Series combination : if a number of condensers are connected end to end between the fixed points then such combination is called series.
In this combination 1. Charge on each capacitor is equal.
2. P.D's across the capacitors is not equal.
Consider three capacitors of capacitances `C_1C_2 and C_3` are connected in series across a battery of P.D 'V' as shown in figure.
Let 'Q' be the charge on each capacitor.
Let `V_1,V_2 and V_3` be the P.D's of three capacitors then `V=V_(1)+V_(2)+V_(3)---------(1)`
P.D across `I^("st")` condenser `V_(1)=(Q)/(C_1)`
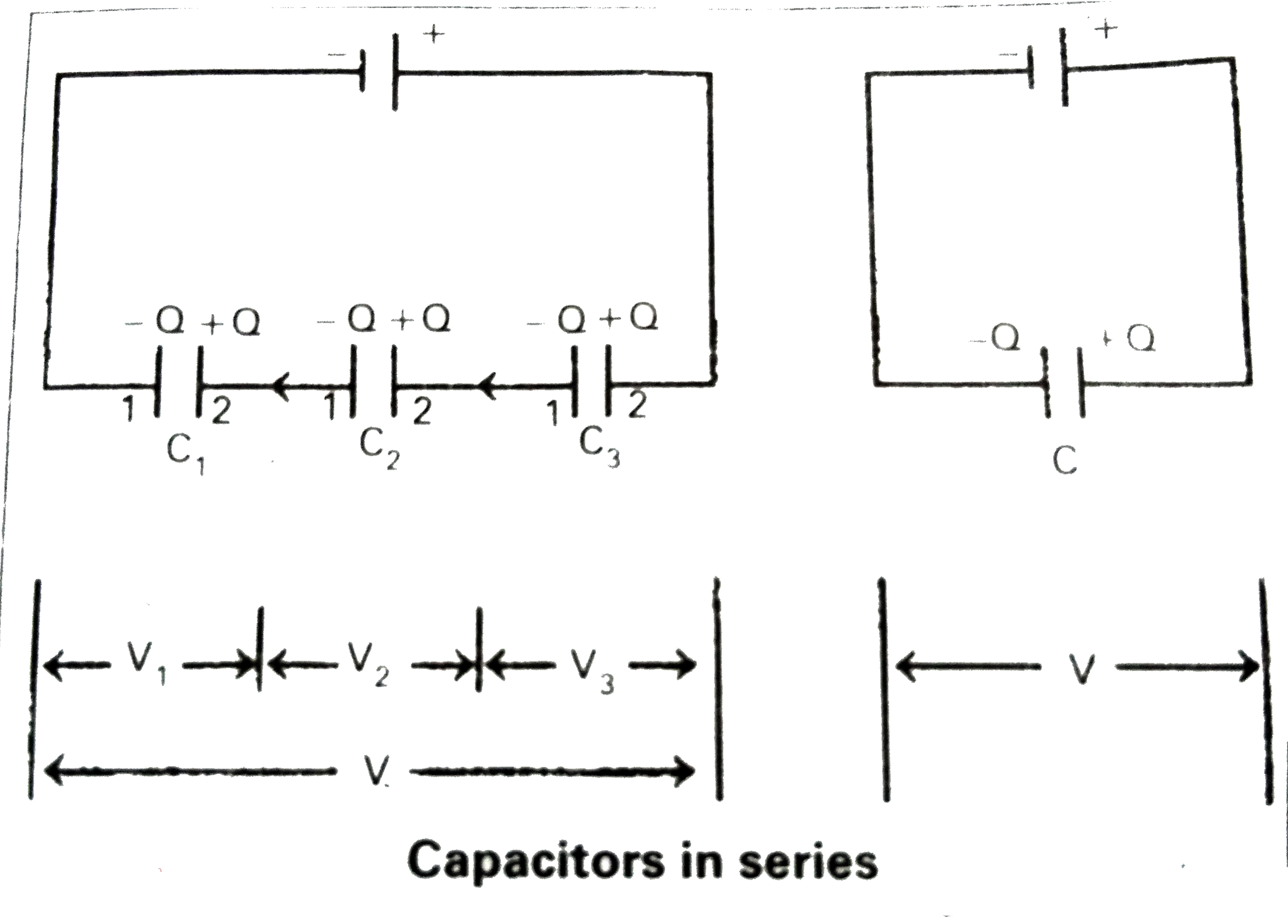
P.D across `II^("nd")` condenser `V_(2)=(Q)/(C_2)`
P.D across `III^("rd")` condenser `V_(3)=(Q)/(C_3)`
`therefore` From the equation (1) , `V=V_1+V_2+V_3=(Q)/(C_1)+(Q)/(C_2)+(Q)/(C_3)=Q[(1)/(C_1)+(1)/(C_2)+(1)/(C_3)]`
`(V)/(Q)=(1)/(C_1)+(1)/(C_2)+(1)/(C_3)`
For 'n' number of capacitors, the effective capacitance can be written as
`(1)/(C)=(1)/(C_1)+(1)/(C_2)+(1)/(C_3)+.....+(1)/(C_n)`
