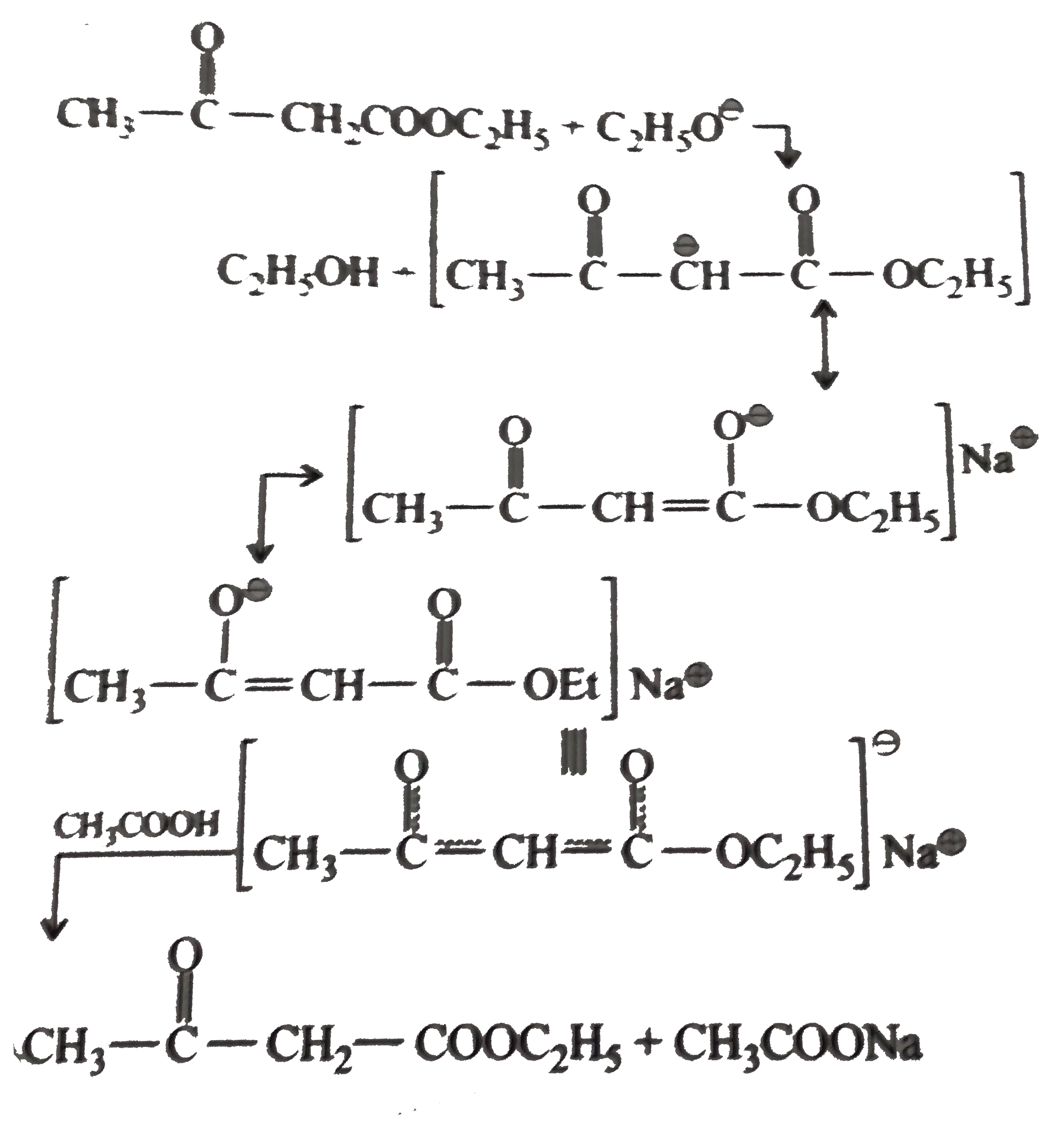
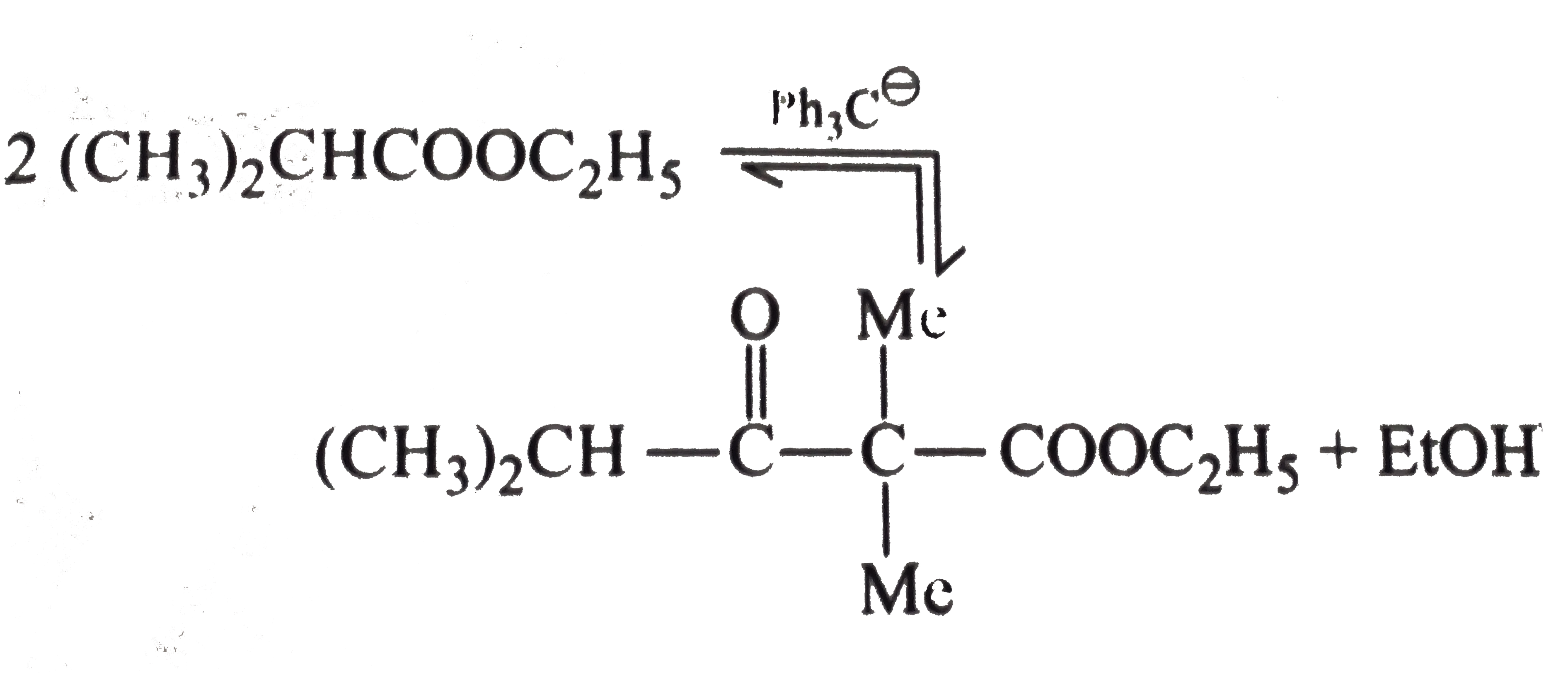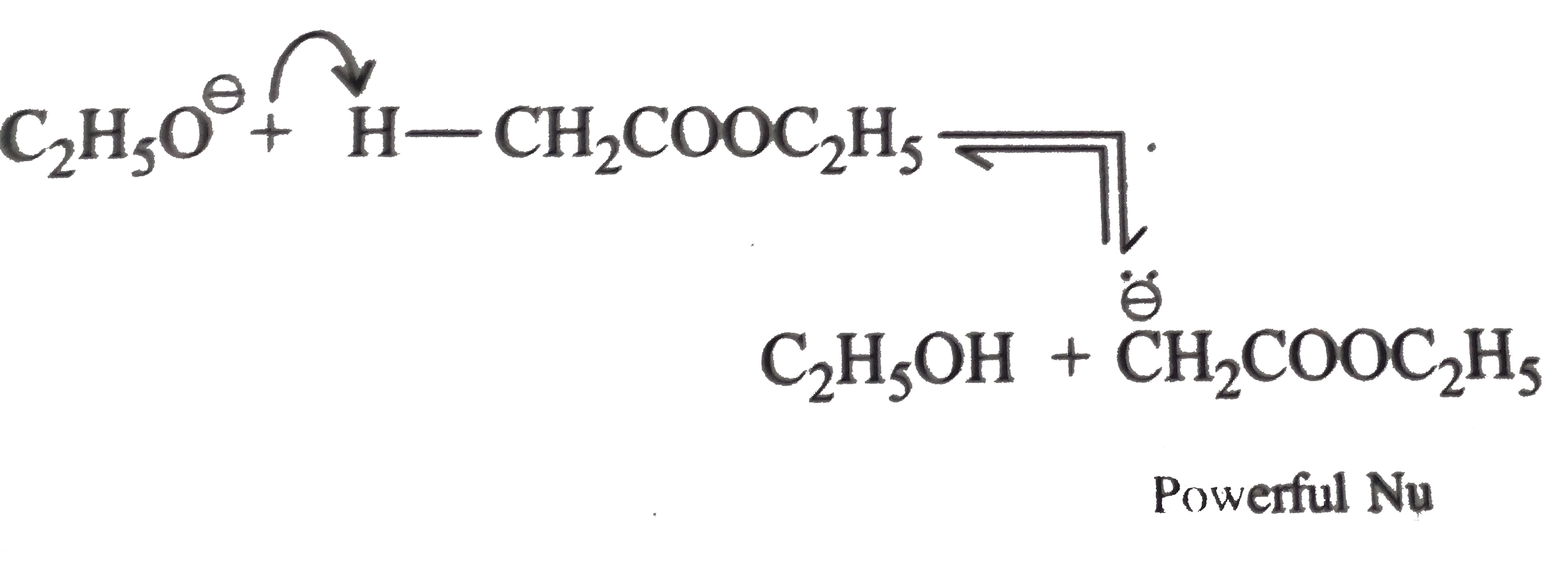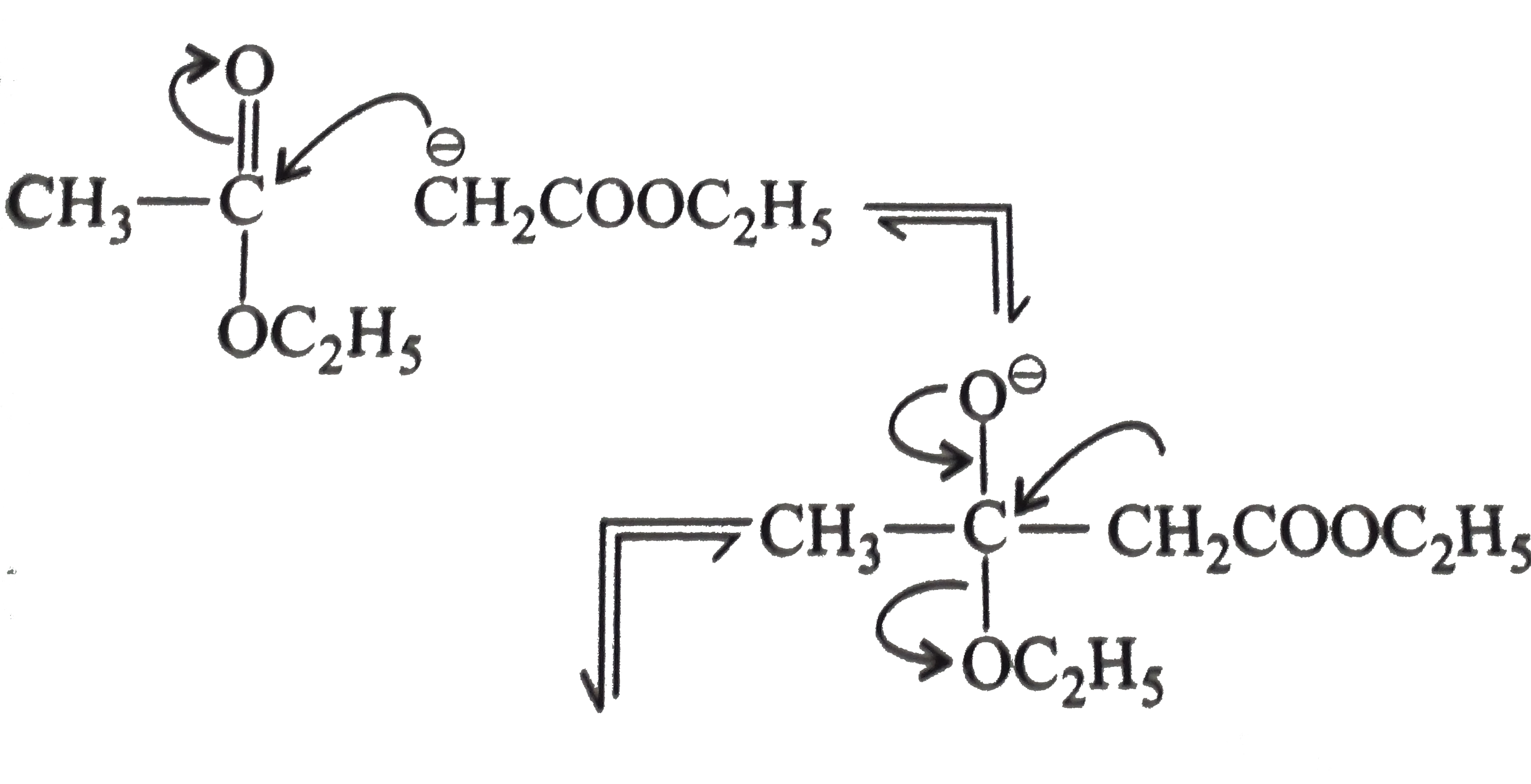Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Subjective)|19 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Linked Comprehension)|34 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)|34 