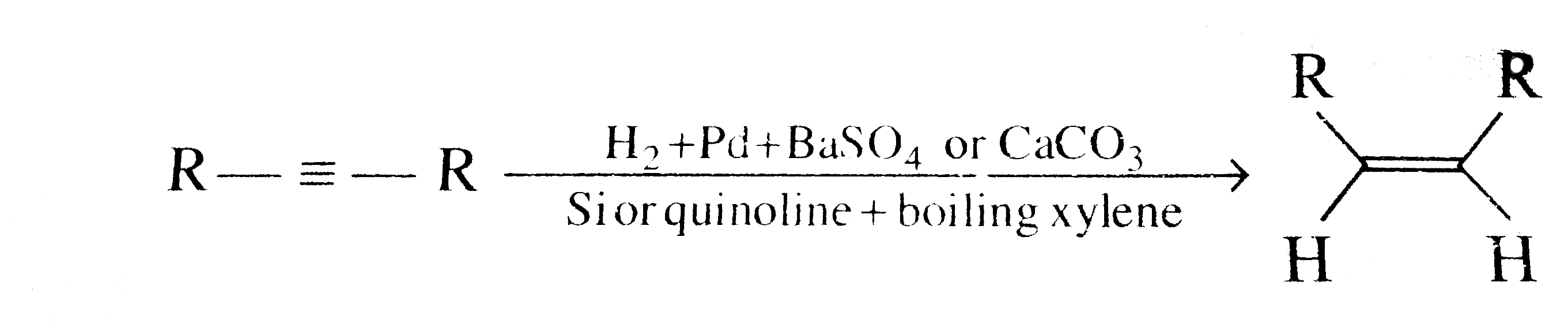A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Single Correct Answers Type)|30 VideosALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Archives - Single Correct Answer Type)|6 VideosALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Linked Comprehension Type)|51 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Single correct Answer|14 VideosAPPENDIX - INORGANIC VOLUME 1
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise chapter-7 Single correct answer|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ALKYNES-Exercises (Multiple Correct Answers Type)
- In the following sequence of reactions, Which of the statements a...
Text Solution
|
- Acetylene is thermodynamically unstable and readily explodes, therefor...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the statements are correct for alkyne with molecular formula ...
Text Solution
|
- For the conversion of alkyne to cis-alkene, H2+ Lindlar's catalyst is ...
Text Solution
|
- i. Me--=-Hunderset((ii)H2O2//overset(Ө)OH)overset((i) Sia2BH)rarrA i...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are correct?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct:
Text Solution
|
- Compound (B) is same when (A) is:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the statements are correct? R--=-R^'underset(+EtOH)overset(...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the statements are correct? R--=-Runderset(Catalyst)overset...
Text Solution
|
- Hydroboration oxidation and acid hydration will yield the same product...
Text Solution
|
- C4H6underset(1 mol)overset(H2+Pt)rarrC4H8overset(O3//H2O)rarr Acedic a...
Text Solution
|
- All reagents, [Cu(NH3)2]^(o+), [Ag(NH3)2]^(o+), CH3MgBr, and NaNH2 r...
Text Solution
|
- Compound (A) does not react with Tollens or Grignard reagent, but afte...
Text Solution
|
- Compound (A) reacts with [Cu(NH3)2]^(+) and Tollens reagent, but after...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the statements are correct?
Text Solution
|
- Reagents used in conversion from (A) to (B) are:
Text Solution
|
- Which gas is in an antidote of Lewisite (a poisonous gas used in World...
Text Solution
|
- Which statements are correct:
Text Solution
|
- Which statements are correct for reagents A, B, C, and D?
Text Solution
|