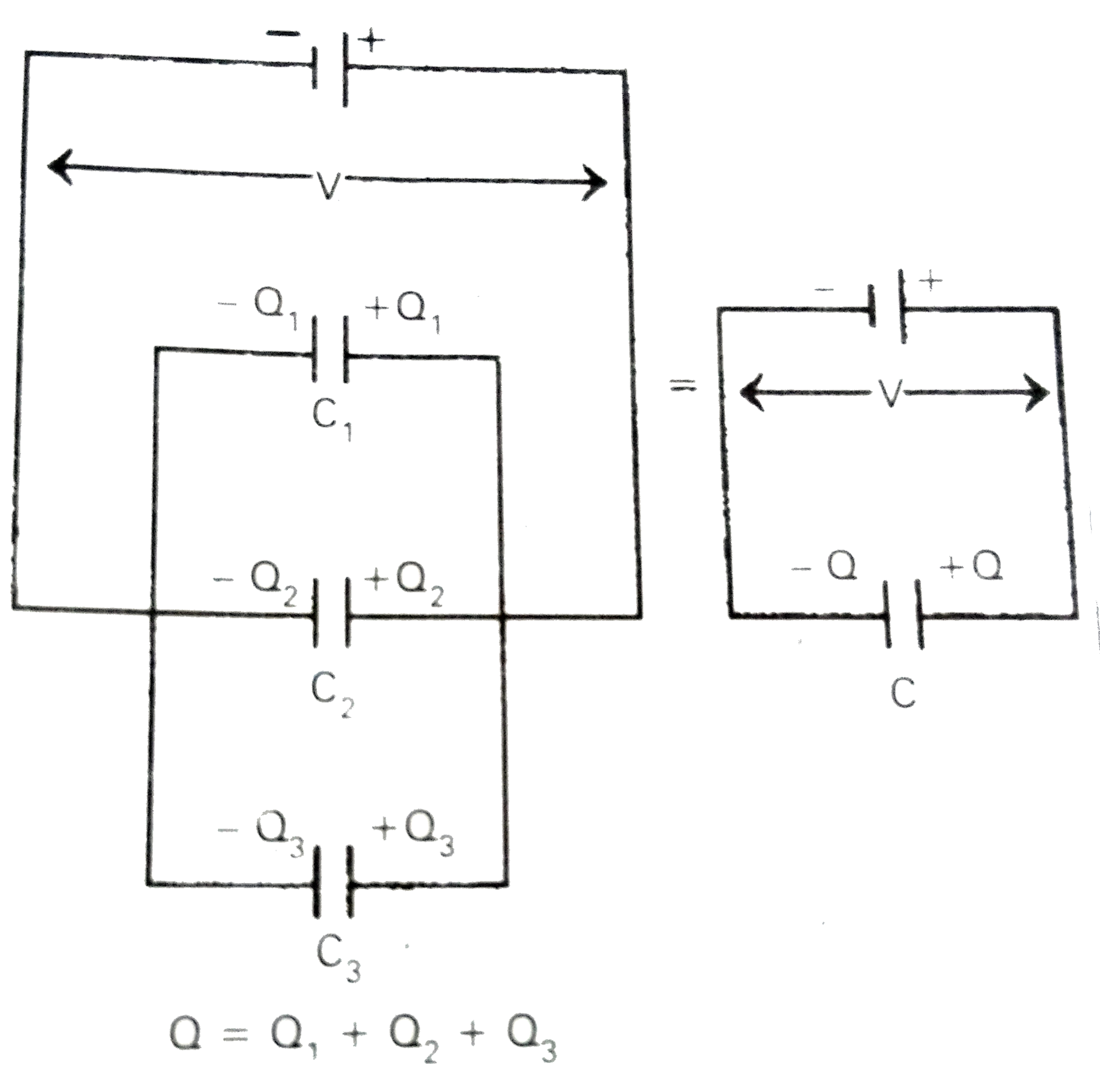
Parallel Combination : The first plates of different capacitors are connected at one terminal and all the second plates of the capacitors are connected at another terminal then the two terminals are connected to the two terminals of battery is called parallel combination.
In this combination,
1. The P.D's between each capacitor is equal (or) same.
2. Charge on each capacitor is not equal, Consider three capacitors of capacitance `C_1,C_2 and C_3` are connected in parallel across a P.D 'V' as shown in fig.
The charge on Ist capacitor `Q)1=C_1V`
The chage of IInd capcitor `Q_2=C_2V`
The charge on IIIrd capacitor `Q_3=C_3V`
`therefore` The total charge `Q=Q_1+Q_2+Q_3`
`=C_1V+C_2V+C_3V`
`Q=V(C_1+C_2+C_3)rArr (Q)/(V)=C_1+C_2+C_3`
`C=C_1+C_2+C_3[ because C=(Q)/(V)]`
for 'n' number of capacitors connected in parallel , the equivalent capacitance can be written as `C=C_1+C_2+C_3+.....+C_n`