Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
BIOMOLECULES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Linked Comprehension)|38 VideosBIOMOLECULES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Multiple Correcttype)|31 VideosBIOMOLECULES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Solved Examples|45 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Subjective|18 VideosBIOMOLECULES, POLYMERS AND CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise QUESTION BANK|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-BIOMOLECULES-Exercises (Concept Application)
- Write two functions of carbohydrates in plants.
Text Solution
|
- Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides: Ribose,...
Text Solution
|
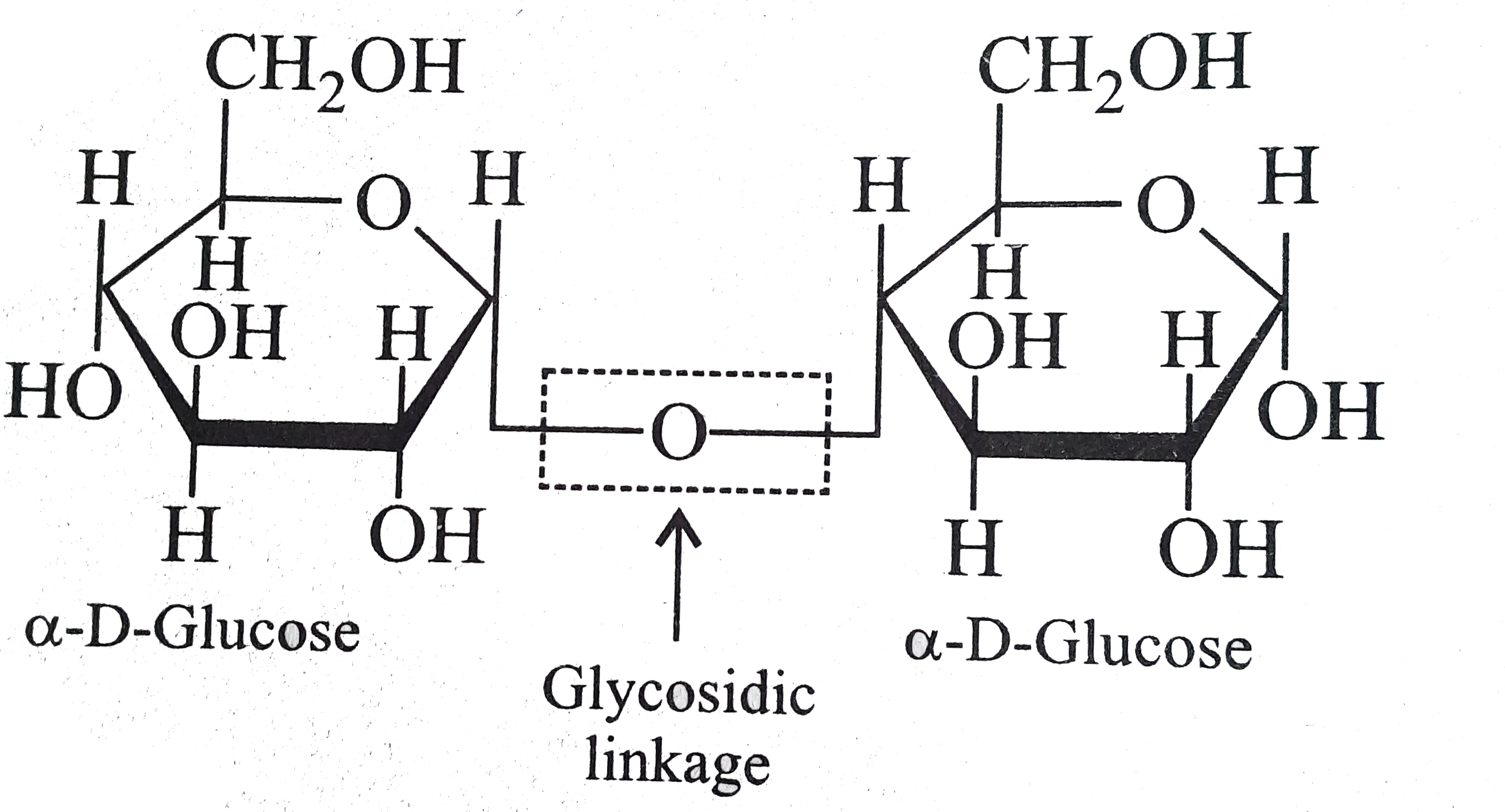
- What do you understand by the term glycosidic linkage?
Text Solution
|
- What is glycogen? How is it different from starch?
Text Solution
|
- What are the hydrolysis products of (i) sucrose and (ii) lactose?
Text Solution
|
- What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Text Solution
|
- What happenes when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents? ...
Text Solution
|
- Enumerate the reactions of D-Glucose which cannot be explained by its ...
Text Solution
|
- What are the essential and non-essential amino acids?Give two examples...
Text Solution
|
- Define the following as related to proteins: (i)Peptide linkage (ii)...
Text Solution
|
- What are the common types of secondary structures fo proteins?
Text Solution
|
- What are of bonding helps in stabilising thealpha-helix structure of p...
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between globular and fibrous proteins.
Text Solution
|
- How do you explain the amphoteric behaviour of amino acids?
Text Solution
|
- what are enzymes?
Text Solution
|
- What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
Text Solution
|
- How are vitamines classified? Name the vitamin responsible for the coa...
Text Solution
|
- Why are vitamin A and vitamin C essential for us? Give their important...
Text Solution
|
- Why are nucleic acids? Mention their two important functions.
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between a nucleoside and a complementary. Expla...
Text Solution
|