VideosBIOMOLECULES, POLYMERS AND CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise QUESTION BANK|8 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Subjective|23 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES-Solved Examples
- Convert the following : (a) (b)underset((I))(PhH("Benzene"))under...
Text Solution
|
- There are two paths for the preparation of 2-methyl pentanoic acid (II...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reactions : (a)
Text Solution
|
- Explain the formation of the compound in the following reaction. .
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between the following : (a) (I) Propanoic acid (C2 H5...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the products and explain their formation. (a) (b) ( c...
Text Solution
|
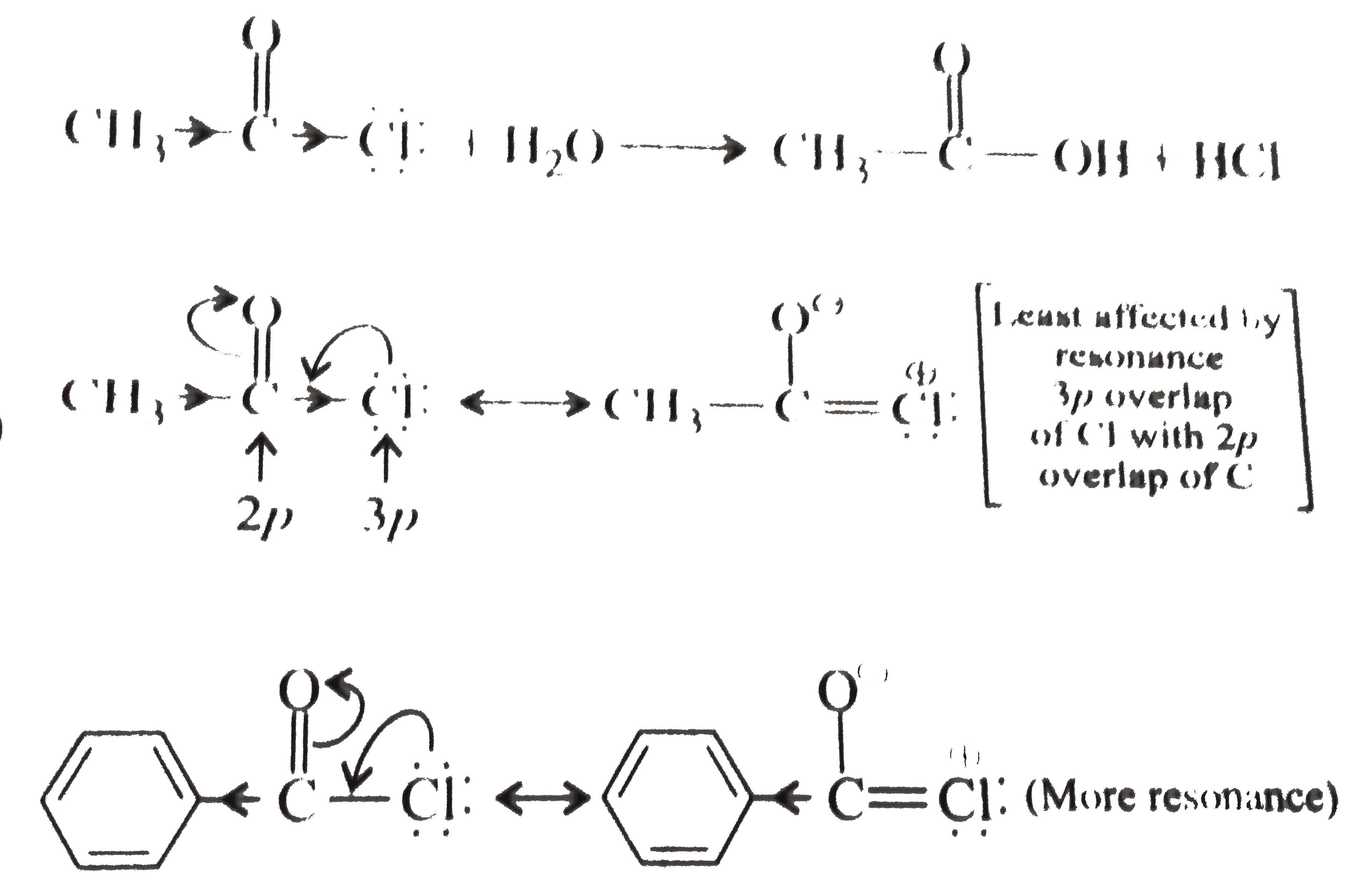
- Distinguish between the following : (a) MeCOCl (ethanoyl chloride) a...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reaction : (a) (b) ( c) (d) ( e) ...
Text Solution
|
