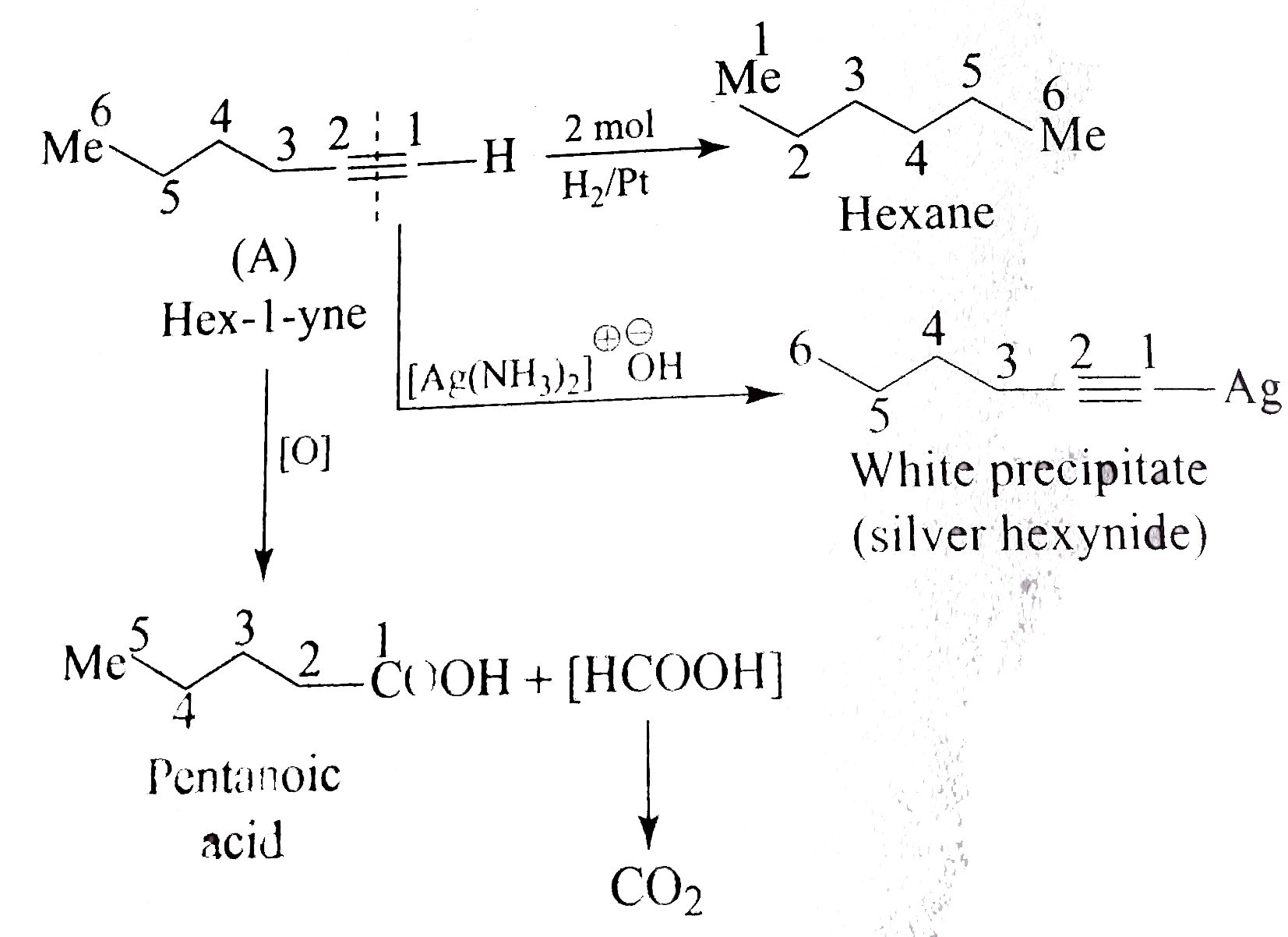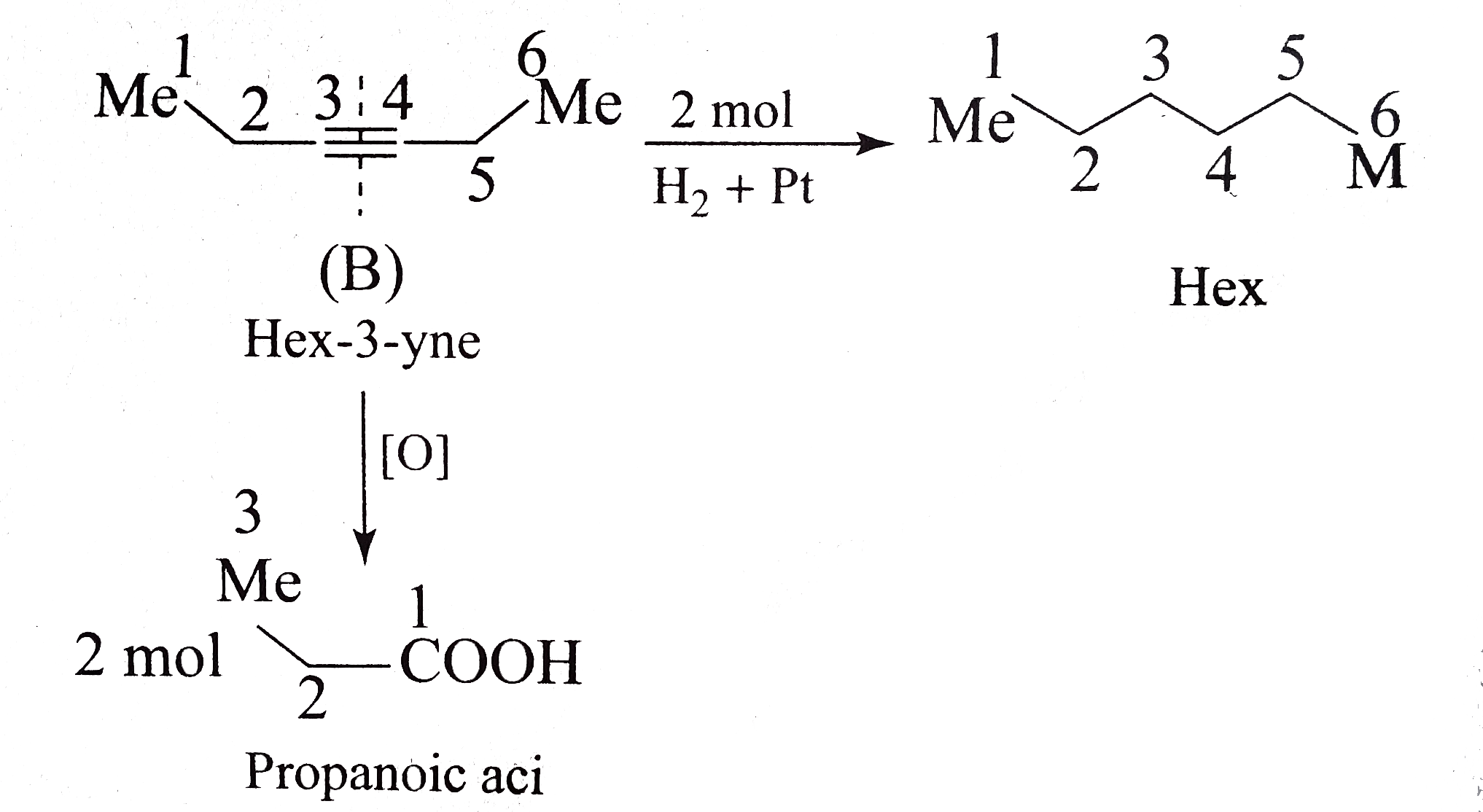Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Subjective Type)|31 VideosALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Linked Comprehension Type)|51 VideosALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Archives - Analytical and Desriptive Type)|4 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Single correct Answer|14 VideosAPPENDIX - INORGANIC VOLUME 1
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise chapter-7 Single correct answer|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ALKYNES-Solved Examples
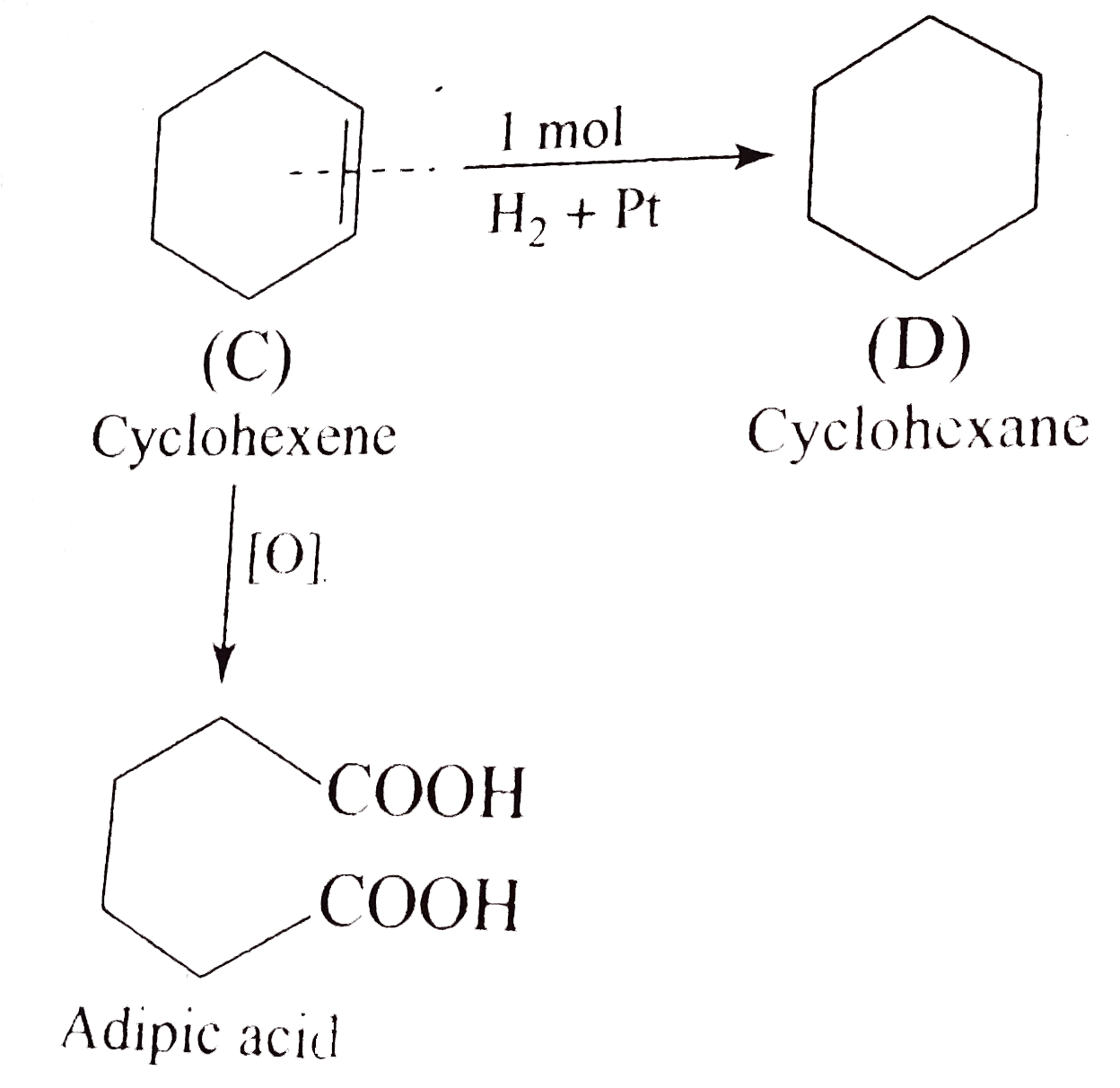
- Identify A to D.
Text Solution
|