- Give the decreasing order of reactivity of the following amides in Hof...
Text Solution
|
- Give the decreasing order of reactivity of the following towards hydro...
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between the following acids : (a) (b)
Text Solution
|
- Explain the machanism of the following reaction : .
Text Solution
|
- Complete the missing reactants : (a) (b) ( c) (d) .
Text Solution
|
- Identify : (a) (b)
Text Solution
|
- Identify : (a) (b) ( c)
Text Solution
|
- Identify (A) and (B). .
Text Solution
|
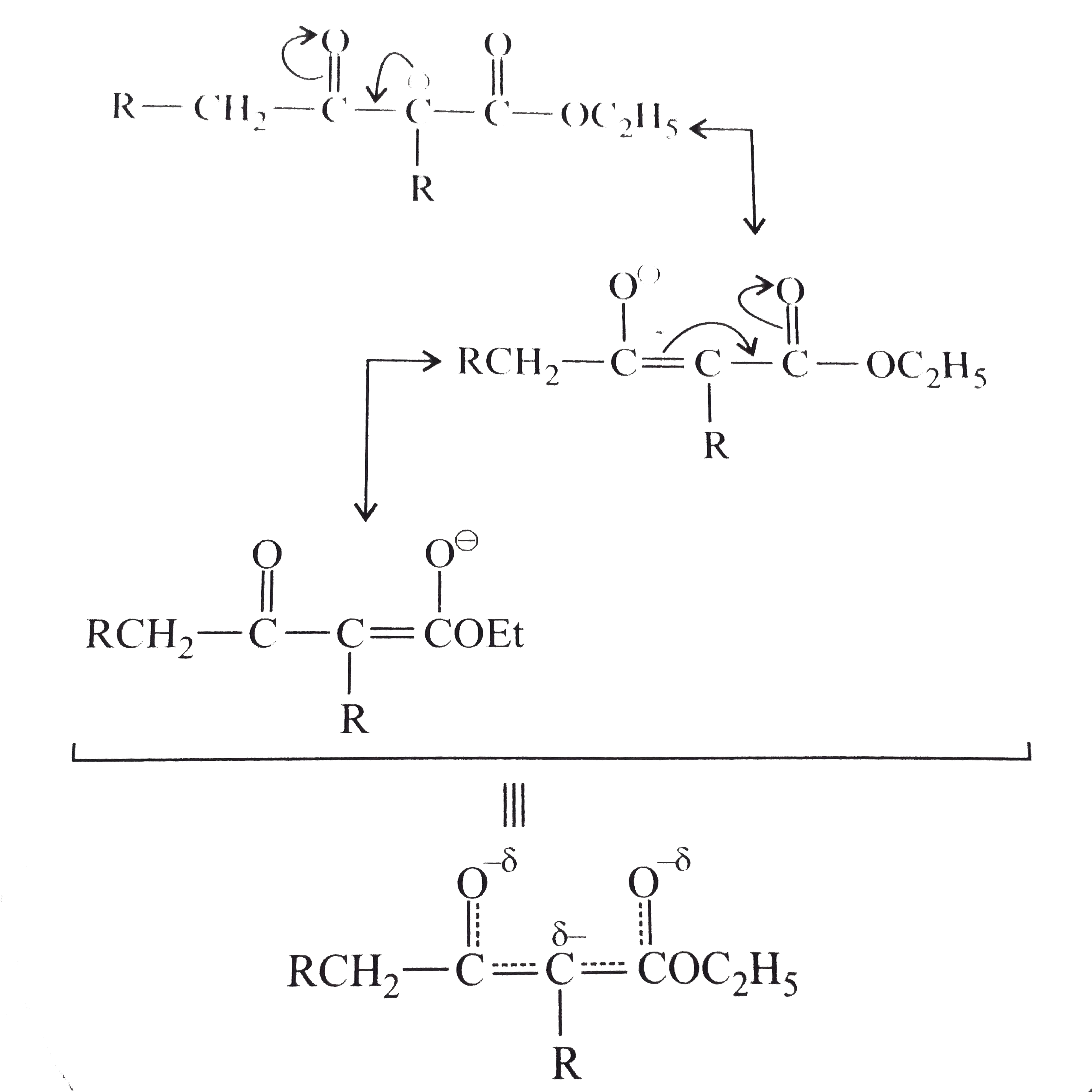
- Explain : (a) Ethyl isobutyrate does not undergo Claisen condensatio...
Text Solution
|
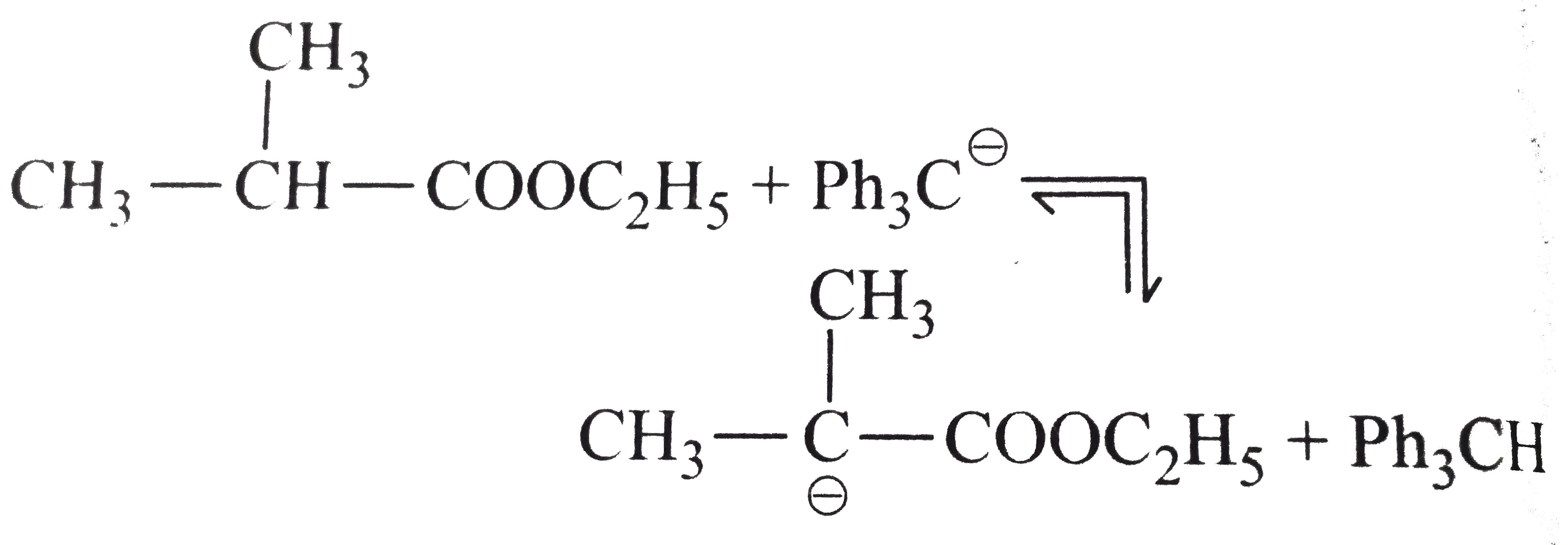 .
.