- Alkenes are more reactive than alkynes towards electrophillic addition...
Text Solution
|
- There are two paths (a) and (b) for the preparation of a compound (A) ...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following missing reagents: i. ii. There are two dis...
Text Solution
|
- i. Complete the following missing reagents. ii. Write the form...
Text Solution
|
- Convert the following:
Text Solution
|
- Convert propyne (Me--=-H) (A) to
Text Solution
|
- i. 27.8gm mixture of alkyne and alkane (both containing same number of...
Text Solution
|
- Identify A, B, and C. A, B, and C(C6H(10))overset(Br2//C CI2)rarrund...
Text Solution
|
- Convert:
Text Solution
|
- Convert: HC-=CH(A)overset(?)rarroverset(?)rarroverset(?)rarroverset(...
Text Solution
|
- (A)overset(H(2)+P-2)underset(Catalyst)rarr underset("Cyclopent-2-en-1-...
Text Solution
|
- Terminal alkynes (RC-=CH) are not reduced by alkali metals (e.g., Na, ...
Text Solution
|
- Identify (A) to (G).
Text Solution
|
- Convert the following: overset(?)rarr(B)overset(?)rarr(C)overset(?...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following: Give the major and minor products (C and ...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following:
Text Solution
|
- In the conversion of (B) to (C), how many moles of NaNH2 are used?
Text Solution
|
- Give the products of the following reactions.
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reactions: a.(A) + (B) underset(CH(3)ONa+CH(3...
Text Solution
|